Abstract
Background
Recently, sildenafil was introduced to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH); however, there are currently few studies on the pharmacokinetics of sildenalfil in children. Therefore, we aimed to carry out a pharmacokinetic study of sildenafil in children with PAH using a single dose.
Methods
Twelve children diagnosed with PAH, consisting of with ten males and two females, were recruited for the study after obtaining written consent from their parents or guardians. Blood samples were obtained predose and at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 and 12 hours after the oral administration of 1 mg/kg of sildenafil using an extemporal pediatric formulation developed in our laboratory. The samples were analyzed using a previously validated high performance liquid chromatography method.
Results
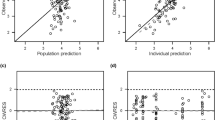
A pharmacokinetic analysis using the WinNonlin 3.1 program that considered the Akaike information criterion (AIC) for selecting a more adjustable model was performed. The following pharmacokinetic parameters were obtained: maximal concentration (Cmax): 366±179 ng/mL, time to maximal concentration: 0.92±0.30 hours, elimination half-life (t1/2): 2.41±1.18 hours, total clearance (CLtot/F): 5.85±2.81 L/hour, volume of distribution (Vd/F): 20.13±14.5 L, absorption rate constants (Ka): 0.343 hour–1, elimination rate (Ke): 0.35 hour–1, area under curve from zero to infinity: 2061±618 ng/mL/hour. The data of all patients adjusted to the model of one compartment were corroborated using AIC.
Conclusions
The parameters Ka, Ke and t1/2 were found to be similar to those reported in adults; however, the values of Cmax and Vd/F were significantly higher. Based on these findings, we propose that treatment regimen of sildenafil be adjusted in children with PAH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sandoval J, Seoane M, Beltrán ME. Pulmonar circulation. In: Vargas-Barrón J, eds. Cardiology text. Mexican society of cardiology. Mexico DF: Intersystem SA of CV, 2006:825–871.
Rich S. Classification and clinical features of pulmonary hypertension. In: Peacock A, Rubin LJ, eds. Pulmonary circulation, 2nd ed. London: Arnold, 2004:147–153.
Simonneau G, Galié N, Rubin LJ, Langleben D, Seeger W, Domenighetti G, et al. Clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;43:5S–12S.
Barst RJ, McGoon M, Torbicki A, Sitbon O, Krowka MJ, Olschewski H, et al. Diagnosis and differential assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;43:40S–47S.
Farber HW, Loscalzo J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension, mechanisms of disease. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1655–1665.
Peiravian F, Amirghofran AA, Borzouee M, Ajami GH, Sabri MR, Kolaee S. Oral sildenafil to control pulmonary hypertension after congenital heart surgery. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 2007;15:113–117.
Launay D, Hachulla E, Hatron PY, Jais X, Simonneau G, Humbert M. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: a rare complication of primary Sjögren syndrome: report of 9 new cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2007;86:299–315.
Juliana AE, Abbad FC. Severe persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn in a setting where limited resources exclude the use of inhaled nitric oxide: successful treatment with sildenafil. Eur J Pediatr 2005;164:626–629.
Fraisse A, Habib G. Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension in children. Arch Pediatr 2004;11:945–950.
Barst RJ, Ivy DD, Gaitan G, Szatmari A, Rudzinski A, Garcia AE, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, doseranging study of oral sildenafil citrate in treatment-naive children with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 2012;125:324–334.
Turko IV, Ballard SA, Francis SH, Corbin JD. Inhibition of cyclic GMP-binding cyclic GMP-specific phosphodiesterase (Type 5) by sildenafil and related compounds. Mol Pharmacol 1999;56:124–130.
Apitz C, Reyes JT, Holtby H, Humpl T, Redington AN. Pharmacokinetic and hemodynamic responses to oral sildenafil during invasive testing in children with pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:1456–1462.
Ahsman MJ, Witjes BC, Wildschut ED, Sluiter I, Vulto AG, Tibboel D, et al. Sildenafil exposure in neonates with pulmonary hypertension after administration via a nasogastric tube. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2010;95:F109–F114.
Marcelín-Jiménez G, Angeles-Moreno AP, Contreras-Zavala L, García-González A, Ramírez-San Juan E. Comparison of fasting bioavailability among 100-mg commercial, 100-mg generic, and 50-mg chewable generic sildenafil tablets in healthy male Mexican volunteers: a single-dose, 3-period, crossover study. Clin Ther 2012;34:689–698.
Kanjanawart S, Gaysonsiri D, Tangsucharit P, Vannaprasaht S, Phunikhom K, Kaewkamson T, et al. Comparative bioavailability of two sildenafil tablet formulations after singledose administration in healthy Thai male volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2011;49:525–530.
Ramirez Mendiola B, Rivera Espinosa L, Juarez Olguin H. Stability, uniform content and therapeutic efficacy of sildenafil extemporaneous capsules. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 2012;6:162–168.
Ramírez-Mendiola B, Flores-Pérez C, García-Álvarez R, Juárez-Olguín H, Flores-Pérez J, Chávez Pacheco JL. A reliable method to quantify sildenafil and its metabolite N-demethylsildenafil by HPLC in plasma of children. Drug Res (Stuttg) 2013;63:473–476.
Glatting G, Kletting P, Reske SN, Hohl K, Ring C. Choosing the optimal fit function: comparison of the Akaike information criterion and the F-test. Med Phys 2007;34:4285–4292.
Dzelaludin J, Bajramovic S. Evaluation of therapeutic response of patients with erectile dysfunction. Med Arh 2009;63:274–277.
Vachiery JL, Huez S, Gillies H, Layton G, Hayashi N, Gao X, et al. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of an intravenous bolus of sildenafil in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2011;71:289–292.
Watt K, Li JS, Benjamin DK Jr, Cohen-Wolkowiez M. Pediatric cardiovascular drug dosing in critically ill children and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2011;58:126–132.
Hill KD, Sampson MR, Li JS, Tunks RD, Schulman SR, Cohen-Wolkowiez M. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous sildenafil in children with palliated single ventricle heart defects: effect of elevated hepatic pressures. Cardiol Young 2016;26:354–362.
Karatza AA, Bush A, Magee AG. Safety and efficacy of sildenafil therapy in children with pulmonary hypertension. Int J Cardiol 2005;100:267–273.
Galiè N, Ghofrani HA, Torbicki A, Barst RJ, Rubin LJ, Badesch D, et al. Sildenafil citrate therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2148–2157.
Samiee-Zafarghandy S, Smith PB, van den Anker JN. Safety of sildenafil in infants*. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2014;15:362–368.
Atz AM, Wessel DL. Sildenafil ameliorates effects of inhaled nitric oxide withdrawal. Anesthesiology 1999;91:307–310.
Chaumais MC, Perrin S, Sitbon O, Simonneau G, Humbert M, Montani D. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of sildenafil as a pulmonary hypertension treatment. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2013;9:1193–1205.
Jamsen KM, McLeay SC, Barras MA, Green B. Reporting a population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study: a journal’s perspective. Clin Pharmacokinet 2014;53:111–122.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Cyril Ndidi Nwoye, a native English speaker and language professor, for the critical review and translation of this manuscript. Besides, the manuscript was edited by Taylor & Francis Editing Services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olguín, H.J., Martínez, H.O., Pérez, C.F. et al. Pharmacokinetics of sildenafil in children with pulmonary arterial hypertension. World J Pediatr 13, 588–592 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-017-0043-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-017-0043-4