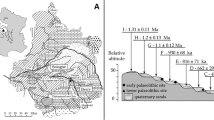
Abstract
The Still Bay is a key technocomplex within the Middle Stone Age (MSA), and Sibudu, in Kwa-Zulu Natal, South Africa, provides one of the longest and richest pre-Still Bay to Still Bay sequences. It has been hypothesised that the Still Bay industry emerged through technological revolution or alternatively through gradual change. In this paper we conduct a geometric morphometric (GM) assessment of the shape differences between the pre-Still Bay and Still Bay points at Sibudu to assess their implication for technological evolution. Pre-Still Bay points are often thought of as unifacial and single-pointed, and Still Bay points as bifacial and double-pointed. Our analysis reveals a more complex and evolving pattern, lending support for the gradual change hypothesis. When the earliest pre-Still Bay points are compared with the Still Bay points, a significant difference in shape is seen. However, intermediate units provide evidence of an evolutionary continuum between those distinct ends of the continuum.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Subject to review.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahler SA (1971) Projectile point form and function at Rodgers Shelter. College of Arts and Science, University of Missouri, Missouri
Archer W, Pop CM, Gunz P, McPherron SP (2016) What is Still Bay? Human biogeography and bifacial point variability. J Hum Evol 97:58–72
Backwell L, Bradfield J, Carlson KJ, Jashashvili T, Wadley L, d’Errico F (2018) The antiquity of bow-and-arrow technology: evidence from Middle Stone Age layers at Sibudu Cave. Antiquity 92(362):289–303
Bordes F (1961) "Typologie du Paléolithique ancien et moyen. Mémoires de l’Institut Préhistorique de l’Université de Bordeaux
Brookes SO, Gray BJ, Inmon B, Rodrigue A (1975) Greenbriar projectile points: a discussion of form and function. Q Bull Archaeol Soc Virginia 30:97–100
Christenson AL (1986) Projectile point size and projectile aerodynamics: an exploratory study. Plains Anthropol 31(112):109–128
Clark JL (2019) The Still Bay and pre-Still Bay fauna from Sibudu cave: taphonomic and taxonomic analysis of the macromammal remains from the Wadley excavations. J Paleolithic Archaeol 2(1):26–73
Clarkson C (2002) An index of invasiveness for the measurement of unifacial and bifacial retouch: a theoretical, experimental and archaeological verification. J Archaeol Sci 29(1):65–75
Conard NJ, Porraz G, Wadley L (2012) What is in a name? Characterising the post-Howieson’s poort’ at sibudu. S Afr Archaeol Bull 67(196):180–199
d’Errico F, Backwell LR, Wadley L (2012) Identifying regional variability in Middle Stone Age bone technology: the case of Sibudu Cave. J Archaeol Sci 39(7):2479–2495
d’Errico F, Vanhaeren M, Wadley L (2008) Possible shell beads from the Middle Stone Age layers of Sibudu cave, South Africa. J Archaeol Sci 35(10):2675–2685
Discamps E, Henshilwood CS (2015) Intra-site variability in the Still Bay fauna at Blombos cave: implications for explanatory models of the Middle Stone Age cultural and technological evolution. PLoS One 10(12):e0144866
Goldberg P, Miller CE, Schiegl S, Ligouis B, Berna F, Conard NJ, Wadley L (2009) Bedding, hearths, and site maintenance in the Middle Stone age of Sibudu cave, KwaZulu-Natal. S Afr Archaeol Anthropol Sci 1(2):95–122
Goodwin AJH, van Riet Lowe C (1929) The stone age cultures of South Africa: AMS Press
Gould SJ, Eldredge N (1977) Punctuated equilibria: the tempo and mode of evolution reconsidered. Paleobiology 3:115–151
Greiser ST (1977) Micro-analysis of wear-patterns on projectile points and knives from the Jurgens site, Kersey. Colorado Plains Anthropologist 22(76):107–116
Hasim A, Herdiyeni Y, Douady S (2016) Leaf shape recognition using centroid contour distance. IOP conference series: earth and environmental science 31:012002
Henshilwood C, d’Errico F, Vanhaeren M, Van Niekerk K, Jacobs Z (2004) Middle stone age shell beads from South Africa. Science 304(5669):404–404
Henshilwood CS (2012) Late Pleistocene techno-traditions in southern Africa: a review of the Still Bay and Howiesons Poort, c. 75–59 ka. J World Prehistory 25(3–4):205–237
Henshilwood CS, d’Errico F, van Niekerk KL, Dayet L, Queffelec A, Pollarolo L (2018) An abstract drawing from the 73,000-year-old layers at Blombos Cave. S Afr Nat 562(7725):115–118
Högberg A (2016) A lithic attribute analysis on blades from the middle stone age site, hollow rock shelter, western Cape Province. S Afr Lithic Technol 41(2):93–113
Högberg A, Lombard M (2016) Still Bay point-production strategies at hollow rock shelter and Umhlatuzana rock shelter and knowledge-transfer systems in southern Africa at about 80–70 thousand years ago. PLoS One 11(12):e0168012
Jacobs Z, Roberts RG, Galbraith RF, Deacon HJ, Grün R, Mackay A, Mitchell P, Vogelsang R, Wadley L (2008a) Ages for the Middle Stone Age of southern Africa: implications for human behavior and dispersal. Science 322(5902):733–735
Jacobs Z, Wintle AG, Roberts RG, Duller GA (2008b) Equivalent dose distributions from single grains of quartz at Sibudu, South Africa: context, causes and consequences for optical dating of archaeological deposits. J Archaeol Sci 35(7):1808–1820
Kandel AW, Bolus M, Bretzke K, Bruch AA, Haidle MN, Hertler C, Märker M (2016) Increasing behavioral flexibility? An integrative macro-scale approach to understanding the Middle Stone Age of southern Africa. J Archaeol Method Theory 23(2):623–668
Key A, Proffitt T, de la Torre I (2020) Raw material optimization and stone tool engineering in the Early Stone Age of Olduvai Gorge (Tanzania). J R Soc Interface 17:20190377. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2019.0377
Klingenberg CP (2011) MorphoJ: an integrated software package for geometric morphometrics. Mol Ecol Resour 11(2):353–357
Klingenberg CP (2013) Visualizations in geometric morphometrics: how to read and how to make graphs showing shape changes. Hystrix, Italian J Mammal 24(1):15–24
Lele SR, Richtsmeier JT (2001) An invariant approach to statistical analysis of shapes: Chapman and Hall/CRC
Lennox SJ, Wadley L (2019) A charcoal study from the Middle Stone Age, 77,000 to 65,000 years ago, at Sibudu, KwaZulu-Natal. Trans R Soc S Afr 74(1):38–54
Lombard M (2006) First impressions of the functions and hafting technology of Still Bay pointed artefacts from Sibudu Cave. S Afr Humanit 18(1):27–41
M Lombard, Högberg A, Wadley L (2019) Temporal perspective on Still Bay point production at Sibudu Cave, KwaZulu-Natal, in the context of southern Africa. Azania Archaeol Res Afr 54(2):141–176
Lombard M, Högberg A (2018) The Still Bay points of Apollo 11 rock shelter, Namibia: an inter-regional perspective. Azania Archaeol Res Afr 53(3):312–340
Mackay A, Stewart BA, Chase BM (2014) Coalescence and fragmentation in the late Pleistocene archaeology of southernmost Africa. J Hum Evol 72:26–51
Mellars PA (1995) The Neanderthal legacy: an archaeological perspective from Western Europe. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey
Porraz G, Parkington JE, Rigaud JP, Miller CE, Poggenpoel C, Tribolo C, Archer W, Cartwright CR, Charrié-Duhaut A, Dayet L, Igreja M (2013) The MSA sequence of Diepkloof and the history of southern African Late Pleistocene populations. J Archaeol Sci 40(9):3542–3552
Robinson JR, Wadley L (2018) Stable isotope evidence for (mostly) stable local environments during the South African Middle Stone Age from Sibudu, KwaZulu-Natal. J Archaeol Sci 100:32–44
Rohlf F (2004a) TpsDig. State University of New York, Stony Brook, NY, Department of Ecology and Evolution
Rohlf FJ (2004b) tpsUtil, file utility program, version 1.26. Department of Ecology and Evolution, State University of New York at Stony Brook
Rots V, Lentfer C, Schmid VC, Porraz G, Conard NJ (2017) Pressure flaking to serrate bifacial points for the hunt during the MIS5 at Sibudu Cave (South Africa). PloS one 12(4):e0175151
Rots V, Plisson H (2014) Projectiles and the abuse of the use-wear method in a search for impact. J Archaeol Sci 48:154–165
Schmid VC, Porraz G, Zeidi M, Conard NJ (2019) Blade technology characterizing the MIS 5 DA layers of Sibudu cave. S Afr Lithic Technol 44(4):199–236
Scholz CA, Johnson TC, Cohen AS, King JW, Peck JA, Overpeck JT, Talbot MR, Brown ET, Kalindekafe L, Amoako PY (2007) East African megadroughts between 135 and 75 thousand years ago and bearing on early-modern human origins. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(42):16416–16421
Soriano S, Villa P, Delagnes A, Degano I, Pollarolo L, Lucejko JJ, Henshilwood C, Wadley L (2015) The Still Bay and Howiesons Poort at Sibudu and Blombos: understanding Middle Stone Age technologies. PLoS One 10(7):e0131127
Soriano S, Villa P, Wadley L (2009) Ochre for the toolmaker: shaping the Still Bay points at Sibudu (KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa). J Afr Archaeol 7(1):41–54
Val A (2016) New data on the avifauna from the Middle Stone Age layers of Sibudu Cave, South Africa: Taphonomic and palaeoenvironmental implications. Quatern Int 421:173–189
Val A, de la Pena P, Wadley L (2016) Direct evidence for human exploitation of birds in the Middle Stone Age of South Africa: The example of Sibudu Cave, KwaZulu-Natal. J Hum Evol 99:107–123
Vanhaeren M, d’Errico F, van Niekerk KL, Henshilwood CS, Erasmus RM (2013) Thinking strings: additional evidence for personal ornament use in the Middle Stone Age at Blombos Cave, South Africa. J Hum Evol 64(6):500–517
Villa P, Soressi M, Henshilwood CS, Mourre V (2009) The Still Bay points of Blombos cave (South Africa). J Archaeol Sci 36(2):441–460
Wadley L (2007) Announcing a Still Bay industry at Sibudu cave, South Africa. J Hum Evol 52(6):681–689
Wadley L (2012) Two ‘moments in time’ during middle stone age occupations of Sibudu South Africa. Southern African Humanities 24(1):79–97
Wadley L (2013) MIS 4 and MIS 3 occupations in Sibudu, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. S Afr Archaeol Bull 41–51
Wadley L, Hodgskiss T, Grant M (2009) Implications for complex cognition from the hafting of tools with compound adhesives in the Middle Stone Age, South Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(24):9590–9594
Wadley L, Jacobs Z (2006) Sibudu Cave: background to the excavations, stratigraphy and dating. S Afr Humanit 18(1):1–26
Will M, Conard NJ (2018) Assemblage variability and bifacial points in the lowermost Sibudan layers at Sibudu South Africa. Archaeol Anthropol Sci 10(2):389–414
Wojcieszak M, Wadley L (2018) Raman spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy confirm ochre residues on 71 000-year-old bifacial tools from Sibudu South Africa. Archaeometry 60(5):1062–1076
Wurz S (2013) Technological trends in the Middle Stone Age of South Africa between MIS 7 and MIS 3. Curr Anthropol 54(S8):305-S319
Acknowledgements
AW would like to thank Lyn Wadley for sponsoring the post-doctoral fellowship which allowed the data for this paper to be collected and for her ongoing support to complete this research. AW would also like to thank Paloma de la Pena for her assistance in accessing the collection and for the many fruitful conversations on MSA lithics. The authors would also like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their attentive review and insightful comments.
Funding
AW was supported by the Department of Science and Technology – National Research Foundation (DST-NRF) Centre of Excellence in Palaeosciences (South Africa) postdoctoral funding. PH was supported by the Tom Austen Brown Endowment, University of Sydney.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AW conceived of the project, formulated the sample, photographed specimens, and undertook the conventional technological analysis. PH landmarked the points and carried out the geometric morphometrics analysis. Both AW and PH contributed to writing the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Way, A.M., Hiscock, P. The evolution of Still Bay points at Sibudu. Archaeol Anthropol Sci 13, 122 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-021-01359-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-021-01359-4