Abstract
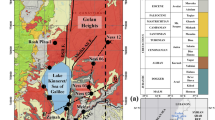
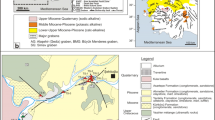
This paper presents the results of extensive geological, geophysical, chemical, and geothermometry investigations on natural thermal and cold water discharging throughout the main geological domains of Hajeb Layoun-Jilma and Oued Hjal basins. These areas are known by the rise of two hydrothermal springs of Hammam Sidi Maamer S1, Chenama S2, and Ouled Farhane deep water well S3. Their distributions are strongly related to the main active tectonic structures. Composite geo-seismic model highlights the deep structuring of the Cretaceous and Miocene horizons and the fluid pathways from the recharge areas (Mghilla, Hmaiema, Nara outcrops) to discharge zones of Sidi Maamer (Baten Damous outcrop) and Chenama (Zaouia outcrop). Chemical features of cold and hot water are mainly controlled by water–rock interactions and the dissolution of evaporate and carbonate minerals leading to mixed Ca-Mg-SO4-Cl, Ca–Cl, and Na-Cl facies. Molar ratios of (Ca2+ + Mg2+)/ (SO42− + HCO3−) and chloro-alkaline indicators implied that ion exchange and reverse ion exchange influenced the hydrogeochemistry of groundwater sources. IIRG diagram reveals two significant aquifer types: one indicating the deep circulation of fluid from the limestone of the Aptian Orbata Formation reservoir and ascends to the surface through S1 and S2 along faults of Hajeb Layoun basin, whereas the second aquifer is characterized by sandstone levels; where water circulates through the late Miocene Saouaf Formation deposits to the surface also along faults of Oued Hjal basin. Silica geothermometers for S1 and S2 give the best results for reservoir temperatures varying from 70.43 to 83 °C and depths range from 1709 to 2153 m. For S3 deep hot water well, K-Mg geothermometer gives the most reasonable temperature estimation of 48 °C and depth up to 910 m. Giggenbach diagram reveals that water samples are not in an equilibrium state with the reservoir rocks.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abbès C (2004) Structurations et évolutions tectono-sédimentaires Mésozoïques etCénozoïques associées aux accidents reghmatiques, à la jonction des marges Téthysienne et nord-Africaine (Chaîne Nord-Sud, Tunisie centrale). ThèseèsSciences, Université Tunis El Manar, Tunisie: 440 p.
Almadani S, Alfaifi H, AlAmri A, Fnais M, Ibrahim E, Abdelrahman K, Shehata M (2017) Zaidi F (2017) Hydrochemical characteristics and evaluation of the granite aquifer in the Alwadeen area, southwest Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 10:139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2873-8
Andolssi M, Alyahyaoui S, Makni J, Charef A, Zouari H, Tarki M, Challouf B (2015) Integrated study of surface and subsurface data for prospecting hydrogeothermal basins of hot water spring Ain El Hammam: case of Utique region basin (extreme north of Tunisia). Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1743-x
Apha, (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. APHA-AWWA-WET, Washington, DC
Arnorsson S (1983) Chemical equilibria in Icelandic geothermal systems-implications for chemical geothermometry in investigations. Geothermics 12:119–128
Arnórsson S, Gunnlaugsson E (1985) New gas geothermometers for geothermal exploration- calibration and application. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 49:1307–1325
Azaiez H, Gabtni H, Chabaane A, Sayem G (2020) Bédir M (2020) Geophysical study of Hammam Sidi Maamar geothermal site in Central Tunisia for sustainable development. J Afr Earth Sc 170:103897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2020.103897
Azaeiz H (2011) Structuration et sismo-stratigraphie des séries du crétacé inférieur et leurs réservoirs associés en Tunisie centrale (régions de Gafsa, Sidi Bouzid et Bir Ali Ben Khalifa). Thèse de Doctorat, Faculté des sciences de Tunis, Université de Tunis El Manar: 256p.
Bédir M (2018) Hydrocarbon traps related to Meso-Cenozoic strike slip salt tectonics and basin subsidence migrations in the Sahel. 13 ème Journées de l’Exploration Pétrolières de l’ETAP.
Bédir M (1995) Mécanismes géodynamiques des bassins associés aux couloirs de coulissements de la marge atlasique de la Tunisie, seismo-stratigraphie, seismo-tectonique et implications pétrolières. Thèse ès Sciences, Université de Tunis El Manar, Tunisie: 412 p.
Ben Dhia H (1983) Les provinces géothermiques de la Tunisie méridionale. Thèse de Doctorat Es- sciences naturelles. Univ. Bordeau I: 196 p + 6 annexes.
Ben Dhia H (1987a) a) Geothermal energy in Tunisia: potential of the Southern Province. Geothermics 16:299–318
Ben Dhia H (1987b) b) La carte du gradient géothermique de Tunisie-établissement à partir des données de température pétrolières. Bulletin Centre Recherche Exploration. Production Elf Aquitaine II:221–231
Ben Dhia H, Bouri S, Meddeb MN (1993) Identification des principaux bassins hydrogéothermiques en Tunisie. Deuxième J.T.G.A, ENI-Sfax: 339–350.
Ben Dhia H, Meddeb MN (1990) Application of chemical geothermometers to some Tunisian hot springs. Geothermics 19:87–104
Ben Dhia H, Bouri S, Meddeb M.N, Zouari K (1992) Hydrothermie de surface etbassinshydrogéothermiques en Tunisie. Coll. Hydr. Marrakech: 66–70.
Ben Ferjani A, Burollet PF, Mejri F (1990) Petroleum geology of Tunisia. Mémoire ETAP, Tunis, Tunisie, n. 1:194 p.
Ben Jemiaa M (1986) Evolution tectonique de la zone des failles Trozza-Labaeid, Tunisie centrale, Université de Paris-Sud centre d’Orsay: 162 p.
Ben Youssef M (1989) Nouvelles précisions sur le Crétacé supérieur de la chaîne de Gafsa. Septième Séminaire National des Sciences de la Terre, Algéria: 41 p.
Ben Youssef M (1999) Stratigraphie génétique du Crétacé de Tunisie, Micropaléontologie, Stratigraphie séquentielle et Géodynamique des bassins de la marge Sud et péri-téthysienne. Thèse ès Sciences, Université Tunis El Manar, Tunisie: 402 p.
Ben Youssef M et al (1985) L’Albien moyen-supérieur à Knémiceras forme la base de la grande transgression crétacée au Tebaga de Médenine (Tunisie méridionale). Comptes Rendus De L’académie Des Sciences De Paris 300:965–968
Bouri S, Gasmi M, Jaouadi M, Souissi I, Lahlou A, Ben Dhia H (2007) Etude intégrée des données de surface et de subsurface pour la prospection des bassins hydrogéothermiques: cas du bassin de Maknassy (Tunisie centrale). J Hydrolog Sci 52:1298–1315
Burollet PF (1956) Contribution à l’étude stratigraphique de la Tunisie centrale. Anale des mines et de la géologie: 345 p.
Chenaker H, Houha B (2017) Valles V (2017) Isotope studies and chemical investigations of hot springs from North Eastern Algeria. J Mater Environ Sci 8(12):4253–4263
Chulli B (2000) Structuration, hydrodynamisme et géothermie des niveaux réservoirs profonds (Crétacé-miocène) de la Tunisie orientale. Université de Tunis El Manar, Tunisie, Thèse de Doctorat
Chulli B, Bédir M, Mejri F, Ben Dhia H (2002) Structuration profonde et géothermie de la marge orientale de la Tunisie. Africa Geosci. Rev. 9(1):39–46
Chulli B, Davraz A, Makni J, Bédir M, Ben Dhia H (2012) Hydrogeological investigations of thermal waters in the Sfax Basin (Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 66:1–16
D’Amore F, Scandiffio G, Panichi C (1983) Some observation on the chemical classification of ground waters. Geothermics 12(2/3):141–148
Diamond RE, Harris C (2000) Oxygen and hydrogen isotope geochemistry of thermal springs of the Western Cape, South Africa: recharge at high altitude. J Afr Earth Sci 31:467–481
Disli E, Gulyuz N (2020) Hydrogeochemical investigation of an epithermal mineralization bearing basin using multivariate statistical techniques and isotopic evidence of groundwater: Kestanelik Sub-Basin. Lapseki, Turkey, Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125661
Doglioni C, Bosellini A, Frare MC, Dhaha FSEA (1990) Aspects tectoniques de la région au sud-ouest de Kairouan, Tunisie centrale. AnnaliDell’universita Di Ferrara (NuovaSerie), Sezione:ScienzedellaTerra; vol.2, N.5. pp 76–94
El Ghali A (1992) Evolution tectono-sédimentaire du bassin de Jebel Trozza au cours du Crétacé moyen et supérieur. Notes du service géologique de Tunisie: 59–75.
Esmaeili VM, Rasa I, Amiri V, Yazdi M, Pazand K (2015) Evaluation of groundwater quality and assessment of scaling potential and corrosiveness of water samples in Kadkan aquifer, Khorasan-e-Razavi Province, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015: 187, 53. [CrossRef] [PubMed].
Fahrurrozie A, Mahesa PS, Tubagus N (2015) The application of Na-K-Mg, Na-K/Mg-Ca and K-Mg/Quartz diagrams to evaluate water geochemistry in West Java Geothermal Prospects, Indonesia. Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2015 Melbourne, Australia:19–25.
Farhat H (1978) Contribution à l’étude hydrogéologique de la cuvette de Maknassy (Tunisie). Thèse de Doctorat en Sciences de la Terre. Université de Bordeaux: 200p.
Fournier RO (1991) Water geothermometers applied to geothermal energy. In: D’Amore F (ed) Application of geochemistry in geothermal reservoir development. UNITAR/UNDP Publication, Roma, pp 37–69
Gassara A (1980) Contribution à l’étude hydrogéologique du bassin de Horchane-Braga (Sidi Bouzid). Thèse de Doctorat, Université Pierre et Marie Crue, France: 89 p+annexes.
Giggenbach WF (1988) Geothermal solute equilibria derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicator. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2749–2765
Giggenbach WF, Glover RB (1992) Tectonic regime and major processes governing. The Chemistry of Water and Gas Discharges from the Rotorua Geothermal Field, New Zealand, Geothermics 21(1992):121–140
Gu X, Xiao Y, Yin S, Shao J, Pan X, Niu Y, Huang J (2017) Groundwater level response to hydrogeological factors in a semi-arid basin of Beijing, China. J. Water Supply: Res. Technol. AQUA 2017, 66, 266–278[CrossRef].
Hajji KS, Ayed B, Riahi I, Allouche N, Boughariou E (2018) Bouri S (2018) Assessment and mapping groundwater quality using hybrid PCA-WQImodel: case of the Middle Miocene aquifer of Hajeb Layoun-Jilma basin (Central Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 11:620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3924-5
Hajji KS,Bouri S,Hachicha W, Ben Dhia H (2013) Implementation and evaluation of multivariate analysis for groundwater hydrochemistry assessment in arid environments: a case study of Hajeb elyoun-Jilma, Central Tunisia. Environ Earth sci.
Hamed Y, Ahmadi R, Demdoum A, Bouri S, Gargouri I, Ben Dhia H, Al Gamal S, Laouar R, Choura A (2014) Use of geochemical, isotopic, and age tracer data to develop models of groundwater flow: a case study of Gafsa mining basin-Southern Tunisia. Journal of African Earth Sciences, Volume 100, December 2014, Pages 418–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2014.07.012.
Hamed Y, Hadji R, Tarki M, Redhaounia B, Zighmi K, Bâali F (2018) El Gayar A (2018) Climate impact on surface and groundwater in North Africa: a global synthesis of findings and recommendations. Euro-Mediterranean Journal for Environmental Integration 3:25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-018-0067-8
Hamed Y, Lassaad D, Tarki M, Ahmadi R, Khalid M, Ben Dhia H (2010) Groundwater origins and mixing pattern in the multilayer aquifer system of the Gafsa-south mining district: a chemical and isotopic approach. Environ Earth Sci 63:1355–1368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0806-x
HamedY, Zairi M, Ali W, Ben Dhia H (2010b) Estimation of residence times and recharge area of groundwater in the Moulares Mining Basin by using carbon and oxygen isotopes (South Western Tunisia). Journal of Environmental Protection, 2010;1:466–474. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2010.14054. Published Online December 2010. http://www.SciRP.org/journal/jep.
Houatmia F (2010) Etude géophysique et hydrogéologique du bassin de Sidi Saad:impact de la tectonique sur la structuration et la géométrie des réservoirs oligo-néogènes. Master thesis. University of Tunis El Manar, 157p.
Islam MA, Zahid A, Rahman MM, Rahman MS, Islam MJ, Akter Y, Shammi M, BodrudDoza M, Roy B (2017) Investigation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the South Central Part of the Coastal Region in Bangladesh. Expo Health 9:27–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0220-z.[CrossRef][GoogleScholar]
Jellalia D (2016) Etude hydrogéologique, hydrochimique et géophysique des réservoirs aquifères tertiaires des bassins HajebLayoun-Jilma-Ouled Asker-Oued Hjal (Sidi Bouzid, Tunisie centrale). Thèse de Doctorat, Faculté des Sciences de Tunis, Tunis El Manar: 188 p.
Jellalia D, Lachaal F, Andoulsi M, Zouaghi T, Hamdi M, Bédir M (2015) Hydro-geophysical and geochemical investigation of shallow and deep Neogene aquifers system in Hajeb Layoun-Jilma-Ouled Asker area, Central Tunisia. J Afr Earth Sc 110:227–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.06.016AES2308
Jellalia D (2010) Etude hydrogéologique, Hydrochimique et Géophysique des systèmes aquifères Néogènes de Hajeb Layoun- Jilma (Région de Sidi Bouzid) Tunisie Centrale. Mastère de recherche, Faculté des Sciences de Tunis, 109 p.
Khazri D (2014) Caractérisation géométrique des nappes profondes d’Oued Hjal et d’ouled asker par les méthodes gravimétriques et sismiques (région de sidi bouzid). Mastère de recherche en sciences geologiques. 123p.
Khazri D, Gabtni H (2014) Geophysical contribution in the characterization of deep watertables geometry (sidi bouzid, Central Tunisia). International Journal of Geophysics, Volume 2015, 16 p.https:// DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/239797.
Koschell R (1980) Etude hydrogéologique de la nappe de Hajeb Layoun-Jilma-Ouled Askar. Projet de coopération technique Tuniso-Allemande N° 6520/7, Direction des ressources en eau et en sol, Ministère de l’Agriculture, 245 p.
Makni J, Ben Brahim F, Hassine S, Bouri S, Ben Dhia H (2013) Hydrogeological and mixing process of waters in deep aquifers in arid regions: south east Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 7:799–809 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0793-1
Mamou A (1981) Etude hydrogéologique du bassin versant de Sebkhat En Noual. Bureau de l’Inventaire et des Recherches Hydrologique (B.I.R.H.), 37p+Annexes.
Mansouri R (1980) Contribution à l’étude hydrogéologique de la plaine de Sebkhat El Bhira (Sud Ouest de Kairouan). Université de Bordeaux-France, Thèse de Doctorat en Sciences de la Terre, p 107p
Meddeb MN (1993) Potentialités géothermiques de la Tunisie Septentrionale. Thèse de Doctorat de spécialité. Fac. Sci. Tunis-Univ. Tunis El Manar: 193 p.
M’rabet A (1981) Stratigraphie, sédimentation et diagenèse carbonatée des séries du Crétacé inférieur de la Tunisie centrale. Thèse ès Sciences, Université Paris sud, Centre d’Orsay: 540 p.
Nematollahi MJ, Ebrahimi P, Razmara M, Ghasemi A (2016) Hydrogeochemical investigations and groundwater quality assessment of Torbat-Zaveh plain, Khorasan Razavi, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess., 188, 2. [CrossRef] [PubMed].
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Rodier J (2009) L’analyse de l’eau: eaux naturelles, eaux résiduaires, eau de mer, 9th edn. Dunod, Belgique, p 1530
Sadki O (1998) Etude des systèmes hydrothermaux du Nord de la Tunisie: Géochimie des interactions eaux- roches et circulation hydrothermale. Thèse de Doctorat. Faculté des sciences de Tunis. Université Tunis El Manar: 246 p.
Saidi S (2006) Etude de la vulnérabilité des ressources hydriques du bassin Hajeb-Jilma (Tunisie centrale). Université de Sfax, DEA, p 121p
Sangree JB, Widmier JM (1977) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level, Part 9: Seismic interpretation of clastic depositional facies. See Payton, 165–84.
Sangree JB, Widmier JM (1979) Interpretation of depositional facies from seismic data. Geophysics 44:131–160
Sayem G (2012) Etude géophysique par sismique réflexion et tomographie électrique du site thermal de Hammam Sidi Maamar (Hajeb Layoun-Kairouan). DEA, Université Tunis El Manar, Tunisie: 91 p.
Schoeller H (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In Methods and Techniques of Groundwater Investigations and Development. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO): Paris, France: 54–83.
Simler R (2013) DIAGRAMMES: Logiciel d’hydrochimie multilangage en distribution libre, version 6. Laboratoire d’Hydrogéologie d’Avignon.
Smida H (2008) Apports des systèmes d’informations géographiques (SIG) pour une approche intégrée dans l’étude et la gestion des ressources en eau des systèmes aquifères de la région de Sidi Bouzid (Tunisie centrale). Thèse de Doctorat, Universite de Sfax, Faculté des Sciences de Sfax, département des sciences de la terre; 341 p.
Soussi M (1990) Les faciès argilo-carbonatés jurassiques en Tunisie centrale: stratigraphie, sédimentologie, Diagenèse (dolomitisation) et intéret pétrolier. Thèse 3éme cycle, Université Tunis El Manar, 281 p.
Tanfous D, Soussi M, Bedir M, Azaeiz H (2007) Seismic sequence stratigraphy of the Jurassic of the Central Atlas, Tunisia. Journal of African Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2007.12.005.
Thebti S, Jellalia D, Azaiez H, Bédir M (2018) Basin structuring and hydro-geophysical characterization of Upper Cretaceous and Eocene fractured deep carbonate reservoirs in the Hajeb Layoun-Jilma-Ouled Asker area (Central Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 11:107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3445-2
Tonami F (1980) Some remarks on the application of geochemical techniques in geothermal exploration. Proceedings, Adv. Eur. Geoth. Res., Second Symp. 428–443.
Truesdell A (1976) Summary of section III - geochemical techniques in exploration. Proceedings, Second United Nations Symposium on the Development and Use of Geothermal Resources. San Francisco, CA, 1975, 1, 1iii-1xiii.
Truesdell and Fournier (1975) Calculation of deep temperatures in geothermal systems from the chemistry of boiling spring waters of mixed origin. Proceedings, Second U.N. Symposium on Geothermal Resources, San Francisco, CA, 837–844.
Wang L, Dong Y,Xie Y, Song F, Wei Y, Zhang J (2016) Distinct groundwater recharge sources and geochemical evolution of two adjacent sub-basins in the lower shule river basin, northwest China. Hydrogeol. Journal, 24, 1967–1979. [CrossRef]
Wu J, Li P, Qian H, Duan Z, Zhang X. Using correlation and multivariate statistical analysis to identify hydrogeochemical processes affecting the major ion chemistry of waters: a case study in Laoheba phosphorite mine in Sichuan, China. Arab J Geosci. 2014;7:3973–3982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1057-4. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar].2016, 24, 2017.
Xu PP, Feng WW, Qian H, Zhang QY (2019) Hydrogeochemical characterization and irrigation quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the Central-Western Guanzhong Basin, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16091492.[PMCfreearticle][PubMed][CrossRef][GoogleScholar]
Zitouni L (1997) Evolution géodynamique des bassins mésozoïques de subsurface des régions de Sidi Aïch-Majoura (Tunisie centrale), sismostratigraphie, sismotectonique et implications pétrolières. PhD Thesis. Univ. Tunis El Manar, Tunisia: 335 p.
Zouaghi T (2008) Distribution des séquences de dépôt du crétacé (Aptien-Maastrichtien) en subsurface: déformation tectonique, halocinése, évolution géodynamique (Atlas central de Tunisie). Unpublished PhD thesis, UniversitéTunis El Manar (Tunisia): 367 p.
Zouari K (1998) Etude isotopique et hydrochimique des systèmes multicouches de Gafsa et de Hajeb Layoun–Jilma. Rapport final de coopération scientifique et technique. Projet AIEA. Code : TUN/8/012, 70p.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
We, all authors, give our consent for the participation in the present paper entitled: Hydrogeothermal potential Assessment in a complex tectonic environment by geophysical and hydrogeochemical tools: a case of the geothermal province of Hajeb Layoun-Jilma-Oued Hjal basins (Central Tunisia).
Consent for publication
We, all authors, give our consent for the publication of this work in the Arabian Journal of Geosciences.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Anis Chekirbane
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Water Quality, Global Changes and Groundwater Responses
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jellalia, D., Makni, J., Andolssi, M. et al. Hydrogeothermal potential assessment in a complex tectonic environment by geophysical and hydrogeochemical tools: a case of the geothermal province of Hajeb Layoun-Jilma-Oued Hjal basins (Central Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 14, 2533 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08820-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08820-7