Abstract
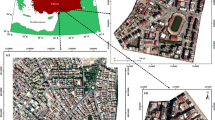
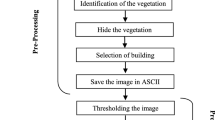
Accurately obtaining the structures and damage types of buildings in earthquake stricken areas is fundamental to supporting rescue forces and estimating economic losses and casualties. As the stricken areas are often much larger than the areas covered by very high resolution (VHR) images, the information obtained from VHR images cannot satisfy practical needs. This study developed a method for estimating the structures and types of damaged buildings by combining VHR images, statistics and ground survey data. First, the rates of damaged buildings with different structures and damage types were manually interpreted from VHR images covering a small part of the stricken area, and further corrected by ground survey data. Second, the corrected rates were reallocated to the seismic intensity zones. Third, the rates in the seismic intensity zones and the statistical data were combined to estimate the numbers and areas of damaged buildings in villages, towns and counties. The presented method was applied to estimate the damages caused by the Lushan earthquake in China. The results indicated that our method can efficiently estimate the amount of the damages and complement existing work on only automatic extracting damaged buildings from VHR images.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, L. C., & Lin, L. J. (2010). Detection of building changes from aerial images and light detection and ranging (LIDAR) data. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 4, 1–19.
Christine, S., & Michael, M. (2006). Classification of collapsed buildings for fast damage and loss assessment. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 4, 177–192.
Ehrlich, D., Guo, H. D., Molch, K., Ma, J. W., & Pesaresi, M. (2009). Identifying damage caused by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake from VHR remote sensing data. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2, 309–326.
Hussain, E., Serkan, U., KyoHyouk, K., Fu, C. S., & Shan, J. (2011). Building extraction and rubble mapping for city Port-au-Prince post-2010 earthquake with GeoEye-1 imagery and Lidar Data. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 77, 1011–1023.
Kaya, S., Curran, P. J., & Llewellyn, G. (2005). Post-earthquake building collapse: a comparison of government statistics and estimates derived from SPOT HRVIR data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26, 2731–2740.
Khoshelham, K., Elberink, S. O., & Xu, S. (2013). Segment-based classification of damaged building roofs in aerial laser scanning data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 10, 1258–1262.
Oude, E. S., Shoko, M., Fathi, A., & Rutzinger, M.A. (2011). Detection of collapsed buildings by classifying segmented airborne laser scanner data. In: Proceeding of International Archives Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing, Spatial Information Science, Calgary, AB, Canada, vol. XXXVIII, pp. 307–312.
Rehor, M. (2007). Classification of building damage based on LASER scanning data. The Photogrammetric Journal of Finland, 20, 54–63.
Rezaeian, M. (2010). Assessment of earthquake damages by image-based techniques. Ph.D dissertation, ETH Zurich.
Rezaeian, M. (2012). Automatic classification of collapsed buildings using stereo aerial images. International Journal of Computer Applications, 46, 35–42.
Rezaeian, M., & Grün, A. (2011). Automatic 3D building extraction from aerial and space images for earthquake risk management. Journal of Georisk: Assessment and Management of Risk for Engineered Systems and Geohazards, 5, 77–96.
Sertel, E., Kaya, S., & Curran, P. J. (2007). Use of semivariograms to identify earthquake damage in an urban area. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 45, 1590–1594.
Wang, L. T., Wang, S. X., Zhou, Y., & Wei, C. (2010). Urgent monitoring and analysis on Yushu Earthquake using remote sensing. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 14, 1053–1066.
Wang, J. F., Jiang, C. S., Hu, M. G., Cao, Z. D., Guo, Y. S., Li, L. F., & Meng, B. (2013). Design based spatial sampling: theory and implementation. Environmental Modelling & Software, 40, 280–288.
Wikantika, K., Sinaga, A., Hadi, F., & Darmawan, S. (2007). Quick assessment on identification of damaged building and land-use changes in the post-tsunami disaster with a quick-look image of IKONOS and Quickbird (a case study in Meulaboh City, Aceh). International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28, 3037–3044.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2012AA121305), and National Science and Technology Major Project of China High Resolution Earth Observation system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, J., Du, S., Fan, Y. et al. Estimating the Numbers and the Areas of Collapsed Buildings by Combining VHR Images, Statistics and Survey Data: a Case Study of the Lushan Earthquake in China. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 44, 101–110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-015-0473-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-015-0473-1