Abstract
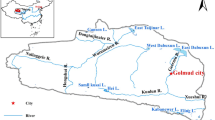
Poyang Lake is the largest freshwater lake in China. Because the lake is faced with a series of ecological and environmental problems, it is important and necessary to study the land use changes in the Poyang Lake region. In this study, Landsat images from 1976, 1989, 1999 and 2009, were used along with other evaluation methods (quantitative analysis of changes in land use, land use dynamic, degree and transfer matrix analyses) to investigate the changes in land use within the Poyang Lake region from 1976 to 2009. Land use was classified into seven types: cropland, woodland, grassland, the water body, construction land, bottomland and unused land. Areas of cropland, bottomland and the water body were decreasing although the area of the water body decreased relatively slowly. However, areas of construction land, grassland, woodland and unused land increased to a certain extent, with unused land increasing the most rapidly given its smaller proportion compared to the other types. All land types in the study region had different levels of conversion between other types of land. As a whole, the decrease in cropland and the increase in construction land, woodland and grassland were caused by human activities and the conservation policies such as Grain-for-Green and “returning farm to lake”. However, the decrease in the water body area was mainly influenced by natural factors and human activities. Changes in the area of bottomland were mainly influenced by water levels and human farming activities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai, Y. L. (2001). A study on land use/cover change: the need for a new integrated approach. Geographical Research, 20, 645–652 (in Chinese with English abstract).
China’s National Standard (GB/T21010-2007). (2007). Current land use condition classification (in Chinese).
Congalton, R. G. (1991). A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 37, 35–46. doi:10.1016/0034-4257(91)90048-B.
Editorial institute of Poyang Lake Research. (1988). Poyang lake research. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press (in Chinese).
ESRI. (1999). ArcGIS desktop help. USA: ESRI. http://www.esri.com.
Foody, G. M., Campbell, N. A., Trodd, N. M., Wood T. F. (1992). Derivation and applications of probabilistic measures of class membership from the maximum-likelihood classification. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 58, 1335–1341.
Gan, H., Liu, Y. S., & Wang, D. W. (2004). Simulation and analysis of the human driving factors of land use type conversion. Resources Science, 26, 88–93 (in Chinese with English abstract).
He, C. Y., Chen, J., Chen, Y. H., Shi, P. J. (2001). Land use/cover change detection based on hybrid method. Journal of Natural Resources, 16, 255–262 (in Chinese with English abstract).
IGBP Secretariat. 2005. GLP (2005). Science plan and implementation strategy. IGBP Report No. 53/IHDP Report No.19, Stockholm: 64.
Jerson, J. R. (1996). Introductory digital image process: A remote sensing perspective (2nd ed.). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Lindquist, E. J., Hansen, M. C., Roy, D. P., Justice, C. O. (2008). The suitability of decadal image data sets for mapping tropical forest cover change in the Democratic Republic of Congo: implications for the global land survey. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 29, 7269–7275. doi:10.1080/01431160802275890.
Liu, L. M. (2004). Land resource science. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, J. Y., Zhang, Z. X., Zhuang, D. F., Liu, M. (2003). A study on the spatial-temporal dynamic changes of land use and driving force analyses of China in 1990s. Geographical Research, 22, 1–12 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, J. Y., Zhang, Z. X., Xu, X. L., Kuang, W., Zhou, W., Zhang, S., et al. (2009). Spatial patterns and driving forces of land use change in China in the early 21st century. Acta Geographica Sinica, 64, 1411–1420 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Min, Q. (2000). Study on the relationship between shape, water regime and innings of Poyang Lake. Advances in Water Science, 11, 76–81 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ojima, D., Lavorel, S., Graumlich, L., Moran, E. (2005). Terrestrial human-environment systems: the future of land research in IGBP II. IGBP Global Change Newsletter, 50, 31–34.
Primack, R. B. (1996). Introduction to conservation biology, QI C J translated. Changsha: Hunan Science & Technology press,139–152 (in Chinese).
Rindfuss, R., Walsh, S., Turner, B. L., Fox, J., Mishra, V. (2004). Developing a science of land change: challenges and methodological issues. PNAS, 101, 13976–13981. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401545101.
Turnel, B. L., Moss, R. H., & Skole, D. (1993). Relating land Use and global land cover change: A proposed for an IGBP-IHDP core project. Sweden: International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme.
Turner, B. L., II, Lambin, E. F., & Reenberg, A. (2007). The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. PNAS, 104, 20666–20671.
Zhu, H. Y., & Li, X. B. (2003). Discussion on the index method of regional land use change. Acta Geographica Sinica, 58, 643–650 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Acknowledgments
The data set was provided by the International Scientific Data Service Platform, Computer Network Information Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (http://datamirror.csdb.cn). The reviews from the referees and the editor improved the quality of this paper and we acknowledge them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Ke, C. & Shang, Y. Studying Changes in Land Use Within the Poyang Lake Region. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 42, 633–643 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-013-0348-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-013-0348-2