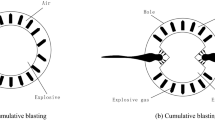
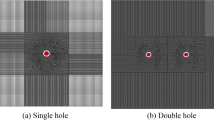
Abstract
As shallow coal resources deplete in industrialized nations, mining operations expand to the deeper resources to meet the requirements of the society. Deep coal seams in China have the characteristics of high gas pressure and high gas content. There is a persistent track record of gas-related accidents in Chinese coal mines. In an effort to eliminate gas explosions and gas outbursts, a new permeability improvement technology of “hydraulic punching plus air blasting” is developed for soft and low-permeability coal seams. To intensively enhance the permeability and achieve efficient extraction of gas from low-permeability coal seams, hydraulic punching is performed first, followed by air blasting. The LS-DYNA software was used to simulate the blasting process by the air cannons. Results were obtained from the Guhanshan mine. Comparisons were done for the stress field, deformation field of the coal body using the law of coal body deformation. Deformation at different blasting times was compared in combination with the field air blasting tests. With 40 times air blasting, the gas drainage increased by about two times compared to drainage without air blasting. The pure gas extraction volume was also observed to be about 2.2 times higher than that without air blasting. The results proved improvement of the coal permeability and gas drainage by this new technology.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao S, Li Y, Liu Y, Zhang L, Xu A (2009) Effectiveness analysis of methane-drainage by deep-hole controlled pre-splitting blasting for preventing coal and gas outburst. J Coal Sci Eng China 15:166–170
Chen H, Wang Z, Chen X, Chen X, Wang L (2017) Increasing permeability of coal seams using the phase energy of liquid carbon dioxide. J CO2 Util 19:112–119
Cheng X, Zou Y (2019) Coal Bed Methane (CBM) Stimulation by liquid CO2 phase-transition Fracturing (LCPF) Technology. Int J Oil Gas Coal T 7(5):103–108
Elwegaa K, Emadi H, Soliman M, Gamadi T, Elsharafi M (2019) Improving oil recovery from shale oil reservoirs using cyclic cold carbon dioxide injection - an experimental study. Fuel 254:115586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.05.169
Hou P, Gao F, Ju Y, Cheng H, Gao Y, Xue Y, Yang Y (2016) Changes in pore structure and permeability of low permeability coal under pulse gas fracturing. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 34:1017–1026
Hu G, He W, Sun M (2018) Enhancing coal seam gas using liquid CO2 phase-transition blasting with cross-measure borehole. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 60:164–173
Jiang J, Yang W, Cheng Y, Lu B, Zhang K, Zhao K (2018) Application of hydraulic flushing in coal seams to reduce hazardous outbursts in the Mengjin Mine. China, Environ Eng Geosci 24(4):425–440
Karacan CÖ, Ruiz FA, Cotè M, Phipps S (2011) Coal mine methane: a review of capture and utilization practices with benefits to mining safety and to greenhouse gas reduction. Int J Coal Geol 86:121–156
Lee E, Hornig H, Kury J (1968) Adiabatic expansion of high explosive detonation products. United States. https://doi.org/10.2172/4783904
Liu J, Wang H, Yuan Z, Fan X (2011) Experimental study of pre-splitting blasting enhancing pre- drainage rate of low permeability heading face. Procedia Engineering 26:818–823
Liu J, Liu Z, Xue J, Gao K, Zhou W (2015) Application of deep borehole blasting on fully mechanized hard top-coal pre-splitting and gas extraction in the special thick seam. Int J Min Sci Techno 25:755–760
Liu X, Nie B, Guo K, Zhang C, Wang Z, Wang L (2021) Permeability enhancement and porosity change of coal by liquid carbon dioxide phase change fracturing. Eng Geol 287(3):106106
Livermore Software Technology Corporation (2006) LS-DYNA keyword user’s manual. Livermore Software Technology Corporation, California
Lu T, Zhao Z, Hu H (2011) Improving the gate road development rate and reducing outburst occurrences using the waterjet technique in high gas content outburst-prone soft coal seam. Int J Rock Mech Mining Sci 48:1271–1282
Nozhkin NV, Slastunov SV, Varypaev VV (1989) Control of properties and condition of a coal bed by hydro-fracturing with liquid gas. Soviet Mining 25(2):174–177
Shen C, Lin B, Sun C, Zhang Q, Li Q (2015) Analysis of the stress-permeability coupling property in water jet slotting coal and its impact on methane drainage. J Petrol Sci Eng 126:231–241
Su E, Liang Y, Zou Q (2021) Structures and fractal characteristics of pores in long-flame coal after cyclical supercritical CO2 treatment. Fuel 286:119305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119305
Wang L, Xu Y (2019) Study of the law of gradual change of the influence of hydraulic punching under a rational coal output. Arab J Geosci 12:427
Wang H, Cheng Y, Wang W, Xu R (2014) Research on comprehensive CBM extraction technology and its applications in China’s coal mines. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 20:200–207
Wang Z, Sun Y, Wang Y, Zhang J, Sun Z (2020) A coupled model of air leakage in gas drainage and an active support sealing method for improving drainage performance. Fuel 237:1217–1227
Zhai C, Li M, Sun C, Zhang J, Yang W, Li Q (2012) Guiding-controlling technology of coal seam hydraulic fracturing fractures extension. Int J Mining Sci Technol 22:831–836
Zhang H, Cheng Y, Liu Q, Yuan L, Dong J, Wang L, Qi Y, Wang W (2017) A novel in-seam borehole hydraulic flushing gas extraction technology in the heading face: Enhanced permeability mechanism, gas flow characteristics, and application. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 46:498–514
Zhang Y, Hu S, Xia T, Liu Y, Pan Z (2020) A novel failure control technology of cross-measure borehole for gas drainage: a case study. Process Saf Environ 135:144–156
Zhou H, Yang Q, Cheng Y, Ge C, Chen J (2014) Methane drainage and utilization in coal mines with strong coal and gas outburst dangers: a case study in Luling mine China. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 20:357–365
Zou Q, Lin B, Liu T, Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Yan F (2014) Variation of methane adsorption property of coal after the treatment of hydraulic slotting and methane predrainage: a case study. J Petrol Sci Eng 20:396–406
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51874122), Key Scientific Research Projects Plan of Henan Higher Education Institutions (19A440008), Key Laboratory of Gas and Fire Control for Coal Mines (China University of Mining and Technology), and Program for Innovative Research Team of Henan Polytechnic University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santanu Banerjee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Wang, L., Bhattacharyya, S. et al. Improving safety by further increasing the permeability of coal seams using air cannons after hydraulic punching. Arab J Geosci 14, 2126 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08511-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08511-3