Abstract
Choosing the optimal location for a city based on sound environmental geomorphology planning is of the utmost importance for achieving environmental sustainability, as it can spare the state and other decision-making entities a great deal of stress in the long run. GIS offers great potential for environmental planners to choose the most appropriate places for the cities of the future, especially when coupled with environmental geomorphological analyses. The State of Kuwait seeks sustainable development through the implementation of clear and specific urban plans, some of which suffer from a severe lack of geomorphological and spatially based environmental planning. This study aims to (1) conduct suitability modeling for establishing new cities in Kuwait, (2) assess the current 2005–2030 urban plan, and (3) propose possible recommendations and solutions for potential urban problems. The study relies on integrating several methods to devise a framework that will aid researchers and decision-makers in selecting optimal locations for built structures based on analysis and modeling (e.g., digital elevation model, geologic mapping, geomorphology, natural hazards, heritage/archeological sites, military areas, oil fields, soils). Using this methodology in choosing city sites contributes to achieving sustainable development, reducing problems during construction processes, saving countries’ budgets, and saving lives. Results from this study enhance understanding of how environmental geomorphology, when combined with GIS, can be harnessed to achieve sustainable urban development in the Arabian Gulf countries and other desert countries.


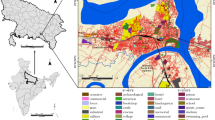
Source: EMISK, 2011)




source: Live traffic, Google Maps, 16 November 2018


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeli Z, Khorshiddoust A (2011) Application of geomorphology in urban planning: case study in landfill site selection. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences 19:662–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.05.183
Adolfo, Quesada-Román, Ernesto Villalobos-Portilla & Daniela Campos Durán. Hydrometeorological disasters in urban areas of Costa Rica, Central America, Environmental Hazards, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1080/17477891.2020.1791034.
AlAli EH (2008) Groundwater history and trends in Kuwait. WIT Trans Ecol Environ 112:153–164
Alghais N, Pullar D (2017) Modelling future impacts of urban development in Kuwait with the use of ABM and GIS. Trans. GIS 20:20e42. https://doi.org/10.1111/tgis.12293
Alghais, N and Pullar, D. Projection for new city futures-a case study for Kuwait. In: 15th International Conference on Computers in Urban Planning and Urban Management. Adelaide, Australia, 2017b. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00590.
Al-Matar M, Hassan A, Hassan A (2020) Investigating land-use and land-cover changes of Failaka Island: a study in geography and geoarchaeology. Journal of the social sciences, Kuwait university. 48(2):33–57. https://doi.org/10.34120/0080-048-002-014
Al-Mutairi, H. Islamic archaeology on the Northwest Coast of Failaka Island-a comparative analytical archaeological study; National Council for Culture, Arts and Letters, 2017, Kuwait City, Kuwait.
A1-Sarawi M (1995) Surface Geomorphology of Kuwait. GeoJournal 35(4):493–503
Al-Sulamimi J, Mukhopadhyay A (2000) An overview of the surface and near surface geology, geomorphology, and natural resources of Kuwait. Earth Sci Rev 50(3–4):227–267
Ayhan, Çiğdem., Tülay, Taşlı., Ferah, Özkök., Hasan, Tatlı. Land use suitability analysis of rural tourism activities: Yenice, Turkey, Tourism Management, Volume, 2020, 76, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2019.07.003.
Bathrellos G, Kalliopi P, Hariklia S, Dimitrios P, Konstantinos C (2012) Potential suitability for urban planning and industry development using natural hazard maps and geological-geomorphological parameters. Environ Earth Sci 66:537–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1263-x
Carr, M. Zwick, P. Using GIS suitability analysis to identify potential future land use conflicts in North Central Florida. Journal of Conservation Planning, 2005, 58–73.
Digital elevation model, ALOS PALSAR RTC, 12.5-m. 2020 https://asf.alaska.edu/data-sets/derived-data-sets/alos-palsar-rtc/alos-palsar-radiometric-terrain-correction/
Dong J, Zhuang D, Xu X, Ying L (2008) Integrated evaluation of urban development suitability based on remote sensing and GIS techniques – a case study in Jingjinji Area. China Sensors 8:5975–5986
El-Baz, F., Al-Sarawi, M. Atlas of the state of kuwait from satellite images; Kuwait Foundation for the Advancement of Sciences: Kuwait, 2000. Kuwait.
Fadlelmawla A, Fayad M, El-Gamily H, Rashid T, Mukhopadhyay A, Kotwicki V (2011) A land surface zoning approach based on three-component risk criteria for groundwater quality protection. Water Resour Manage 25(6):1677–1697
Feizizadeh B, Blaschke T (2013) Land suitability analysis for Tabriz County, Iran: a multi-criteria evaluation approach using GIS. J Environ Plan Manag 56(1):1–23
Garcia, P., Augustin, C., and Casagrande, P. Geomorphological index as support to urban planning. Mercator, 2020, Vol, 19. https://doi.org/10.4215/rm2020.e19003
Girvetz E, Thorne J, Berry A (2008) Jaeger, J, Integration of landscape fragmentation analysis into regional planning: a statewide multi-scale case study from California, USA. Landsc Urban Plan 86(3):205–218
Hamdy Badawi. Population imbalance in the state of Kuwait: a study in population geography, Kuwait Research and Studies Center, 2009, Kuwait.
Hassaan, Mahmoud., Ahmed, Hassan., Hassan Al-Dashti, GIS-based suitability analysis for siting solar power plants in Kuwait, The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2020.11.004.
Hassan AG, Almatar M, Torab M, Allen CD (2020) Environmental urban plan for Failaka Island, Kuwait: a study in urban geomorphology. Sustainability 12(17):7125. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177125
Hassan A, Hassaan MA (2020) Potential impact of sea level rise on the geomorphology of Kuwait state coastline. Arab J Geosci 13:1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06084-1
Herold M, Couclelis H, Clarke KC (2005) The role of spatial metrics in the analysis and modeling of urban land use change. Comput Environ Urban Syst 29:369–399
Ignacio C (2018) Fernández, & Jianguo Wu A GIS-Based Framework to Identify Priority Areas for Urban Environmental Inequity Mitigation and Its Application in Santiago De Chile. App Geograph 94:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2018.03.019
József, Szabó., Lóránt Dávid., and Dénes Lóczy.Anthropogenic geomorphologya guide to man-made landforms, Springer Netherlands, 2010 , https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3058-0
KISR. Soil survey for the State of Kuwait - vol II Reconnaissance survey. ACM International, Adelaide, 1999. Kuwait.
KISR, Kuwait national seismic network. 2020. http://www.kisr.edu.kw/en/projects/64/details/.
Kleo, AbdelHamid., Abu Al-Enein, Hassan., Al-Husseini, S. Alasfour, T., Al-Sheikh, M. Selected studies in the geomorphology of Kuwaiti Lands, Kuwait Research and Studies Center, 2003, Kuwait.
Kuwait Municipality. Third Kuwait Master Plan Review, Executive Summary, 2005, Kuwait. https://www.baladia.gov.k.
Kuwait News agency (KUNA), (2016, 2018, 2020), https://www.kuna.net.kw/ArticleDetails.aspx?id=2832486&language=en.
Maarseveen, Martin., Javier, Martinez and Johannes Flacke. GIS in sustainable urban planning and management a global perspective, 2019 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC, https://taylorandfrancis.com/.
Marull J, Pino J, Mallarach J, Cordobilla M (2007) Aland suitability index for strategic environmental assessment in metropolitan areas. Landsc Urban Plan 81:200–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2006.11.005
Matsuoka R, Kaplan R (2008) People needs in the urban landscape: analysis of landscape and urban planning contributions. Landsc Urban Plan 84:7–19
Meadows, M and J. C. Lin. Geomorphology and society, Advances in Geographical and Environmental Sciences, Springer Japan 2016, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-56000-5.
Mierzwiak M, Calka B (2017) Multi-criteria analysis for solar farm location suitability. Rep Geod Geoinform 104:20–32
Ministry of Planning, Central Statistical Administration, 2020, https://www.csb.gov.kw/Pages/Statistics
Ministry of Planning. Statistical Collection in 25 Years, Central Statistics Administration, Special Issue, 1990, Kuwait.
Ministry of Public Works accessed on 17 April 2019.
Misak R.F., Khalaf F.I., Omar S.A.S. Managing the hazards of drought and shifting sands in dry lands: the case study of Kuwait. In: Shahid S., Taha F., Abdelfattah M. (eds) Developments in Soil Classification, Land Use Planning and Policy Implications. Springer, Dordrecht, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5332-7_41
Al-Shalakany M (1994) Population and demographic statistics: methods of demographic analysis, 2nd edn. Kuwait University, Kuwait
Qian, Li., Yang, Yu., Xiaoqian, Jiang., Yuntao, Guan., Multifactor-based environmental risk assessment for sustainable land-use planning in Shenzhen, China, Science of The Total Environment, Volume 657, 2019, Pages 1051–1063, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.118.
Rashoud, Al-Khorayef. Population, concepts, methods and applications, King Saud University, 2003. Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Saha A, Roy R (2021) An integrated approach to identify suitable areas for built-up development using GIS-based multi-criteria analysis and AHP in Siliguri planning area. India SN Appl Sci 3:395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04354-5
Samira, O and Shabbir, A. Reconnaissance soil survey for the state of Kuwait., chapter 3 in Book “Developments in Soil Classification, Land Use Planning and Policy Implications: Innovative Thinking of Soil Inventory for Land Use Planning and Management of Land Resources”, 2013, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-5332-73, © Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht.
Sandipan D, Anirban B, Sagar M (2013) Study on urban land suitability assessment using remote sensing and GIS: a case study of Khairagarh, in Chhattisgarh. Int J Comput Appl 74:20–26
Shukla, A., Kumar, V., Jain, K. Site suitability evaluation for urban development using remote sensing, GIS, and analytic hierarchy process (AHP). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision and Image Processing; Springer Science+Business Media: Singapore City, Singapore, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1007/978–981-10–2107-7_34
Steiner F, McSherry L, Cohen J (2000) Land suitability analysis for the upper Gila River watershed. Landsc Urban Plan 50:199–214
Store R, Kangas J (2001) Integratin21 g spatial multi-criteria evaluation and expert knowledge for GIS-based habitat suitability modelling. Landsc Urban Plan 55:79–93
System of environmental monitoring information (EMISK). Various maps: surface sediments, geology, Geomorphology unites, Air Quality, and Land use, 2011, https://epa.org.kw/en-us/eMISK.
The Public Authority for Civil Information. Population statistics department, 2017, Kuwait.
The Public Authority for Civil Information. Population, Statistics Department, 2020, Kuwait.
Thornbush, M.J. and C.D. Allen, Eds. Urban geomorphology: landforms and processes in cities, Elsevier, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811951-8.00017-5
UNDESA. World urbanization prospects: the 2014 revision. New York, New York: United Nations, 2014, Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Mahmoud Adel Hassaan (Alexandria University), and Professor Raafat Misak (KISR), for their contributions to reviewing and improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology: Ahmed Hassan, Mahmoud Fayad, and Maha Alfaraj; writing—original draft, Ahmed Hassan, Maha Alfaraj, Mahmoud Fayad, and Casey D Allen; writing—review and editing, Ahmed Hassan and Casey D Allen.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, A., Alfaraj, M., Fayad, M. et al. Optimizing site selection of new cities in the desert using environmental geomorphology and GIS: a case study of Kuwait. Appl Geomat 13, 953–968 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-021-00403-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-021-00403-1