Abstract
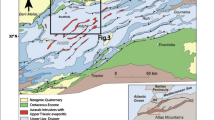
We used Airborne Visible Infrared Imaging Spectrometer-Next Generation data for mapping possible mineral alterations, which aid in mineral exploration over larger areas. The data were subjected to various advanced processing techniques like Minimum Noise Fraction, Pixel Purity Index, N-Dimensional visualization and Spectral angle mapper classification. End-member spectra were matched with those of the minerals as available in the United States Geological Survey Spectral Library. In the present study, the Ambaji–Deri area of northwestern India was mapped for mineral alterations. The area has thick forest cover along with rugged topography, which warranted the use of hyperspectral remote sensing approach. The minerals such as calcite, muscovite and chlorite have been mapped, which are showing a good correlation with the ground geological records, barring epidote, whose distribution is scattered. We attribute the possible reason to be the spectral similarities between epidote and chlorite, which makes them difficult to differentiate only on the basis of the present hyperspectral study. The hyperspectral technique, as illustrated, provides powerful tool for mapping mineral alteration to mineral deposits. This enables scrutiny of a wider area of interest to being narrowed down for first-hand field investigations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams, M. (2000). The advanced spaceborne thermal emission and re ection radiometer ( ASTER): Data products for the high spatial resolution imager on NASA’s Terra platform. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21(5), 847–859.
Amato, U., Cavalli, R. M., Palombo, A., Pignatti, S., & Santini, F. (2009). Experimental approach to the selection of the components in the minimum noise fraction. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002953
Bharti, R., Kalimuthu, R., & Ramakrishnan, D. (2015). Spectral pathways for exploration of secondary uranium: An investigation in the desertic tracts of Rajasthan and Gujarat India. Advances in Space Research, 56(8), 1613–1626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2015.07.015
Bharti, R., & Ramakrishnan, D. (2014).In Geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS), 2014 IEEE international, (pp 2902–2905).
Bhattacharya, S., Majumdar, T. J., Rajawat, A. S., Panigrahy, M. K., & Das, P. R. (2012). Utilization of Hyperion data over Dongargarh, India, for mapping altered/weathered and clay minerals along with field spectral measurements. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 33(17), 5438–5450. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2012.661094
Boardman, J. W. (1994). Geometric mixture analysis of imaging spectrometry data. In Geoscience and remote sensing symposium, 1994. IGARSS ’94. Surface and atmospheric remote sensing: technologies, data analysis and interpretation., international. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.1994.399740.
Boardman, J. W., Kruse, F. A., & Green, R. O. (1993). Mapping target. Jet Propulsion, 23, 23–26.
Carranza, E. J. M., & Hale, M. (2002). Mineral imaging with Landsat Thermatic mapper data for hydrothermal alteration mapping in heavily vegetated terrane. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(22), 4827–4852. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160110115014
Cŕosta, A. P., De Souza Filho, C. R., Azevedo, F., & Brodie, C. (2003). Targeting key alteration minerals in epithermal deposits in Patagonia, Argentina, using ASTER imagery and principal component analysis. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 24(21), 4233–4240. https://doi.org/10.1080/0143116031000152291
Dalton, J. B., Bove, D. J., Mladinich, C. S., & Rockwell, B. W. (2004). Identification of spectrally similar materials using the USGS Tetracorder algorithm: The calcite-epidote-chlorite problem. Remote Sensing of Environment, 89(4), 455–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.11.011
Deb, M. (1979). Polymetamorphism of ores in Precambrian stratiform massive sulfide deposits at Ambaji-Deri Western India. Mineralium Deposita. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00201865
Deb, M. (1980). Genesis and metamorphism of two stratiform massive sulfide deposits at Ambaji and Deri in the Precambrian of Western India. Economic Geology. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.75.4.572
Deb, M., Thorpe, R. I., Krstic, D., Corfu, F., & Davis, D. W. (2001). Zircon U–Pb and galena Pb isotope evidence for an approximate 1. 0 Ga terrane constituting the western margin of the Aravalli–Delhi orogenic belt, northwestern India. Precambrian Research, 108, 195–213.
Gaffey, S. J. (1987). Spectral reflectance of carbonate minerals in the visible and near infrared (0.35–2.55 um): Anhydrous carbonate minerals. Journal of Geophysical Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB092iB02p01429
Galley, A. G. (1993). Characteristics of semi-conformable alteration zones associated with volcanogenic massive sulphide districts. Journal of Geochemical Exploration. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6742(93)90004-6
Galley, A. G., Hannington, M. D., & Jonasson, I. R. (2007). Volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits. Special Publication, 5, 141–161.
Goetz, A. F. H. (2009). Three decades of hyperspectral remote sensing of the Earth: A personal view. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(1), S5–S16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.12.014
González, C., Resano, J., Mozos, D., Plaza, A., & Valencia, D. (2010). FPGA Implementation of the pixel purity index algorithm for remotely sensed hyperspectral image analysis. Eurasip Journal on Advances in Signal Processing. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/969806
Graham, G. E., Kokaly, R. F., Kelley, K. D., Hoefen, T. M., Johnson, M. R., & Hubbard, B. E. (2017). Airborne hyperspectral surveying as a tool for mineral exploration at high latitudes: a pilot study over porphyry Cu deposits, eastern Alaska Range, Alaska. In 14th SGA Biennial Meeting (Vol. 3, pp. 1077–1080).
Green, A. A., Berman, M., Switzer, P., & Craig, M. D. (1988). A Transformation for ordering multispectral data in terms of image quality with implications for noise removal. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 26(1), 65–74. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.3001
GSI. (1967). Geological survey of India geological mapping in parts of Chamba District. Unpublished.
GSI. (2012a). Geology and mineral resources of Gujarat. Unpublished.
GSI. (2012b). Use of hyperspectral remote sensing data for the search of mineralised provinces/areas in Precambrian Terrain. Unpublished.
Gupta S N, Arora Y K, Mathur R K, Iqbaludin p, Sahai T N, & Sharma S B. (1980). Lithostratigraphic map of Aravalli region. Kolkata.
Harraden, C. L., McNulty, B. A., Gregory, M. J., & Lang, J. R. (2013). Shortwave infrared spectral analysis of hydrothermal alteration associated with the Pebble porphyry copper-gold-molybdenum deposit, Iliamna Alaska. Economic Geology, 108(3), 483–494. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.108.3.483
Heron, A. M., & Ghosh, P. K. (1938). Geology of Palanpur, Danta and parts of Idar states. Record of Geological Survey of India.
Herzig, P. M., & Hannington, M. D. (1995). Polymetallic massive sulfides at the modem seafloor A review. Ore Geology Reviews, 10(10), 95–115.
Hunt, G. R. (1979). Near-infrared (1.3–2.4 μm) spectra of alteration minerals—Potential for use in remote sensing. Geophysics, 44(12), 197–198.
Incorporated Research Systems. (2004). ENVI User’s guide, (September), (pp. 1–1150).
Khanna, S., Santos, M. J., Ustin, S. L., Shapiro, K., Haverkamp, P. J., & Lay, M. (2018). Comparing the potential of multispectral and hyperspectral data for monitoring oil spill impact. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020558
Kokaly, R. F., Hoefen, T. M., Graham, G. E., Kelley, K. D., Johnson, M. R., Hubbard, B. E., et al. (2016). Mineral information at micron to kilometer scales: Laboratory, field, and remote sensing imaging spectrometer data from the orange hill porphyry copper deposit, Alaska, USA. In International geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS), 2016–Nov,(pp. 5418–5421).https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730411
Krishna Mohan, B., & Porwal, A. (2015). Hyperspectral image processing and analysis. Current Science, 108(5), 833–841.
Kruse, F. A. (1988). Use of airborne imaging spectrometer data to map minerals associated with hydrothermally altered rocks in the northern grapevine mountains, Nevada, and California. Remote Sensing of Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(88)90004-1
Kruse, F. A., Lefkoff, A. B., Boardman, J. W., Heidebrecht, K. B., Shapiro, A. T., Barloon, P. J., & Goetz, A. F. H. (1993). The spectral image processing System (SIPS) interactive visualization and analysis of imaging spectrometer data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 44, 145–163.
Laakso, K., Middleton, M., Heinig, T., Bärs, R., & Lintinen, P. (2018). Assessing the ability to combine hyperspectral imaging (HSI) data with mineral liberation analyzer (MLA) data to characterize phosphate rocks. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 69, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2018.02.018
Laakso, K., Peter, J. M., Rivard, B., & White, H. P. (2016). Short-wave infrared spectral and geochemical characteristics of hydrothermal alteration at the Archean Izok Lake Zn–Cu–Pb–Ag volcanogenic massive sulfide deposit, Nunavut, Canada: Application in exploration target vectoring. Economic Geology. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.111.5.1223
Laakso, K., Rivard, B., Peter, J. M., White, H. P., Maloley, M., Harris, J., & Rogge, D. (2015). Application of airborne, laboratory, and field hyperspectral methods to mineral exploration in the Canadian arctic: Recognition and characterization of volcanogenic massive sulfide-associated hydrothermal alteration in the Izok Lake Deposit Area Nunavut. Economic Geology. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.110.4.925
Large, R. R. (1992). Australian volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits: Features, styles, and genetic models. Economic Geology. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.87.3.471
Laukamp, C., Cudahy, T., Thomas, M., Jones, M., Cleverley, J. S., & Oliver, N. H. S. (2011). Hydrothermal mineral alteration patterns in the Mount Isa Inlier revealed by airborne hyperspectral data. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 58(8), 917–936. https://doi.org/10.1080/08120099.2011.571287
Li, Z., Yang, R., Dang, F., Du, P., Zhang, X., Tan, B., et al. (2012). A review on the geological applications of hyperspectral remote sensing technology. Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing, Evolution in Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1109/WHISPERS.2012.6874235
Luo, G., Chen, G., Tian, L., Qin, K., & Qian, S. E. (2016). Minimum noise fraction versus principal component analysis as a preprocessing step for hyperspectral imagery denoising. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 42(2), 106–116. https://doi.org/10.1080/07038992.2016.1160772
Mars, J. C., & Rowan, L. C. (2006). Regional mapping of phyllic- and argillic-altered rocks in the zagros magmatic arc, Iran, using advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (ASTER) data and logical operator algorithms. Geosphere, 2(3), 161–186. https://doi.org/10.1130/GES00044.1
Mauger, A. J., Keeling, J. L., & Huntington, J. F. (2007). Alteration mapping of the Tarcoola Goldfield (South Australia) using a suite of hyperspectral methods. Applied Earth Science, 116(1), 2–12. https://doi.org/10.1179/174327507X167028
Mishra, B. (2015). Chapter 22 precambrian metallic mineralization in India. Geological Society, London, Memoirs, 43(1), 327–337.
Neal, L. C., Wilkinson, J. J., Mason, P. J., & Chang, Z. (2018). Spectral characteristics of propylitic alteration minerals as a vectoring tool for porphyry copper deposits. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 184, 179–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.10.019
Nidamanuri, R. R., & Ramiya, A. M. (2013). Spectral identification of materials by reflectance spectral library search. Geocarto International, 29(6), 609–624. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2013.821175
Nidamanuri, R. R., & Ramiya, A. M. (2014). Spectral identification of materials by reflectance spectral library search. Geocarto International. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2013.821175
Porwal, A., Carranza, E. J. M., & Hale, M. (2006). Tectonostratigraphy and base-metal mineralization controls, Aravalli province (western India): New interpretations from geophysical data analysis. Ore Geology Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.10.003
Pour, A. B., & Hashim, M. (2012). Identifying areas of high economic-potential copper mineralization using ASTER data in the Urumieh–Dokhtar volcanic belt Iran. Advances in Space Research, 49(4), 753–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2011.11.028
Pour, A. B., & Hashim, M. (2015). Structural mapping using PALSAR data in the central gold belt peninsular Malaysia. Ore Geology Reviews, 64(1), 13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.011
Pour, A. B., Hashim, M., Hong, J. K., & Park, Y. (2017). Lithological and alteration mineral mapping in poorly exposed lithologies using Landsat-8 and ASTER satellite data: North-eastern Graham Land Antarctic Peninsula. Ore Geology Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.07.018
Ramakrishnan, D., & Bharti, R. (2016). Hyperspectral remote sensing and geological applications. Current Science, 108, 879–891.
Ross, P. S., & Mercier-Langevin, P. (2014). Igneous rock associations 14. The volcanic setting of VMS and SMS deposits: A review. Geoscience Canada. https://doi.org/10.12789/geocanj.2014.41.045
Sabins, F. (1999). Remote sensing for mineral exploration. Ore Geology Reviews, 14(3–4), 157–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1368(99)00007-4
Shaw, G. A., & Burke, H. K. (2003). Spectral imaging for remote sensing. Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 14(1), 3–28.
Swayze, G. A., Clark, R. N., Goetz, A. F. H., Livo, K. E., Breit, G. N., Kruse, F. A., et al. (2014). Mapping advanced argillic alteration at Cuprite, Nevada, using imaging spectroscopy. Economic Geology. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.109.5.1179
Taylor, P., Gens, R., & Genderen, J. L. V. A. N. (2007). Review Article SAR interferometry—issues, techniques, applications. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17, 37–41.
Tiwary, A., & Deb, M. (1997). Geochemistry of hydrothermal alteration at the Deri massive sulphide deposit, Sirohi district, Rajasthan. NW India. Journal of Geochemical, 59(59), 99–121.
van der Meer, F. D., van der Werff, H. M. A., van Ruitenbeek, F. J. A., Hecker, C. A., Bakker, W. H., Noomen, M. F., et al. (2012). Multi- and hyperspectral geologic remote sensing: A review. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2011.08.002
Wu, X., Huang, B., Plaza, A., Li, Y., & Wu, C. (2014). Real-time implementation of the pixel purity index algorithm for endmember identification on GPUs. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 11(5), 955–959. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2013.2283214
Acknowledgement
SPP would like to thank DG and Director ISR for encouragement and support. The paper forms part of ongoing AMBAJI research project of Government of Gujarat. We would like to thank ISRO-SAC for providing the AVIRIS-NG data for research purpose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Samani, P., Prizomwala, S.P. & Rajawat, A.S. Assessing the Mineral Alteration in Ambaji–Deri Region (Northwestern India) Using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 49, 249–257 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01208-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01208-2