Abstract
Background
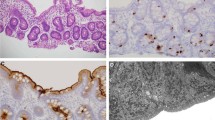
Congenital tufting enteropathy (CTE), an inherited autosomal recessive rare disease, is a severe diarrhea of infancy which is clinically characterized by absence of inflammation and presence of intestinal villous atrophy. Mutations in the EpCAM gene were identified to cause CTE. Recent cases of syndromic tufting enteropathy harboring the SPINT2 (19q13.2) mutation were described.
Methods
Four CTE Italian patients were clinically and immunohistochemically characterized. Direct DNA sequencing of EpCAM and SPINT2 genes was performed.
Results
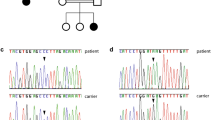
All patients were of Italian origin. Three different mutations were detected (p.Asp219Metfs*15, Tyr186Phefs*6 and p.Ile146Asn) in the EpCAM gene; one of them is novel (p.Ile146Asn). Two patients (P1 and P2) showed compound heterozygosity revealing two mutations in separate alleles. A third patient (P3) was heterozygous for only one novel EpCAM missense mutation (p.Ile146Asn). In a syndromic patient (P4), no deleterious EpCAM mutation was found. Additional SPINT2 mutational analysis was performed. P4 showed a homozygous SPINT2 mutation (p.Y163C). No SPINT2 mutation was found in P3. CLDN7 was also evaluated as a candidate gene by mutational screening in P3 but no mutation was identified.
Conclusion
This study presented a molecular characterization of CTE Italian patients, and identified three mutations in the EpCAM gene and one in the SPINT2 gene. One of EpCAM mutations was novel, therefore increasing the mutational spectrum of allelic variants of the EpCAM gene. Molecular analysis of the SPINT2 gene also allowed us to identify a SPINT2 substitution mutation (c.488A>G) recently found to be associated with syndromic CTE subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reifen RM, Cutz E, Griffiths AM, Ngan BY, Sherman PM. Tufting enteropathy: a newly recognized clinicopathological entity associated with refractory diarrhea in infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1994;18:379–385.
Abely M, Hankard GF, Hugot JP, Cezard JP, Peuchmaur M, Navarro J. Intractable infant diarrhea with epithelial dysplasia associated with polymalformation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1998;27:348–352.
Bird LM, Sivagnanam M, Taylor S, Newbury RO. A new syndrome of tufting enteropathy and choanal atresia, with ophthalmologic, hematologic and hair abnormalities. Clin Dysmorphol 2007;16:211–221.
Roche O, Putterman M, Salomon J, Lacaille F, Brousse N, Goulet O, et al. Superficial punctate keratitis and conjunctival erosions associated with congenital tufting enteropathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2010;150:116–121.e1.
Al-Mayouf SM, Alswaied N, Alkuraya FS, Almehaidib A, Faqih M. Tufting enteropathy and chronic arthritis: a newly recognized association with a novel 1 gene mutation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009;49:642–644.
Goulet O, Kedinger M, Brousse N, Cuenod B, Colomb V, Patey N, et al. Intractable diarrhea of infancy with epithelial and basement membrane abnormalities. J Pediatr 1995;127:212–219.
Goulet O, Salomon J, Ruemmele F, De Serres NP, Brousse N. Intestinal epithelial dysplasia (tufting enteropathy). Orphanet J Rare Dis 2007;2:20.
Sivagnanam M, Mueller JL, Lee H, Chen Z, Nelson SF, Turner D, et al. Identification of 1 as the gene for congenital tufting enteropathy. Gastroenterology 2008;135:429–437.
Sivagnanam M, Schaible T, Szigeti R, Byrd RH, Finegold MJ, Ranganathan S, et al. Further evidence for 1 as the gene for congenital tufting enteropathy. Am J Med Genet A 2010;152A:222–224.
Ko JS, Seo JK, Shim JO, Hwang SH, Park HS, Kang GH. Tufting enteropathy with 1 mutations in two siblings. Gut Liver 2010;4:407–410.
Salomon J, Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Goulet O, Al-Qabandi W, Guigue P, Canioni D, et al. A founder effect at the 1 locus in congenital tufting enteropathy in the Arabic Gulf. Eur J Med Genet 2011;54:319–322.
Schnell U, Kuipers J, Mueller JL, Veenstra-Algra A, Sivagnanam M, Giepmans BN. Absence of cell-surface 1 incongenital tufting enteropathy. Hum Mol Genet 2013;22:2566–2571.
Salomon J, Goulet O, Canioni D, Brousse N, Lemale J, Tounian P, et al. Genetic characterization of congenital tufting enteropathy: epcam associated phenotype and involvement of 1 in the syndromic form. Hum Genet 2014;133:299–310.
Sivagnanam M, Janecke AR, Müller T, Heinz-Erian P, Taylor S, Bird LM. Case of syndromic tufting enteropathy harbors 1 mutation seen in congenital sodium diarrhea. Clin Dysmorphol 2010;19:48.
Heinz-Erian P, Müller T, Krabichler B, Schranz M, Becker C, Rüschendorf F, et al. Mutations in 1 cause a syndromic form of congenital sodium diarrhea. Am J Hum Genet 2009;84:188–196.
Slae MA, Saginur M, Persad R, Yap J, Lacson A, Salomon J, et al. Syndromic congenital diarrhea because of the 1 mutation showing enterocyte tufting and unique electron microscopy findings. Clin Dysmorphol 2013;22:118–120.
Berni Canani R, Terrin G, Cardillo G, Tomaiuolo R, Castaldo G. Congenital diarrheal disorders: improved understanding of gene defects is leading to advances in intestinal physiology and clinical management. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2010;50:360–366.
Terrin G, Tomaiuolo R, Passariello A, Elce A, Amato F, Di Costanzo M, et al. Congenital diarrheal disorders: an updated diagnostic approach. Int J Mol Sci 2012;13:4168–4185.
Ranganathan S, Schmitt LA, Sindhi R. Tufting enteropathy revisited: the utility of MOC31 (EpCAM) immunohistochemistry in diagnosis. Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:265–272.
Ladwein M, Pape UF, Schmidt DS, Schnölzer M, Fiedler S, Langbein L, et al. The cell-cell adhesion molecule 1 interacts directly with the tight junction protein claudin-7. Exp Cell Res 2005;309:345–357.
Trzpis M, McLaughlin PM, De Leij LM, Harmsen MC. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule: more than a carcinoma marker and adhesion molecule. Am J Pathol 2007;171:386–395.
Balzar M, Winter MJ, De Boer CJ, Litvinov SV. The biology of the 17-1A antigen (Ep-CAM). J Mol Med 1999;77:699–712.
Guerra E, Lattanzio R, La Sorda R, Dini F, Tiboni GM, Piantelli M, et al. mTrop1/1 knockout mice develop congenital tufting enteropathy through dysregulation of intestinal E-cadherin/b-catenin. PLoS One 2012;7:e3.
Patey N, Scoazec JY, Cuenod-Jabri B, Canioni D, Kedinger M, Goulet O, et al. Distribution of cell adhesion molecules in infants with intestinal epithelial dysplasia (tufting enteropathy). Gastroenterology 1997;113:833–843.
Ding L, Lu Z, Foreman O, Tatum R, Lu Q, Renegar R, et al. Inflammation and disruption of the mucosal architecture in claudin-7-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 2012;142:303–315.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
d’Apolito, M., Pisanelli, D., Faletra, F. et al. Genetic analysis of Italian patients with congenital tufting enteropathy. World J Pediatr 12, 219–224 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-015-0070-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-015-0070-y