Abstract
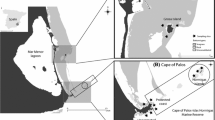
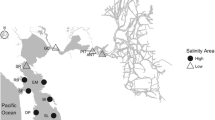
The red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) was introduced from the northern Pacific to the Russian Murman coast during the 1960s and 1970s. Over the subsequent decades, the crab has become established in northern Norwegian waters, where it continues spreading westward. The crab is an active predator on benthic fauna, especially feeding in deep soft-bottom environments. The present studies, carried out in the Varanger area close to the Russian border in 2007-2009, indicate that soft-bottom epifauna and infauna have become markedly reduced in crab-invaded areas. For infauna, quantitative data from 1994 were used as a basis to compare faunal composition before and after the crab became abundant in the area. It appeared that echinoderms, non-moving burrowing and tube-dwelling polychaetes, and most bivalves were reduced, whereas some small-sized polychaetes and small bivalves had increased. In situ sediment profile imagery (SPI) was used to examine sediment structure and biogenic activity. At several locations, the sediment habitat quality was degraded due to hypoxic conditions and low biological activity below surface layers. It is suggested that the crab has removed organisms performing important functions such as bio-irrigation and sediment reworking. Hence, it appears that the crab may reduce the functional diversity of the resident species assemblages, which may have overall implications for ecosystem function, production and responses to other environmental stressors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller RC (1982) The effect of macrobenthos on chemical properties of marine sediment and overlying water. In: McCall PL, Tevesz MJS (eds) Animal-sediment relations. Plenum Press, New York, pp 53–102
Anisimova N, Manushin I (2008) Benthos as prey for the red king crab. In: Sundet JH, Berenboim B (eds) Research on the red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) from the Barents Sea in 2005-2007. IMR/PINRO Joint Report Series 3-2008, pp 32-36
Anisimova N, Berenboim B, Gerasimova O, Manushin I, Pinchukov M (2005) On the effect of red king crab on some components of the Barents Sea ecosystem. Report PINRO, Murmansk
Britayev TA, Rzhavsky AV, Pavlova LV, Dvoretskij AG (2010) Studies on impact of the alien Red King Crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) on the shallow water benthic communities of the Barents Sea. J Appl Ichthyol 26(suppl 2):66–73
Cunningham DT (1969) A study of the food and feeding relationship of the Alaskan king crab Paralithodes camtschatica. Master thesis, State College California, San Diego
Didham RK, Hutchinson MA, Ewers RM, Gemmel NJ (2005) Are invasive species the drivers of ecological change? Trends Ecol Evol 20:470–474
Feder HM, Paul AJ (1980) Food of the king crab Paralithodes camtschatica and the Dungeness crab, Cancer magister in Cook Inlet, Alaska. Proc Natl Shellfish Assoc 70:240–246
Gray JS, Elliot M (2009) Ecology of marine sediments: from science to management, 2nd edn. OUP, Oxford
Holte B, Oug E, Cochrane S (2004) Depth-related benthic macrofaunal biodiversity patterns in three undisturbed north Norwegian fjords. Sarsia 89:91–101
Jewett SC, Feder HM (1982) Food and feeding habits of the king crab Paralithodes camtschatica near Kodiak Island, Alaska. Mar Biol 66:243–250
Jørgensen LL (2005) Impact scenario for an introduced decapod on Arctic epibenthic communities. Biol Invasions 7:949–957
Karakassis I, Tsapakis M, Smith CJ, Rumohr H (2002) Fish farming impacts in the Mediterranean studied through sediment profiling imagery. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 227:125–133
Kuzmin S, Olsen S (1996) Barents Sea king crab (Paralithodes camtschatica). The transplantion experiments were successfull. ICES CM 1994/ K:12 Shellfish Committee
Kuzmin S, Sundet JH (2000) Joint report for 2000 on the red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) investigations in the Barents Sea. Basic requirements for management of the stock. Norwegian Institute of Fisheries and Aquaculture, Bergen
Larsen LH (1997) Soft-bottom macro invertebrate fauna of North Norwegian coastal waters with particular reference to sill-basins. Part one: Bottom topography and species diversity. Hydrobiologia 355:101–113
Lohrer A, Trush SF, Gibbs M (2004) Bioturbators enhance ecosystem function through complex biogeochemical interactions. Nature 43:1092–1095
Manushin I, Anisimova N (2008a) Ecology of the red king crab in the Barents Sea. In: Sundet JH, Berenboim B (eds) Research on the red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) from the Barents Sea in 2005-2007. IMR/PINRO Joint Report Series 3-2008, pp 17-20
Manushin I, Anisimova N (2008b) Selectivity in the red king crab feeding in the Barents Sea. In: Sundet JH, Berenboim B (eds) Research on the red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) from the Barents Sea in 2005-2007. IMR/PINRO Joint Report Series 3-2008, pp 24-28
Mermillod-Blondin F, Rosenberg R, Francois-Carcaillet F, Norling K, Mauclaire L (2004) Influence of bioturbation by three benthic infaunal species on microbial communities and biogeochemical processes in marine sediment. Aquat Microb Ecol 36:271–284
Nilssen EM (2003) Kongekrabbe i Barentshavet – biologi og utbredelse. Ottar 4/2003:7-12 (In Norwegian)
Nilsson HC, Rosenberg R (1997) Benthic habitat quality assessment of an oxygen stressed fjord by surface and sediment profile images. J Mar Syst 11:249–264
Nilsson HC, Rosenberg R. (2003) Effects on marine sedimentary habitats of experimental trawling analysed by sediment profile imagery. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 285-286: 453-463
Norling K, Rosenberg R, Hulth S, Grémare A, Bonsdorff E (2007) Importance of functional biodiversity and species-specific traits of benthic fauna for ecosystem functions in marine sediment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 332:11–23
O’Connor BDS, Costelloe J, Keegan BF, Roads DC (1989) The use of REMOTS technology in monitoring coastal enrichment resulting from mariculture. Mar Pollut Bull 8:384–390
Olsgard F, Schaanning MT, Widdicombe S, Kendall MA, Austen MC (2008) Effects of bottom trawling on ecosystem functioning. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 366:123–133
Orlov YI, Ivanov BG (1978) Introduction of Kamtchatka king crab Paralithodes camtschatica (Decapoda, Anomura, Lithodidae) into the Barents Sea. Mar Biol 48:373–375
Pielou EC (1969) An introduction to mathematical ecology. Wiley, New York
Pimentel D, Lach L, Zuniga R, Morrison D (2000) Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. Bioscience 50:53–65
Rhoads DC, Cande S (1971) Sediment profile camera for in situ study of organism–sediment relations. Limnol Oceanogr 16:110–114
Rosenberg R, Nilsson HC, Diaz RJ (2001) Response of benthic fauna and changing sediment redox profiles over a hypoxic gradient. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 53:343–350
Rosenberg R, Agrenius S, Hellman B, Nilsson HC, Norling K (2002) Recovery of marine benthic habitats and fauna in a Swedish fjord following improved oxygen conditions. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 234:43–53
Rosenberg R, Blomqvist M, Nilsson HC, Cederwall H, Dimming A (2004) Marine quality assessment by use of benthic species-abundance distributions: a proposed new protocol within European Union Water Framework Directive. Mar Pollut Bull 49:728–739
Rumohr H, Schomann H (1992) REMOTS sediment profiles around an exploratory drilling rig in the southern North Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 91:303–311
Skei J, Rygg B, Sørensen K (1995) Miljøundersøkelser i fjordsystemet utenfor Kirkenes i Finnmark, bløtbunnsfauna, sedimenter og partikler i vann juni 1994. Norwegian Institute for Water Research, report 3281, Oslo [in Norwegian]
Solan M, Wigham BD, Hudson IR, Kennedy R, Coulon CH, Norling K, Nilsson HC, Rosenberg R (2004a) In situ quantification of bioturbation using time-lapse fluorescent sediment profile imaging (f-SPI), luminophore tracers and model simulation. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 271:1–12
Solan M, Cardinale BJ, Downing AL, Engelhardt KAM, Ruesink JL, Srivastava DS (2004b) Extinction and ecosystem function in the marine benthos. Science 306:1177–1180
Sundet JH (2009) Kongekrabbe. Chapter 2.8, Institute of Marine Research report, Kyst og Havbruk 2009, pp 105-107
Sundet JH, Berenboim B (eds) (2008) Research on the red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) from the Barents Sea in 2005–2007. IMR/PINRO Joint Report Series 3/2008
Sundet JH, Hjelset AM (2009) Seasonal depth distribution of the red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in Varangerfjorden, northern Norway. Proceedings from Symposium on Biology and Management of Exploited Crab Populations. Alaska Sea Grant Program, Anchorage (in press)
Sundet JH, Rafter EE, Nilssen E (1999) Sex and seasonal variation in the stomach content of the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus in the southern Barents Sea. In: Klein CVV, Schram FR (eds) The biodiversity crisis and Crustacea. Balkema Publishers, Rotterdam, pp 193–200
Takeuchi I (1967) Food of king crab, Paralithodes camtschatica, of the west coast of Kamchatka Peninsula, 1958-1964. Bull Hokkaido Reg Fish Res Lab 33:32-44 [in Japanese with English summary]
Trimmer M, Petersen J, Sivyer BD, Mills C, Young E, Parker ER (2005) Impact of long-term benthic trawl disturbance on sediment sorting and biogeochemistry in the southern North Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 298:79–94
Wallentinus I, Nyberg CD (2007) Introduced marine organisms as habitat modifiers. Mar Pollut Bull 55:323–332
Wassmann P, Svendsen H, Keck A, Reigstad M (1996) Selected aspects of the physical oceanography and particle fluxes in fjords of northern Norway. J Mar Syst 8:53–71
Acknowledgements
We thank the captain and crew of RV Johan Ruud, of the University of Tromsø, and Einar M. Nilssen for fieldwork support. Macrofauna samples in Bøkfjorden in 2007 were collected by Sten-Richard Birkely and Bent Barman Skaare. We further acknowledge Vera Remen, Andrey Sikorski, Andrey Y. Voronkov, Rune Palerud, Halldis Ringvold, Hans Petter Mannvik, Brage Rygg, Hans Tore Rapp and Lies Vansteenbrugge for sample sorting and identification and Trond Thangstad for graphical work. We thank Stephen Jewett, Rutger Rosenberg and one anonymous reviewer for helpful criticism of the manuscript. This study was financed by the Norwegian Directorate of Nature Management, with additional support from Institute of Marine Research, Norwegian Institute for Water Research and Akvaplan-niva. S. Cochrane’s participation was additionally financed by Eni Norge, through the Arctic Seas Biodiversity (ASBD) project. The samples in Bøkfjorden were taken as part of an environmental assessment study for Sydvaranger Gruve AS in Kirkenes. This publication was originally presented at the Arctic Frontiers Conference in Tromsø, January 2010. The support and initiative of ARCTOS and Arctic Frontiers are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oug, E., Cochrane, S.K.J., Sundet, J.H. et al. Effects of the invasive red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) on soft-bottom fauna in Varangerfjorden, northern Norway. Mar Biodiv 41, 467–479 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-010-0068-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-010-0068-6