Abstract
Background
Wilson’s disease (WD) is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of copper metabolism, caused by mutations in the ATP7B gene, resulting in copper accumulation in the liver, brain, kidney, and cornea and leading to significant disability or death if untreated. Early diagnosis and proper therapy usually predict a good prognosis, especially in pre-symptomatic WD. Genetic testing is the most accurate and effective diagnostic method for early diagnosis.
Methods
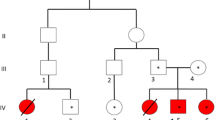
The clinical and biochemical features of three unrelated Han Chinese families with pre-symptomatic WD were reported. The molecular defects in these families were investigated by polymerase chain reaction and DNA sequencing. Hundred healthy children with the same ethnic background served as controls. Bioinformatic tools (polymorphism phenotyping-2, sorting intolerant from tolerant, protein analysis through evolutionary relationships, and predictor of human deleterious single nucleotide polymorphisms) were combined and used to predict the functional effects of mutations.
Results
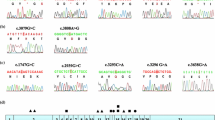
We identified 2 novel ATP7B mutations (p.Leu692Pro and p.Asn728Ser) and 3 known mutations (p.Met769fs, p.Arg778Leu and p.Val1216Met) in these Chinese WD families. These mutations were not observed in the 100 normal controls. The bioinformatic method showed that p.Leu692Pro and p.Asn728Ser mutations are pathogenic.
Conclusions
Our research enriches the mutation spectrum of the ATP7B gene worldwide and provides valuable information for studying the mutation types and mode of inheritance of ATP7B in the Chinese population. Liver function analysis and genetic testing in young children with WD are necessary to shorten the time to the initiation of therapy, reduce damage to the liver and brain, and improve prognosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geng J, Wang J, Yao RE, Liu XQ, Fu QH. Identification of one novel and nine recurrent mutations of the ATP7B gene in 11 children with Wilson disease. World J Pediatr 2013;9:158–162.
Coffey AJ, Durkie M, Hague S, McLay K, Emmerson J, Lo C, et al. A genetic study of Wilson’s disease in the United Kingdom. Brain 2013;136:1476–1487.
Aggarwal A, Bhatt M. Update on Wilson disease. Int Rev Neurobiol 2013;110:313–348.
Li XH, Lu Y, Ling Y, Fu QC, Xu J, Zang GQ, et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of Wilson’s disease in China: identification of 14 novel mutations. BMC Med Genet 2011;12: 6.
Squitti R, Polimanti R, Siotto M, Bucossi S, Ventriglia M, Mariani S, et al. ATP7B variants as modulators of copper dyshomeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Med 2013;15:515–522.
European Association for Study of Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wilson’s disease. J Hepatol 2012;56:671–685.
Wang LH, Huang YQ, Shang X, Su QX, Xiong F, Yu QY, et al. Mutation analysis of 73 southern Chinese Wilson’s disease patients: identification of 10 novel mutations and its clinical correlation. J Hum Genet 2011;56:660–665.
Vrabelova S, Letocha O, Borsky M, Kozak L. Mutation analysis of the ATP7B gene and genotype/phenotype correlation in 227 patients with Wilson disease. Mol Genet Metab 2005;86:277–285.
Squitti R, Siotto M, Bucossi S, Polimanti R. In silico investigation of the ATP7B gene: insights from functional prediction of non-synonymous substitution to protein structure. Biometals 2014;27:53–64.
Hui J, Yuen YP, Chow CM, Chong J, Chiang G, Cheung CK, et al. Isolated persistent elevation of alanine transaminase for early diagnosis of pre-symptomatic Wilson’s disease in Chinese children. World J Pediatr 2013;9:361–364.
Lin LJ, Wang DX, Ding NN, Lin Y, Jin Y, Zheng CQ. Comprehensive analysis on clinical features of Wilson’s disease: an experience over 28 years with 133 cases. Neurol Res 2014;36:157–163.
El-Balkhi S, Trocello JM, Poupon J, Chappuis P, Massicot F, Girardot-Tinant N, et al. Relative exchangeable copper: a new highly sensitive and highly specific biomarker for Wilson’s disease diagnosis. Clin Chim Acta 2011;412:2254–2260.
Seo JK. Diagnosis of Wilson disease in young children: molecular genetic testing and a paradigm shift from the laboratory diagnosis. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2012;15:197–209.
Kenney SM, Cox DW. Sequence variation database for the Wilson disease copper transporter, ATP7B. Hum Mutat 2007;28:1171–1177.
Ferenci P. Regional distribution of mutations of the ATP7B gene in patients with Wilson disease: impact on genetic testing. Hum Genet 2006;120:151–159.
Bem RS, Raskin S, Muzzillo DA, Deguti MM, Cançado EL, Araújo TF, et al. Wilson’s disease in Southern Brazil: genotypephenotype correlation and description of two novel mutations in ATP7B gene. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2013;71:503–507.
Deguti MM, Genschel J, Cancado EL, Barbosa ER, Bochow B, Mucenic M, et al. Wilson disease: novel mutations in the ATP7B gene and clinical correlation in Brazilian patients. Hum Mutat 2004;23: 398.
Wu ZY, Wang N, Lin MT, Fang L, Murong SX, Yu L. Mutation analysis and the correlation between genotype and phenotype of Arg778Leu mutation in chinese patients with Wilson disease. Arch Neurol 2001;58:971–976.
Gu YH, Kodama H, Du SL, Gu QJ, Sun HJ, Ushijima H. Mutation spectrum and polymorphisms in ATP7B identified on direct sequencing of all exons in Chinese Han and Hui ethnic patients with Wilson’s disease. Clin Genet 2003;64:479–484.
Yoo HW. Identification of novel mutations and the three most common mutations in the human ATP7B gene of Korean patients with Wilson disease. Genet Med 2002;4 Suppl 6:43–48.
Okada T, Shiono Y, Hayashi H, Satoh H, Sawada T, Suzuki A, et al. Mutational analysis of ATP7B and genotype-phenotype correlation in Japanese with Wilson’s disease. Hum Mutat 2000;15:454–462.
Panichareon B, Taweechue K, Thongnoppakhun W, Aksornworanart M, Pithukpakorn M, Yenchitsomanus PT, et al. Six novel ATP7B mutations in Thai patients with Wilson disease. Eur J Med Genet 2011;54:103–107.
Liu XQ, Zhang YF, Liu TT, Hsiao KJ, Zhang JM, Gu XF, et al. Correlation of ATP7B genotype with phenotype in Chinese patients with Wilson disease. World J Gastroenterol 2004;10:590–593.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, ZF., Wu, W., Yu, YL. et al. Novel mutations of the ATP7B gene in Han Chinese families with pre-symptomatic Wilson’s disease. World J Pediatr 11, 255–260 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-015-0031-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-015-0031-5