Abstract
Background
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease caused by mutations in the adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette D1 (ABCD1) gene. This study aimed to retrospectively investigate the clinical characteristics of 25 patients with X-ALD including members of large pedigrees, to analyze ABCD1 gene mutations, the effect of gene novel variants on ALD protein (ALDP) structure and function, and to expand gene mutation spectrum of Chinese patients.
Methods
Twenty-five male patients diagnosed with X-ALD were enrolled in this study. The clinical characteristics of the patients were retrospectively summarized by reviewing medical records or telephone consultation. ABCD1 gene mutations were analyzed. The pathogenicity of novel missense variants was analyzed using cobalt constraint-based multiple protein alignment tool, polymorphism phenotyping, sorting intolerant from tolerant, Align-Grantham variation and Grantham deviation, and Swiss-Program Database Viewer 4.04 software, respectively.
Results
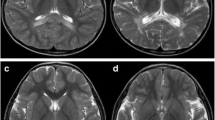
Childhood cerebral form ALD (CCALD) is the most common phenotype (64%) in the 25 patients with X-ALD. The progressive deterioration of neurological and cognitive functions is the main clinical feature. The demyelination of the brain white matter and elevated plasma very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) were found in all patients. Different phenotypes were also presented within family members of the patients. Twenty-two different mutations including 8 novel mutations in the ABCD1 gene were identified in the 25 patients. Of the mutations, 63.6% were missense mutations and 34.8% located in exon 1. The amino acid residues of three novel missense mutations in eight species were highly conserved, and were predicted to be "probably" damaging to ALDP function. The other five novel mutations were splice, nonsense, deletion or duplication mutations.
Conclusions
CCALD is the most common phenotype (64%) in our patients with X-ALD. Eight novel mutations in the ABCD1 gene identified are disease-causing mutations. Brain magnetic resonance imaging and plasma VLCFA determination should be performed for the patients who present with progressive deterioration of neurological development.
World J Pediatr 2015;11(4):366-373
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kemp S, Berger J, Aubourg P. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: clinical, metabolic, genetic and pathophysiological aspects. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012;1822:1465–1474.
Schluter A, Espinosa L, Fourcade S, Galino J, Lopez E, Ilieva E, et al. Functional genomic analysis unravels a metabolicinflammatory interplay in adrenoleukodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet 2012;21:1062–1077.
Mosser J, Douar AM, Sarde CO, Kioschis P, Feil R, Moser H, et al. Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters. Nature 1993;361:726–730.
Berger J, Forss-Petter S, Eichler FS. Pathophysiology of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Biochimie 2014;98:135–142.
Jack GH, Malm-Willadsen K, Frederiksen A, Glintborg D, Andersen M. Clinical manifest x-linked recessive adrenoleukodystrophy in a female. Case Rep Neurol Med 2013;2013:491790.
Pereira Fdos S, Matte U, Habekost CT, de Castilhos RM, El Husny AS, Lourenco CM, et al. Mutations, clinical fi ndings and survival estimates in South American patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. PLoS One 2012;7:e34195.
Wang Z, Yan A, Lin Y, Xie H, Zhou C, Lan F. Familial skewed x chromosome inactivation in adrenoleukodystrophy manifesting heterozygotes from a Chinese pedigree. PLoS One 2013;8:e57977.
Ping LL, Bao XH, Wang AH, Pan H, Wu Y, Xiong H, et al. Clinical features and genotype-phenotype studies of 9 Chinese patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2007;45:203–207. [In Chinese]
Ping LL, Bao XH, Wang AH, Pan H, Wu Y, Xiong H, et al. The genotype and phenotype studies of 40 Chinese patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD). Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao 2006;38:66–70.
Mathe E, Olivier M, Kato S, Ishioka C, Hainaut P, Tavtigian SV. Computational approaches for predicting the biological effect of p53 missense mutations: a comparison of three sequence analysis based methods. Nucleic Acids Res 2006;34:1317–1325.
Ng PC, Henikoff S. SIFT: predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res 2003;31:3812–3814.
Fanen P, Guidoux S, Sarde CO, Mandel JL, Goossens M, Aubourg P. Identification of mutations in the putative ATPbinding domain of the adrenoleukodystrophy gene. J Clin Invest 1994;94:516–520.
Barceló A, Girós M, Sarde CO, Martínez-Bermejo A, Mandel JL, Pàmpols T, et al. Identifi cation of a new frameshift mutation (1801delAG) in the ALD gene. Hum Mol Genet 1994;3:1889–1890.
Fuchs S, Sarde CO, Wedemann H, Schwinger E, Mandel JL, Gal A. Missense mutations are frequent in the gene for X-chromosomal adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD). Hum Mol Genet 1994;3:1903–1905.
Takano H, Koike R, Onodera O, Sasaki R, Tsuji S. Mutational analysis and genotype-phenotype correlation of 29 unrelated Japanese patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Arch Neurol 1999;56:295–300.
Lachtermacher MB, Seuánez HN, Moser AB, Moser HW, Smith KD. Determination of 30 X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy mutations, including 15 not previously described. Hum Mutat 2000;15:348–353.
Kok F, Neumann S, Sarde CO, Zheng S, Wu KH, Wei HM, et al. Mutational analysis of patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Hum Mutat 1995;6:104–115.
Kemp S, Ligtenberg MJ, van Geel BM, Barth PG, Sarde CO, van Oost BA, et al. Two intronic mutations in the adrenoleukodystrophy gene. Hum Mutat 1995;6:272–273.
Shimozawa N, Honda A, Kajiwara N, Kozawa S, Nagase T, Takemoto Y, et al. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: diagnostic and follow-up system in Japan. J Hum Genet 2011;56:106–109.
Kemp S, Pujol A, Waterham HR, van Geel BM, Boehm CD, Raymond GV, et al. ABCD1 mutations and the X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy mutation database: role in diagnosis and clinical correlations. Hum Mutat 2001;18:499–515.
Takemoto Y, Suzuki Y, Tamakoshi A, Onodera O, Tsuji S, Hashimoto T, et al. Epidemiology of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in Japan. J Hum Genet 2002;47:590–593.
Bezman L, Moser AB, Raymond GV, Rinaldo P, Watkins PA, Smith KD, et al. Adrenoleukodystrophy: incidence, new mutation rate, and results of extended family screening. Ann Neurol 2001;49:512–517.
Jardim LB, da Silva AC, Blank D, Villanueva MM, Renck L, Costa ML, et al. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: clinical course and minimal incidence in South Brazil. Brain Dev 2010;32:180–190.
Kumar N, Taneja KK, Kalra V, Behari M, Aneja S, Bansal SK. Genomic profiling identifies novel mutations and SNPs in ABCD1 gene: a molecular, biochemical and clinical analysis of X-ALD cases in India. PLoS One 2011;6:e25094.
Bruyn RP. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Neurology 1996;46:1192.
van Geel BM, Bezman L, Loes DJ, Moser HW, Raymond GV. Evolution of phenotypes in adult male patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Ann Neurol 2001;49:186–194.
Moser HW, Mahmood A, Raymond GV. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2007;3:140–151.
Raymond GV, Seidman R, Monteith TS, Kolodny E, Sathe S, Mahmood A, et al. Head trauma can initiate the onset of adrenoleukodystrophy. J Neurol Sci 2010;290:70–74.
Smith KD, Kemp S, Braiterman LT, Lu JF, Wei HM, Geraghty M, et al. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: genes, mutations, and phenotypes. Neurochem Res 1999;24:521–535.
Iwasa M, Yamagata T, Mizuguchi M, Itoh M, Matsumoto A, Hironaka M, et al. Contiguous ABCD1 DXS1357E deletion syndrome: report of an autopsy case. Neuropathology 2013;33:292–298.
Berger J, Molzer B, Fae I, Bernheimer H. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD): a novel mutation of the ALD gene in 6 members of a family presenting with 5 different phenotypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994;205:1638–1643.
Asheuer M, Bieche I, Laurendeau I, Moser A, Hainque B, Vidaud M, et al. Decreased expression of ABCD4 and BG1 genes early in the pathogenesis of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet 2005;14:1293–1303.
Moser HW, Moser AB, Smith KD, Bergin A, Borel J, Shankroff J, et al. Adrenoleukodystrophy: phenotypic variability and implications for therapy. J Inherit Metab Dis 1992;15:645–664.
Maestri NE, Beaty TH. Predictions of a 2-locus model for disease heterogeneity: application to adrenoleukodystrophy. Am J Med Genet 1992;44:576–582.
Terre’Blanche G, van der Walt MM, Bergh JJ, Mienie LJ. Treatment of an adrenomyeloneuropathy patient with Lorenzo’s oil and supplementation with docosahexaenoic acid—a case report. Lipids Health Dis 2011;10:152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, SS., Ye, J., Zhang, HW. et al. Eight novel mutations in the ABCD1 gene and clinical characteristics of 25 Chinese patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. World J Pediatr 11, 366–373 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-015-0044-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-015-0044-0