Abstract
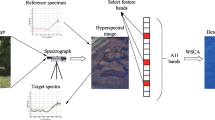
In order to accurately identify ground objects in the hyperspectral imagery by spectral matching, it is important to analyze the absorption-band parameters. This paper presents a new spectral matching method which is based mainly on analysis of the absorption-band position. A measured spectrum of a ground object can be subject to shifts from its real wavelength position; meanwhile an absorption band in the spectrum can also be shifted relatively. Both these shifts are due to the environmental effects. Our spectral matching method stresses the quantification of the total shift of the absorption-band position, thus to get a possible offset range of the measured absorption bands. This offset range is taken as a constraint on the matching process. The pixel spectrum in the image is then compared to each known reference spectrum in a spectral library previously built, so that the ground object corresponding to the reference spectrum is identified. A case study is conducted in Pulang Porphyry Copper deposit, Zhongdian county, Yunnan, China. Five types of ground objects were studied and it is shown that our methods can get more accurate identification results than the approach which does not consider the shift ranges.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baugh WM, Kruse FA and Atkinson Jr WW (1998) Quantitative geochemical mapping of am0monium minerals in the southern Ceder mountains, Nevada, using Airborne visible/infrared imaging spectrometer(AVIRIS). Remote Sensing of Environment 65(3): 292–308
Debba P, van Ruitenbeek FJA and van der Meer FD (2005) Optimal field sampling for targeting minerals using hyperspectral data. Remote Sensing of Environment 99(4): 373–386
Kruse FA, Boardman JW and Huntington JF (2003) Comparison of airborne hyperspectral data and EO-1 hyperion for mineral mapping. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 41(6): 1388–1400
Lass LW, Thill DC and Shafii B (2002) Detecting spotted knapweed (Centaurea maculosa) with hyperspectral remote sensing technology. Weed Technology 16: 426–432
Silvestri S, Marani M and Marani A (2003) Hyperspectral remote sensing of salt marsh vegetation, morphology and soil topography. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth 28(1–3): 15–25
Sohn YS, Moran E and Gurri F (1999) Deforestation in north-central Yucatan (1985–1995): Mapping secondary succession of forest and agricultural land use in Sotuta using the cosine of the angle concept. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 65: 947–958
van der Meer F and Bakker W (1997) Cross correlogram spectral matching: Application to surface mineralogical mapping by using AV IR IS data from Cuprite, Nevada. Remote Sensing of Environment 61: 371–382
van der Meer F, De Jong S and Bakker W (2001) Imaging spectrometry: basic analytical techniques, In: van der Meer, F., de Jong S. (Eds.), Imaging Spectrometry: Basic Principles and Prospective Applications, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 17–61
van der Meer F (2004) Analysis of spectral absorption features in hyperspectral imagery. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 5(1): 55–68
van der Meer F (2006) The effectiveness of spectral similarity measures for the analysis of hyperspectral imagery. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 8(1): 3–17
Xu YJ, Hu GD and Chen ZJ (2007) Application of spectral exhaustive method for object identification and mapping using EO-1 hyperion data. In: Proceedings — Fourth International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, FSKD 2007, v2, Haikou, China, pp.124–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Zhang, Z. & Hu, G. Ground object identification-based on absorption-band position using EO-1 hyperion data. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 38, 169–178 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-010-0016-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-010-0016-8