Abstract
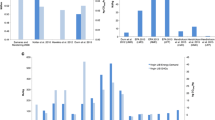
In order to explore the difference between EREV (extended range electric vehicles) and BEV (battery electric vehicles) in terms of energy consumption and pollution emissions, two representative models in the Chinese market are taken as research object. Meanwhile, mineral resources, fossil energy consumption, and pollution emissions are selected as comparative evaluation indexes, and corresponding mathematical evaluation difference models are established. Then, an analysis model for vehicles and components is constructed by using GaBi software based on the evaluation indexes and mathematical evaluation difference models. In addition, energy consumption and pollution emission of two vehicles under different operation modes are compared based on the structural differences of two power systems. From the respective of life cycle assessment (LCA), mineral resources consumption of BEV is 0.184 kg Sb eq, fossil energy consumption is 1.85 E + 05 MJ, and carbon emission is 1.69 E + 04 kg, which is approximately 1.29 times, 0.52 times, and 1.23 times of EREV. In the three electric system, mineral resources consumption of battery, motor, and electronic control of BEV is approximately 2.7 times, 1.29 times, and 1.22 times of that of EREV, respectively. Fossil energy consumption in raw material acquisition stage is approximately 1.92 times, 1.29 times, and 1.22 times, respectively, and that in manufacturing and assembly stage is approximately 2.03 times, 1.29 times, and 1.22 times, respectively. Carbon emissions are approximately 1.92 times, 1.29 times, and 1.22 times, respectively. In the pure electric mode, crude oil consumption of the EREV is 283.43 kg, which is approximately 4.06 times of that of the BEV; raw coal consumption of the BEV is 5231.7 kg, which is approximately 4.71 times that of the EREV; and natural gas consumption is approximately 7.4 times that of the EREV. In the extended range mode, natural gas consumption of the EREV is 515.45 kg, which is approximately 3.16 times that of the BEV in pure electric mode. Finally, from the aspects of manufacturing process optimization, body lightweight, and low-carbon energy structure, some suggestions are given to provide reference for policy formulation and filed research on energy saving and pollution emission reduction, so that the technology route of new energy vehicles in China is promoted and application of LCA in the field of new energy vehicles is improved.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available and included within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bickert S, Kampker A, Greger D (2015) Developments of CO2 emissions and costs for small electric and combustion engine vehicles in Germany. J Transp Res D 36:138–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2015.02.004
Burnham A, Wang M, Wu Y (2012) Development and applications of GREET2.7—the transportation vehicle-cycle model. U.S.: Energy Systems Division, Argonne National Laboratory. https://doi.org/10.2172/898530
Chen Y, Lin Lawell CYC, Wang Y (2020) The Chinese automobile industry and government policy. J Res Transp Econ 84:100849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.retrec.2020.100849
Correa G, Muñoz P, Falaguerra T, Rodriguez CR (2017) Performance comparison of conventional, hybrid, hydrogen and electric urban buses using well to wheel analysis. J Energy 141:537–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.09.066
Dordrecht (2001) Assessment—operational Guide to the ISO Standards. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands
Evangelisti S, Tagliaferri C, Brett DJL, Lettieri P (2017) Life cycle assessment of a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell system for passenger vehicles. J J Clean Prod 142:4339–4355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.11.159
GaBi (2019) GaBi sustainability software. Official website. http://www.gabisoftware.com/index/
Gu GG (2011) Comparative study on life cycle assessment of power system of electric vehicle and internal combustion engine vehicle. Dissertation, University of Hefei Technology
Hao H, Cheng X, Liu Z, Zhao FQ (2017a) Electric vehicles for greenhouse gas reduction in China: a cost-effectiveness analysis. J Transp Res D Transp Environ 56:68–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2017.07.025
Hao H, Mu ZX, Jiang SH, Liu ZW, Zhao FQ (2017b) GHG emissions from the production of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles in China. Sustainability 9(4):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040504
Hawkins TR, Singh B, Majeau-Bettez G, Strømman AH (2012a) Comparative environmental life cycle assessment of conventional and electric vehicles. J J Ind Ecol 17(1):53–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2012.00532.x
Hawkins TR, Gausen OM, Strømman AH (2012b) Environmental impacts of hybrid and electric vehicles—a review. Int J Life Cycle Assess 17(8):997–1014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-012-0440-9
Hawkins TR, Singh B, Majeau-Bettez G, Strømman AH (2013) Comparative environmental life cycle assessment of conventional and electric vehicles. J J Ind Ecol 17(1): 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2012.00532.x
Hooftman N, Maarten M, Joint F, Segard JB, Thierry C (2018) In-life range modularity for electric vehicles: the environmental impact of a range-extender trailer system. Appl Sci 8(7):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8071016
Hu ZY, Pu GQ, Fang F, Wang CT (2004) Economics, environment, and energy life cycle assessment of automobiles fueled by bio-ethanol blends in China. J Renewable Energy 29:2183–2192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2004.03.014
ISO, 2006. ISO14040. ISO/TC 207/SC 5 Life cycle assessment; 13.020.10 Environmental management 13.020.60 Product life-cycles
Lewis AM, Kelly JC, Keoleian GA (2014) Vehicle light weighting vs. electrification: life cycle energy and GHG emissions results for diverse powertrain vehicles. J Appl Energy 126:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.023
Li SH (2014) Life cycle analysis and environmental benefit evaluation of electric vehicles. Dissertation, University of Jilin
Li J (2015) Life cycle assessment and analysis of battery electric vehicle and fuel vehicle power system. Dissertation, University of Hunan
Liu ZC (2013) Life cycle assessment method of engine original manufacturing and remanufacturing. Dissertation, University of Dalian Technology
Liu KH, Xu JQ (2016) Life cycle assessment of battery electric vehicle drive motor. J Journal of environmental science 36 (09):3456–3463. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2016.0022
Lu Q (2014) Life cycle analysis and evaluation of electric vehicle power battery. Dissertation, University of Jilin
Ma JQ (2019) Life cycle assessment of battery electric vehicles with different power batteries. Dissertation, University of Chang'an University
Mu XZ, Xu GQ, Hu GW (2021) Environmental impact analysis of nuclear power based on lif-e cycle assessment. J/OL J Saf Environ 1–8. http://doi-org-s.vpn.chd.edu.cn:8080/10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2021.1289
Noori M, Gardner S, Tatari O (2015) Electric vehicle cost, emissions, and water footprint in t-he United States: development of a regional optimization model. J Energy 89:610–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.05.152
Onat NC, Kucukvar M, Tatari O (2015) Conventional, hybrid, plug-in hybrid or electric vehicles? State-based comparative carbon and energy footprint analysis in the United States. J Appl Energy 150:36–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.04.001
Peng TD, Ou XM, Yan XY (2018) Development and application of an electric vehicle’s life cycle energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions analysis model. J Chem Eng Res Des 131:699–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.12.018
Qiao QY, Zhao FQ, Liu ZW, Jiang SH, Hao H (2017) Comparative study on life cycle CO2 emissions from the production of electric and conventional vehicles in China. J Energy Procedia 105:3584–3595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.827
Shi SN, Zhang HR, Yang W, Zhang QR, Wang XJ (2019) A life-cycle assessment of battery electric and internal combustion engine vehicles: a case inHebei Province, China. J J Clean Prod 228: 606–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.301
Song XL, Liang ZL, Luo W, Huang D, Yang Z, Xu PP, Hu JP, Liu BC, Yang JK (2021) Study on life cycle assessment of cement preparation process from industrial solid waste raw materials. J J Environ Sci 1–10. http://doi-org-s.vpn.chd.edu.cn:8080/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0276
Tagliaferri C, Evangelisti S, Acconcia F, Domenech T,Ekins P, Barletta D, Lettieri P (2016) Life cycle assessment of future electric and hybrid vehicles: a cradle-to-grave systems engineering approach. J Chem Eng Res Des (112): 298–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2016.07.003
Wang CB, Zhang LX, Pang MY (2015) A review of life cycle assessment methods—also on the development and application of hybrid life cycle assessment. J J Nat Resour 30(07):1232-1242. https://doi.org/10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.07.015
Wu XT (2012) Performance comparison of Qin, Wolanda and Prius plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. J Automob Accessories 41:30–31
Xiong SQ, Ji JP, Ma XM (2019) Comparative life cycle energy and GHG emission analysis for Bevs and Phevs: a case study in China. Energies 12:834. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12050834
Xu X, Xu X (2021) Can resource policy adjustments effectively curb regional “resource curse” ? New evidences from the “energy golden triangle area” of China. J Resour Policy 73:102146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102146
Yu A, Wei YQ, Chen WW, Peng NJ, Peng LH (2018) Life cycle environmental impacts and carbon emissions: a case study of electric and gasoline vehicles in China. J Transp Res D Transp Environ 65:409–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2018.09.009
Zhang L (2011) Research on life cycle assessment of electric vehicles based on GaBi4. Dissertation, University of Hefei Technology
Zhang Z, Sun X, Ding N, Yang JX (2019) Life cycle environmental assessment of charging infrastructure for electric vehicles in China. J J Clean Prod 227:932–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.167
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Youth Science and technology star project of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2021KJXX-15), the Shaanxi Provincial Key Industry Innovation Chain Project (Grant No. 2020ZDLGY16-08), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. 300102221106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Yang Yang; methodology: Yang Yang, Yisong Chen; formal analysis and investigation: Yunxiang Xing, Yisong Chen; writing — original draft preparation: Yunxiang Xing, Ying Cao; writing — review and editing: Pei Fu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Amjad Kallel
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Yang, Y., Xing, Y. et al. Comparative evaluation of energy consumption and emissions in the life cycle of extended-range and battery electric vehicles. Arab J Geosci 15, 512 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09792-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09792-y