Abstract
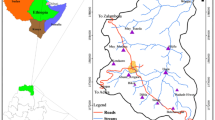
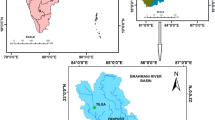
The water balance components are essential to determine the area’s hydrological process and groundwater resource management. This study aims to characterize the water balance components over the Ataye watershed using the WetSpass model. The WetSpass model can simulate water balance components’ spatial and temporal variation, mainly evapotranspiration, surface runoff, and groundwater recharge. The input data for the WetSpass model are land use/land cover, elevation, slope, soil texture, temperature, potential evapotranspiration, wind speed, and groundwater depth. Those spatial datasets were prepared in the raster format and transformed into ASCII file format using GIS spatial analysis techniques. As a result, the findings of this study confirmed that the mean evapotranspiration values of the Ataye watershed in the winter, summer, autumn, spring, and annual seasons were 33.6 mm, 117.35 mm, 100.98 mm, 158.96 mm, and 410.88 mm, respectively. Besides, the computed surface runoff values of the Ataye watershed in the winter, summer, autumn, spring, and annual seasons were 15.30 mm, 376.24 mm, 43.74 mm, 59.89 mm, and 495.16 mm, respectively. Similarly, the mean groundwater recharge values of the Ataye watershed in the summer, autumn, winter, spring, and annual seasons were 148.47 mm, 29.83 mm, 5.62 mm, 13.73 mm, and 197.65 mm, respectively. This study’s findings can be a reference for water resource specialists and policymakers to develop and manage various water resource-related projects in the present study area.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abanish k, Shruti k, Sudhanshu (2018) Water balance assessment using geospatial techniques: a review. I-' 'Manager's J Future Eng Technol 14(1):55. https://doi.org/10.26634/jfet.14.1.15254.
Abu Saleem A, Al-Zu’bi Y, Rimawi O, Al-Zu’bi J, Alouran N (2010) Estimation of water balance components in the Hasa basin with GIS based WetSpass model. J Agron 9(3):119–125. https://doi.org/10.3923/ja.2010.119.125
Abdollahi K, Bazargan A, McKay G (2018a) Water balance models in environmental modeling. Handbook of Environmental Materials Management. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp. 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-58538-3_119-1
Abdollahi K, Bashir I, Batelaan O (2012) WetSpass graphical user interface. Cartography of Higher Swiss Education.
Abdollahi K, Bazargan A, McKay G (2018b) Water balance models in environmental modeling. Handbook of Environmental Materials Management. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp.1-16
Aish AM, Batelaan O, De Smedt F (2010) Distributed recharge estimation for groundwater modeling using WetSpass model, case study—Gaza strip Palestine. Arab J Sci Eng 35(1):155–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-012-0323-1
Alemayehu A, Bewket W (2016) Vulnerability of smallholder ‘farmers’ to climate change and variability in the central highlands of Ethiopia. EJOSSAH 12(2):1–24
Al Kuisi M, El-Naqa A (2013) GIS based spatial groundwater recharge estimation in the Jafr basin, Jordan: application of WetSpass models for arid regions. Rev Mex De Cienc Geol 30(1):96–109
Ashaolu ED, Iroye KA (2018) Rainfall and potential evapotranspiration patterns and their effects on climatic water balance in the Western Lithoral Hydrological Zone of Nigeria. Ruhuna J Sci 9(2):92. https://doi.org/10.4038/rjs.v9i2.45
Asefa T, Water TB, Batelaan O (1999) Open integration of a spatial water balance model and GIS to study the response of a catchment. Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual American Geophysical Union
Hydrology Days, August 16 – 20, 1999, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA: 11 – 22
Arefaine T, Nedaw D, Gebreyohannes T (2012) Groundwater recharge, evapotranspiration and surface runoff estimation using WetSpass modeling method in Illala Catchment Northern Ethiopia. MEJS 4(2):96–110. https://doi.org/10.4314/mejs.v4i2.80119
Armanuos AM, Negm A, Yoshimura C (2016) Application of WetSpass model to estimate groundwater recharge variability in the Nile Delta aquifer. Arab J Geosci 9:553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2580-x
Batelaan O (2012).Wetspass graphical user interface
Batelaan O, DeSmedt F (2007) GIS based recharge estimation by coupling surface subsurface water balance. J Hydrol 337:337–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.02.001
Bitsiet D, Dessie N (2019) Groundwater recharge estimation using WetSpass modeling in Upper Bilate Catchment Northern Ethiopia. MEJS 11(1):37–51. https://doi.org/10.4314/mejs.v11i1.3
Chen J, Shao C, Jiang S, Qu L, Zhao F, Dong G (2019) Effects of changes in precipitation on energy and water balance in a Eurasian meadow steppe. Ecol Process 8(17):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-019-0170-z
Dereje B, Nedaw D (2019) Groundwater recharge estimation using WetSpass modeling in Upper Bilate Catchment Northern Ethiopia. MEJS 11(1):37–51. https://doi.org/10.4314/mejs.v11i1.3
Fernandez-Illescas CP, Porporato A, Laio F, Rodriguez-Iturbe I (2001) The ecohydrological role of soil texture in a water-limited ecosystem. Water Resour Res 37(12):2863–2872. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000WR00012
Gebeyehu A (2007) GIS-based groundwater vulnerability mapping of Holeta River Catchment, Oromia Regional State, West Shewa Zone (Doctoral dissertation, Addis Ababa University)
Gebremeskel G, Kebede A (2017) Spatial estimation of long-term seasonal and annual groundwater resources: application of WetSpass model in the Werii watershed of the Tekeze River Basin Ethiopia. Phys Geogr 38(4):338–359. https://doi.org/10.1080/02723646.2017.1302791
Gebreyohannes T, De Smedt F, Walraevens K, Gebresilassie S, Hussien A, Hagos M, Gebrehiwot K (2013) Application of a spatially distributed water balance model for assessing surface water and groundwater resources in the Geba basin, Tigray Ethiopia. J Hydrol 499:110–123
Grey OP, Webber DFSG, Setegn SG, Melesse AM (2014) Application of the soil and water assessment tool (SWAT Model) on a small tropical island (Great River Watershed, Jamaica) as a tool in integrated watershed and coastal zone management. Rev Biol Trop 62:293–305
Hadadi F, Moazenzadeh R, Mohammadi B (2022) Estimation of actual evapotranspiration: a novel hybrid method based on remote sensing and artificial intelligence. J Hydrol 609:127774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127774
Herrmann F, Keller L, Kunkel R, Vereecken H, Wendland F (2015) Determination of spatially differentiated water balance components including groundwater recharge on the Federal State level–a case study using the mGROWA model in North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany). J Hydrol: Regional Studies 4:294–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2015.06.018
Kahsay GH, Gebreyohannes T, Gebremedhin MA (2019) Spatial groundwater recharge estimation in Raya basin, Northern Ethiopia: an approach using GIS based water balance model. Sustain Water Resour Manag 5:961–975. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-018-0272-2
Kuisi A, Kuisi MAl, El-naqa A, (2013) GIS based spatial groundwater recharge estimation in the Jafr basin, Jordan – Application of WetSpass models for arid regions. Revista Mexicana De Ciencias Geológicas 30(1):96–109
Kumar CP (2012) L 5-Assessment of groundwater potential. National Institute of Hydrology.
Liu YB, De Smedt F (2004) WetSpass extension, a GIS-based hydrologic model for flood prediction and watershed management. Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Belgium, 1, e108
Maurya D, Mishra AR, Jayakumar EP (2017) Assessment of groundwater potential using water balance approach in Pindra Block Varanasi. Inter J Res App Sci Tech 5(9)
Meresa E, Taye G (2019) Estimation of groundwater recharge using GIS-based WetSpass model for Birki watershed, the eastern zone of Tigray Northern Ethiopia. Sustain Water Resour Manag 5(4):1555–1566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-018-0282-0
Mindrila D, Balentyne P, Ed M (2013) Scatterplots and correlation.
Mohammadi B (2021) Review on the applications of machine learning for runoff modeling. Sustain Water Resour Manag 7:98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-021-00584-y
Mohammadi B, Moazenzadeh R, Christian K (2021) Improving streamflow simulation by combining hydrological process-driven and artificial intelligence-based models. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:65752–65768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15563-1
Molla DD, Tegaye TA, Fletcher CG (2019) Simulated surface and shallow groundwater resources in the Abaya-Chamo Lake basin, Ethiopia using a spatially-distributed water balance model. J Hydrol 24:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2019.100615
Neitsch SL, Arnold JG, Kiniry JR, William JR (2011) Soil and water assessment tool theoretical documentation version 2009, Texas Water Resources Institute Technical Report No. 406. System, College Station
Nigussie W (2018) Identification of groundwater potential zones by using radar and optical remote sensing: a case study of Ketar watershed, Ethiopia. M.Sc Dissertation, Addis Ababa University. http://etd.aau.edu.et/handle/123456789/17098
Niaghi AR, Jia X (2019) New approach to improve the soil water balance method for evapotranspiration estimation. Water (switzerland) 11(12):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122478
Nugroho P, Marsono D, Sudira P, Suryatmojo H (2013) Impact of land-use changes on water balance. Procedia Environ Sci 17:256–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2013.02.036
Nyembo L, Larbi I, Mwabumba M, Selemani J, Dotse S, Limantol A, Bessah E (2022) Impact of climate change on groundwater recharge in the lake Manyara catchment, Tanzania. Scientific African, 15, e01072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2021.e01072
Ratner B (2009) The correlation coefficient: its values range between +1/−1, or do they?. J Target Meas Anal Mark 17, 139–142 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1057/jt.2009.5
Rwanga SS, Ndambuki JM (2017) Accuracy assessment of land use/land cover classification using remote sensing and GIS. Int J Geosci 8:611–622. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2017.84033
Saddique N, Mahmood T, Bernhofer C (2020) Quantifying the impacts of land use/land cover change on the water balance in the afforested River Basin Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 79(19):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09206-w
Said M, Hyandye C, Mjemah IC, Komakech HC, Munishi LK (2021) Evaluation and prediction of the impacts of land cover changes on hydrological processes in data constrained southern slopes of Kilimanjaro Tanzania. Earth 2(2):225–247. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth2020014
Schilling KE, Jha MK, Zhang YK, Gassman PW, Wolter CF (2008) Impact of land use and land cover change on the water balance of a large agricultural watershed: historical effects and future directions. Water Resour Res 45(7):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007WR006644
Senay GB, Leake S, Nagler PL, Artan G, Dickinson J, Cordova JT, Glenn EP (2011) Estimating basin scale evapotranspiration (ET) by water balance and remote sensing methods. Hydrol Process 25(26):4037–4049. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8379
Shawul AA, Alamirew T, Dinka MO (2013) Calibration and validation of SWAT model and estimation of water balance components of Shaya mountainous watershed, Southeastern Ethiopia, Hydrol. Earth Syst Sci Discuss 10:13955–13978. https://doi.org/10.5194/hessd-10-13955-2013
Stephen M, Westenbroek, JA, Engott VA, Kelson RJH (2018) Water availability and use science program national water quality program SWB version 2.0-A soil-water-balance code for estimating net infiltration and other water-budget components book 6, Modeling Techniques. https://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/06/a59/tm6a59.pdf
Szwed M (2015) The elements of water balance in the changing climate in Poland. Adv Meteorol 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/149674
Teklebirhan A, Dessie N, Tesfamichael G (2012) Groundwater recharge, evapotranspiration and surface runoff estimation using WetSpass modeling method in Illala Catchment Northern Ethiopia. MEJS 4(2):96–110. https://doi.org/10.4314/mejs.v4i2.80119
Wang H, Kgotlhang L, Kinzelbach W (2005) Using remote sensing data to model groundwater recharge potential in Kanye region, Botswana region. Intl Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inform Sci 37(B8):751–756. https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-b-000012000
Zeabraha A, G/yohannes T, W/Mariyam F (2020) Application of a spatially distributed water balance model for assessing surface and groundwater resources: a case study of Adigrat area, Northern Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour Manag 6:73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00424-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Biswajeet Pradhan
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Anteneh, Z.S., Awoke, B.G., Reda, T.M. et al. Spatio-temporal evaluation of water balance components using WetSpass model: in the case of Ataye watershed, Middle Awash Basin, Ethiopia. Arab J Geosci 16, 207 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11252-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11252-0