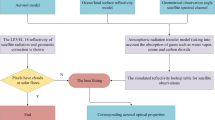
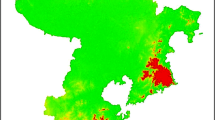
Abstract
Coastal cities are ideal tourist destinations for travel enthusiasts in China and the world. The tourism industry in these cities is very prosperous, which is of great and far-reaching significance to economic and social development. This article mainly studies and analyzes the changes that the strong tourism competitiveness of China’s coastal cities can bring to the overall development of urban tourism, and points out the development direction. Then, based on the conclusions of the research and analysis, explore the factors that may have an impact on the orderly development of urban tourism. This article mainly conducts research and analysis on the competitiveness of China’s coastal city tourism in terms of infrastructure conditions, overall ecological environment, and current development status, because the correct translation during the tourism process determines what it wants to tell you. It can be well received by everyone, so we must solve the problem of inaccurate language translation in the travel process in a targeted manner, and finally achieve the goal of making tourists understand and play well. This article starts the research and analysis of some methods and characteristics of language translation in the process of tourism, in order to improve the professional ability of tourism translators and other related personnel, so that the things introduced in tourism can be correctly understood by tourists. The tourism experience will be better. The weather in tourist destinations will also affect the development of tourism, and the weather is affected by the seasons, and rainfall time series data can indicate the process of climate change, which is of great value to the development of tourism. Enhancing the understanding of local rainfall is of great reference value for agricultural development, tourism, and the improvement of the ecological environment.















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 November 2021
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08911-5
28 September 2021
An Editorial Expression of Concern to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08471-8
References
Ali MA, Assiri M (2019) Analysis of AOD from MODIS-merged DT–DB products over the Arabian Peninsula. Earth Syst Environ 3:625–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-019-00108-x
Bergamaschi P, Hein R, Heimann M, Crutzen PJ (2000) Inverse modeling of the global CO cycle 1: inversion of CO mixing ratio. J Geophys Res 105:1909–1927
Bilal M, Nichol JE, Nazeer M (2016) Validation of aqua-MODIS C051 and C006 operational aerosol products using AERONET measurements over Pakistan. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 9:2074–2080
Cretu M, Deaconu M (2012) Air quality—monitoring and modelling. INCAS Bull 4(4):127–131. https://doi.org/10.13111/2066-8201.2012.4.4.11
Cretu M, Teleaba V, Ionescu S, Ionescu A (2010) Case study on pollution prediction through atmospheric dispersion modeling. WSEAS Environ Dev 8(6):604–613
Dai T, Schutgens N, Goto D, Shi GY, Nakajima T (2014) Improvement of aerosol optical properties modeling over Eastern Asia with MODIS AOD assimilation in a global nonhydrostatic icosahedral aerosol transport model. Environ Pollut 195:319–329
Foley KM, Roselle SJ, Appel KW, Bhave PV, Pleim JE, Otte TL, Mathur R, Sarwar G, Young JO, Gilliam RC, Nolte CG, Kelly JT, Gilliland AB, Bash JO (2010) Incremental testing of the community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) modeling system version 4. 7. Geosci Model Dev 3:205–226 https://www.geosci-model-dev.net/3/205/2010/
Guenther A, Hewitt CN, Erickson D, Fall R, Geron C, Graedel T, Harley P, Klinger L, Lerdau M, Mckay WA, Pierce T, Scholes B, Steinbrecher R, Tallamraju R, Taylor J, Zimmerman P (1995) A global model of natural volatile organic compound emissions. J Geophys Res 100:8873–8892
Guenther A, Baugh B, Brasseur G, Greenberg J, Harley P, Klinger L, Serca D, Vierling L (1999) Isoprene emission estimates and uncertainties for the Central African EXPRESSO study domain. J Geophys Res 104:30625–30639
He KB, Yang FM, Ma YL, Zhang Q, Yao X, Chan CK, Cadle S, Chan T, Mulawa P (2001) The characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Atmos Environ 35(29):4959–4970
Hein R, Crutzen PJ, Heimann M (1997) An inverse modeling approach to investigate the global atmospheric methane cycle. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 11:43–76
Ide K, Courtier P, Ghil M, Lorenc AC (1997) Unified notation for data assimilation: operational, sequential and variational. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 75(1B):181–189
Jia MW, Zhao TL, Cheng X, Gong S, Zhang X, Tang L, Liu D, Wu X, Wang L, Chen Y (2017) Inverse relations of PM2.5 and O3 in air compound pollution between cold and hot seasons over an urban area of east China. Atmosphere 8, 8:–59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8030059
Jiang Z, Liu Z, Wang T, Schwartz CS, Lin HC, Jiang F (2013) Probing into the impact of 3DVAR assimilation of surface PM10 observations over China using process analysis. J Geophys Res-Atmos 118:6738–6749. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50495
Kahnert M (2008) Variational data analysis of aerosol species in a regional CTM: Background error covariance constraint and aerosol optical observation operators. Tellus B 60:753–770. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0889.2008.00377.x
Kukkonen J, Olsson T et al (2012) Operational, regional-scale, chemical weather forecasting models in Europe. Atmos Chem Phys Discuss 2011(11):5985–6162
Li HZ, Guo GL, Zha JF (2017) Study on time-varying characteristics of similar material model strength and the regulation measures. Environ Earth Sci 76:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6857-5
Li W, Zhang QS, Liu RT, Zhang LZ, Li KX, Zhang SJ (2018) Stress analysis of primary support arch cover excavation in metro station based on 3D geomechanical model experiment. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 11, doi:10.1007/s12517-018-4084-3.
Matthew OJ, Igbayo AN, Olise FS, Owoade KO, Abiye OE, Ayoola MA, Hopke PK (2019) Simulation of point source pollutant dispersion pattern: an investigation of effects of prevailing local weather conditions. Earth Syst Environ 3:215–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-019-00087-z
Pagowski M, Grell GA (2012) Experiments with the assimilation of fine aerosols using an ensemble Kalman filter. J Geophys Res-Atmos 117:D21302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012jd018333
Rubin JI, Reid JS, Hansen JA, Anderson JL, Collins N, Hoar TJ, Hogan T, Lynch P, McLay J, Reynolds CA, Sessions WR, Westphal DL, Zhang J (2016) Development of the Ensemble Navy Aerosol Analysis Prediction System (ENAAPS) and its application of the Data Assimilation Research Testbed (DART) in support of aerosol forecasting. Atmos Chem Phys 16:3927–3951. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-3927-2016
Saide PE, Carmichael GR, Liu Z, Schwartz CS, Lin HC, da Silva AM, Hyer E (2013) Aerosol optical depth assimilation for a size-resolved sectional model: impacts of observationally constrained, multi-wavelength and fine mode retrievals on regional scale analyses and forecasts. Atmos Chem Phys 13:10425–10444. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-10425-2013
Schutgens NA, Miyoshi T, Takemura T, Nakajima T (2010) Sensitivity tests for an ensemble Kalman filter for aerosol assimilation. Atmos Chem Phys 10:6583–6600. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-6583-2010
Tombette M, Mallet V, Sportisse B (2009) PM10 data assimilation over Europe with the optimal interpolation method. Atmos Chem Phys 9:57–70. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-57-2009
Wu LX, Lv X, Qin K (2014) On sptatio-temporal features of air pollutants in Xuzhou city during straw burning period (in Chinese) [J]. Geogr Geo-Inform Sci 30(1):18–22 31
Xu XD, Xie LA, Cheng XH, Xu J, Zhou X, Ding G (2008) Application of an adaptive nudging scheme in air quality forecasting in China [J]. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 47:2105–2114
Yin XM, Dai T, Xin JY, Gong DY, Yang J, Teruyuki N, Shi GY (2016) Estimation of aerosol properties over the Chinese desert region with MODIS AOD assimilation in a global model. Adv Clim Chang Res 7:90–98
Zhang J, Reid JS, Westphal D, Baker N, Hyer E (2008) A system for operational aerosol optical depth data assimilation over global oceans. J Geophys Res 113:D10208. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD009065
Funding
This work is funded by Research Program for Foreign language of Economy and Social Development of Heilongjiang Province under the No. WY2019023-B and this work is supported by Philosophy and Social Science Research Program of Heilongjiang Province under the grant No. 14D046.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he/she has no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sheldon Williamson
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Environment and Low Carbon Transportation
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08911-5
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, X. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Rainfall trend based on computer image system and English translation of tourist attractions in coastal cities. Arab J Geosci 14, 1014 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07357-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07357-z