Abstract
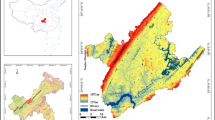
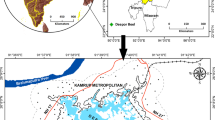
The present study aims to estimate the loss of land use/cover and infrastructure facilities due the submergence by constructing the reservoir over the River Godavari at Polavaram Village. Detailed Land use/cover mapping has been carried out using LISS-III sensor data of IRS P6 satellite and linked to socio-economic data to analyze the administrative boundary wise environmental impact assessment in the study area. Land use/cover features are estimated from the Remote Sensing data through visual interpretation. Area covered below the 45.72 m contour above the mean sea level (MSL) is taken as submerged area due to the dam construction. Total area under submergence is estimated to be 58,658 ha, where 159 villages of three districts are affected by the project. The total population to be rehabilitated is about 1.2 lakhs, out of which maximum affected are Scheduled Tribes (58,781). Besides this, about 311 educational institutions, 202 medical institutions, 37 credit institutions and 55 postal institutions will be submerged due to the project. Further, nine mining sites, 24 tourist/historical sites and 78 agro-based industries will be displaced. The total road length of 673 km will go under submergence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon (2001). Environmental impact assessment and environment management plan with safeguard measures of human river project in Chandrapur District (Maharashtra). Report prepared by Vidarbha irrigation development Corporation in consultation with S.S. Planners, Orissa. 419 pages.
Krishna, A. P., & Sharama, E. (1995). Environmental impact assessment of dynamic anthropogenic activities in Mamalay watershed of Sikkim Himalaya—a remote sensing approach. Asian-Pacific Remote Sensing Journal, 8(1), 23–28.
Louis, G. E., & Magpili, L. M. (2002). Representing inequities in the distribution of socioeconomic benefits and environmental risk. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 79(2), 101–119.
Poch, M., Comas, J., Rodriguez-Roda, I., Sanchez-Marre, M., & Cortes, U. (2004). Designing and building real environmental decision support systems. Environmental Modelling and Software, 19(9), 857–873.
Rao, V. V., & Chakraborthi, A. K. (2000). Water balance study and conjunctive water use planning in an Irrigation canal command area: a remote sensing perspective. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21, 3227–3238.
Ray, S. S., Dadhwal, V. K., & Navalgund, R. R. (2002). Performance evaluation of an irrigation command area using remote sensing: a case study of Mahi command, Gujarat, India. Agricultural Water Management, 56, 81–91.
Sarma, P. B. S., & Venkateshwar Rao, V. (1997). Evaluation of an irrigation water management scheme—a case study. Agricultural Water Management, 32, 181–195.
Satyaprakash, & Sivakumar, R. (2002). Integrated rural mapping, using remote sensing and GPS techniques. Proceedings of the Asian GPS Conference 2002, 24–25 October, 2002 held at Indian International Center (IIC), New Delhi.
Wildlife Institute of India (2003). Ecological, social and hydrological factors affecting the management of wetland systems in Uttar Pradesh, with special reference to Vijaya Sagar and associated water bodies in Mahoba District, Okhala and Associated water bodies in Ghaziabad district, Bakhira Bird Sanctuary and Nawabganj Bird Sanctuary. Final report submitted to UP Forest Department, Wildlife Institute of India.
Wolters, W., Zevendergen, A. W., & Bos, M. G. (1991). Satellite remote sensing in irrigation. Irrigation and Drainage Systems, 5, 307–323.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0164-5
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, D.R., Bosukonda, S. & Mrutyunjayareddy, K. Reservoir Impact Assessment on Land Use/Land Cover and Infrastructure—A Case Study on Polavaram Project. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 39, 271–278 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0086-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0086-2