Abstract
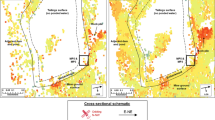
The short-term deformation of Cochin International Airport Limited (CIAL), southwestern India, built on the massive floodplain of the Periyar River, is the topic of inquiry in this study. An unprecedented flood of August 2018 instigated a refined understanding of the ground deformation, if any, of the CIAL property. Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PSInSAR), using Sentinel-1A images, was used for documenting the ground deformation, which generated 5563 Persistent Scatterer Interferometric (PSI) points. Though the velocity of PSI points swayed positively (maximum velocity of 23.61 mm/y) and negatively (minimum velocity of − 21.83 mm/y), the majority values were negative. Interpolation of velocity values showed the predominance of the negative field for all the components of CIAL infrastructure. Ground deformation was modelled using Settle3, based on standard penetration test (SPT) values of five boreholes in the study area. Comparison between the PSInSAR and Settle3 modelling of deformation shows correlation amongst the mean values of both the approaches. PSInSAR monitoring and Settle3 modelling results relate to the varying thickness and properties of soils both in situ and the landfilled material. Findings also highlight the need for geological and geotechnical site characterization before the construction, and remote monitoring of critical long-term assets, especially strategic ones such as airport.

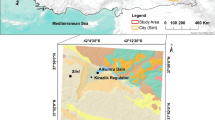
source: www.cial.aero)

source: ALOS PALSAR). c Geological map of the study area (source: GSI 2005)






Similar content being viewed by others
References
AASHTO (2001) American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials. Pavement Management Guide. AASHTO, Washington, D.C., 254 p.
AASHTO (2011) American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials. Transportation Asset Management Guide, Volume 2: A Focus on Implementation. AASHTO, Washington, D.C., 69 p.
ASTM (2018) ASTM D1586/D1586M-18. https://www.astm.org/Standards/D1586.htm. Accessed 15 Mar 2020
Bernhardt SKL, Loehr JE, Huaco D (2003) Asset management framework for geotechnical infrastructure. Infrastruct Syst 9:107–116
Blaschke T, Lang S, Lorup E, Strobl J, Zeil P (2000) Object-oriented image processing in an integrated GIS/remote sensing environment and perspectives for environmental applications. Environ Inform Plan, Pol Pub 2:555–570
Bouali EH, Oommen T, Escobar-Wolf R (2016) Interferometric stacking toward geohazard identification and geotechnical asset monitoring. J Infrastruct Syst 22(2):05016001
Bouali EH, Oommen T, Escobar-Wolf R (2018) Mapping of slow landslides on the Palos Verdes Peninsula using the California landslide inventory and persistent scatterer interferometry. Landslides 15(3):439–452
Bowles JE (1997) Foundation analysis and design.5th Edition. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., New York, p 1143.
Brown T, Hettiarachchi H (2008) Estimating shear strength properties of soil using SPT blow counts: an energy balance approach. In: Alshawabkeh AN, Reddy KR, Khire MV (eds) GeoCongress 2008: Characterization, monitoring, and modeling of geosystems, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 9–12 March 2008. American Society of Civil Engineers, pp 364–371.
CIAL (2018) http://cial.aero/
Del Soldato M, Tomás R, Pont J, Herrera G, Lopex-Davalillos JCG, Mora O (2016) A multi-sensor approach for monitoring a road bridge in the Valencia harbour (SE Spain by SAR Interferometry (InSAR). Rend Online Soc Geol It 41:235–238
DePrekel K, Bouali EH, Oommen T (2018) Monitoring the impact of groundwater pumping on infrastructure using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI). Infrastruct 3(4):57
Duncombe J. (2018) Making sense of landslide danger after Kerala’s floods. Eos, 99. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018EO108061.
Endsley, A., Brooks, C., Harris, D., Ahlborn, T., & Vaghefi, K. (2012, April).Decision support system for integrating remote sensing in bridge condition assessment and preservation. In Sensors and Smart Structures Technologies for Civil, Mechanical, and Aerospace Systems 2012 (Vol. 8345, p. 834548). International Society for Optics and Photonics
EnviSARscape (2016) SARscape’s Basic module Tutorial. https://www.harrisgeospatial.com/
Escobar-Wolf R, Bouali EH, Oommen T, Dobson R, Vitton S, Brooks C, Lautala P (2016) Candidate remote sensing techniques for the different transportation environments, requirements, platforms, and optimal data fusion methods for assessing the state of geotechnical assets. Michigan Technological University, USDOT Cooperative Agreement No.RITARS-14-H-MTU, 152 p.
Escobar-Wolf R, Oommen T, Brooks CN, Dobson RJ, Ahlborn TM (2018) Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based assessment of concrete bridge deck delamination using thermal and visible camera sensors: a preliminary analysis. Research in Nondestructive Evaluation 29(4):183–198
Ferretti A, Prati C, Rocca F (2000) Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 38(5):2202–2212
Ferretti A, Prati C, Rocca F (2001) Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 39(1):8–20
FHWA (1999) Federal Highway Administration. Asset Management Primer. U.S. Department of Transportation, Washington, D.C., 30 p.
FHWA (2014) Federal Highway Administration. Program Overview, https://highways.dot.gov/long-term-infrastructure-performance/ltbp/long-term-bridge-performance.
Gens R, Logan T (2003) Alaska Satellite Facility software tools. University of Alaska, Fairbanks, Alaska, Geophysical Institute
Glendinning S, Hall J, Manning L (2009) Asset-management strategies for infrastructure embankments. Proceed Inst Civil Eng ,Eng Sustain 162(ES2):111–120
Gómez C, White JC, Wulder MA (2016) Optical remotely sensed time series data for land cover classification: A review. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 116:55–72
Han X, Chen X, Feng L (2015) Four decades of winter wetland changes in Poyang Lake based on Landsat observations between 1973 and 2013. Remote Sens Environ 156:426–437
He KS, Rocchini D, Neteler M, Nagendra H (2011) Benefits of hyperspectral remote sensing for tracking plant invasions. Divers Distrib 17(3):381–392
Huang SL, Darrow MM, Calvin P (2009) Unstable slope management program: Background research and program inception – phase I final report. Alaska Department of Transportation and Public Facilities, 90 p.
Jawahar I., Mohamed N., Shuaib K. (2007) A framework for pipeline infrastructure monitoring using wireless sensor networks. In Proc. Wireless Telecommunications Symposium, 26–28 April 2007, Pomona, USA. https://doi.org/10.1109/WTS.2007.4563333
Jiang L, Lin H (2010) Integrated analysis of SAR interferometric and geological data for investigating long-term reclamation settlement of Chek Lap Kok Airport. Hong Kong Eng Geol 110(3–4):77–92
Kääb A, Winsvold SH, Altena B, Nuth C, Nagler T, Wuite J (2016) Glacier remote sensing using Sentinel-2, part 1: radiometric and geometric performance, and application to ice velocity. Remote Sens 8(7):598
Kumar R, Bhargava K, Choudhary D (2016a) Estimation of engineering properties of soils from field SPT using random number generation. INAE Let 1:77–84
Kumar S, Deshpande A, Ho SS, Ku JS, Sarma SE (2016b) Urban street lighting infrastructure monitoring using a mobile sensor platform. IEEE Sensors 16(12):4981–4994
Li X, Yeh AGO (2004) Analyzing spatial restructuring of land use patterns in a fast growing region using remote sensing and GIS. Landsc Urban Plann 69(4):335–354
Martins BH, Suzuki M, Yastika PE, Shimizu N (2020) Ground surface deformation detection in complex landslide area- Bobonaro, Timor-Leste using SBAS DInSAR, UAV. Photogramm Field Observ Geosci 10(6):245
Masino J, Thumm J, Frey M, Gauterin F (2017) Learning from the crowd: road infrastructure monitoring system. J Traffic and Transport Eng 4(5):451–463
McGuire LA, Rengers FK, Kean JW, Staley DM (2017) Debris flow initiation by runoff in a recently burned basin: is grain-by-grain sediment bulking or en masse failure to blame? Geophys Res Lett 44(14):7310–7319
Metternicht G, Hurni L, Gogu R (2005) Remote sensing of landslides: an analysis of the potential contribution to geo-spatial systems for hazard assessment in mountainous environments. Remote Sens Environ 98(2–3):284–303
Moreira A, Krieger G, Hajnsek I, Papathanassiou K, Younis M, Lopez-Dekker P, Huber S, Villano M, Pardini M, Eineder M, De Zan F (2015) Tandem-L: A highly innovative bistatic SAR mission for global observation of dynamic processes on the Earth’s surface. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Magazine 3(2):8–23
Obrzud R, Truty A (2012) The hardening soil model-a practical guidebook. Report PC, 100701.
Oommen T, Baise LG, Gens R, Prakash A, Gupta RP (2013) Documenting earthquake-induced liquefaction using satellite remote sensing image transformations. Environ Eng Geosci 19(4):303–318
Osmanoğlu B, Sunar F, Wdowinski S, Cabral-Cano E (2016) Time series analysis of InSAR data: Methods and trends. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 115:90–102
Park JH.,Tateishi R., Wikantika K., Park JG. (1999) The potential of high resolution remotely sensed data for urban infrastructure monitoring. In Proc. IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.1999.774557
Peck RB, Hanson WE, Thornbury TH (1974) Foundation Engineering.2nd Edition.Wiley p544.
Riquelme A, Del Soldato M, Tomás R, Cano M, Bordehore LJ, Moretti S (2010) Digital landform reconstruction using old and recent open access digital aerial photos. Geomorphol 329:206–223
Schaefer LN, Wang T, Escobar-Wolf R, Oommen T, Lu Z, Kim J, Waite GP (2017) Three-dimensional displacements of a large volcano flank movement during the May 2010 eruptions at Pacaya Volcano. Guatemala Geophys Res Lett 44(1):135–142
Serrano-Juan A, Pujades E, Vázquez-Suñè E, Crosetto M, Cuevas-González M (2017) Leveling vs. InSAR in urban underground construction monitoring: Pros and cons. Case of la sagrera railway station (Barcelona, Spain). Eng Geol 218:1–11
Soga K, Luo L (2018) Distributed fiber optics sensors for civil engineering infrastructure sensing. J Struct Integrity Maint 2(1):1–21
Soilán M, Sánchez-Rodriguez A, del Rio-Narral P, Perez-Collazo C, Arias P, Riveiro B (2019) Review of laser scanning technologies and their applications for road and railway infrastructure monitoring. Infrastruct 4(4):1–29
Solari L, Ciampalini A, Raspini F, Bianchini S, Moretti S (2016)PSInSAR analysis in the Pisa Urban Area (Italy): A case study of subsidence related to stratigraphical factors and urbanization. Remote Sensing, 8, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020120
Stanley DA, Pierson LA (2013) Geotechnical asset management of slopes: Condition indices and performance measures. Special Publication for Geo-Congress 2013: Stability and Performance of Slopes and Embankments III, San Diego, California, March 3–6, 1658–1667.
Vishnu C.L., Rani V.R., Sajinkumar K.S., Oommen T., Bonali F.L., Pareeth S., Thrivikramji K., McAdoo B.G., Anilkumar Y. (2020) Catastrophic flood of August 2018, Kerala, India: Partitioning role of geologic factors in modulating flood level using remote sensing data. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment (Submitted).
Vishnu CL, Sajinkumar KS, Oommen T, Coffman RA, Thrivikramji K, Rani VR, Keerthy S (2019) Satellite-based assessment of the August 2018 Flood in parts of Kerala, India. Geomatics, Nat Hazards Risk 10(1):758–767
White DJ, Take WA, Bolton MD (2003) Soil deformation measurement using particle image velocity and photogrammetry. Géotechnique 53(7):619–631
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12518_2021_387_MOESM3_ESM.docx
Supplementary file3 Modelling of displacement of PK-2, PK-3, PK-4 and PK-5 boreholes using Settle3 for 0, 5, 10, 15, 17, 18 and 28 years (DOCX 338 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pooja, B., Oommen, T., Sajinkumar, K.S. et al. Correspondence of PSInSAR monitoring and Settle3 modelling at Cochin International Airport, SW India. Appl Geomat 13, 735–746 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-021-00387-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-021-00387-y