Abstract
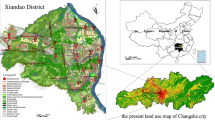
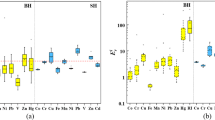
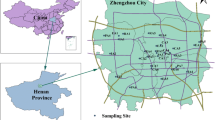
A total of forty-five road dust samples were collected from a steel industry city in China and analyzed for Cr, Ni, Cu, Cd, and Pb. The results indicated that the mean concentrations of Cd, Ni, Cu, Pb, and Cr in road dust samples were 2.29, 83.50, 163.74, 272.04, and 700.19 mg/kg, respectively. The spatial distribution maps of potentially harmful elements revealed that steel industrial district and heavy traffic could serve as the contamination hotspots. The calculated Igeo for the potential harmful elements ranged from uncontaminated to serious contaminated levels. The findings of \( {E}_r^i \) showed that low (Cd, Cr, and Ni) to moderate (Cu and Pb) risks, while those of PRI indicated 64% and 36% samples with low and moderate risks, respectively. The HI values of Cr (3.81) and Pb (1.13) for children were higher than the safe level 1, indicating that children are facing excessive threats of Cr and Pb. Conversely, the RI values of Cd, Cr, and Ni were lower than 1E-04, indicating that children and adults are at acceptable risk of potentially harmful elements. Based on our results, the local government should improve the iron and steel smelting process, control the number of motor vehicles, and strengthen the road traffic dust pollution control.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi K, Tainosho Y (2004) Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ Int 30(8):1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2004.04.004
Al-Dousari A, Doronzo D, Ahmed M (2017) Types, indications and impact evaluation of sand and dust storms trajectories in the Arabian Gulf. Sustainability 9(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/su9091526
Al-Hemoud A, Al-Dousari A, Al-Shatti A, Al-Khayat A, Behbehani W, Malak M (2018) Health impact assessment associated with exposure to PM10 and dust storms in Kuwait. Atmosphere 9(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9010006
Al-Hemoud A, Al-Dousari A, Misak R, Al-Sudairawi M, Naseeb A, Al-Dashti H et al (2019a) Economic impact and risk assessment of sand and dust storms (SDS) on the oil and gas industry in Kuwait. Sustainability 11(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11010200
Al-Hemoud A, Gasana J, Al-Dabbous A, Alajeel A, Al-Shatti A, Behbehani W et al (2019b) Exposure levels of air pollution (PM2.5) and associated health risk in Kuwait. Environ Res 179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108730
Al-Hemoud A, Al-Dousari A, Al-Dashti H, Petrov P, Al-Saleh A, Al-Khafaji S et al (2020) Sand and dust storm trajectories from Iraq Mesopotamian flood plain to Kuwait. Sci Total Environ 710:136291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136291
Apeagyei E, Bank, M. S, Spengler JD (2011) Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmos Environ 45(13):2310–2323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.11.015
Bergthorson JM, Goroshin S, Soo MJ, Julien P, Palecka J, Frost DL, Jarvis DJ (2015) Direct combustion of recyclable metal fuels for zero-carbon heat and power. Appl Energy 160:368–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.09.037
Boldo E, Linares C, Aragones N, Lumbreras J, Borge R, de la Paz D, Lopez-Abente G (2014) Air quality modeling and mortality impact of fine particles reduction policies in Spain. Environ Res 128:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2013.10.009
Bozkurt Z, Gaga EO, Taspinar F, Ari A, Pekey B, Pekey H et al (2018) Atmospheric ambient trace element concentrations of PM10 at urban and sub-urban sites: source apportionment and health risk estimation. Environ Monit Assess 190(3):168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6517-6
Caravanos J, Weiss AL, Blaise MJ, Jaeger RJ (2006) A survey of spatially distributed exterior dust lead loadings in New York City. Environ Res 100(2):165–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2005.05.001
Cui XT, Wang XQ, Liu B (2020) The characteristics of heavy metal pollution in surface dust in Tangshan, a heavily industrialized city in North China, and an assessment of associated health risks. J Geochem Explor 210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.106432
Dehghani S, Moore F, Keshavarzi B, Hale BA (2017) Health risk implications of potentially toxic metals in street dust and surface soil of Tehran, Iran. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 136:92–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.10.037
Doabi SA, Karami M, Afyuni M, Yeganeh M (2018) Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil, atmospheric dust and major food crops in Kermanshah province, Iran. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.057
Dong S, Ochoa Gonzalez R, Harrison RM, Green D, North R, Fowler G, Weiss D (2017) Isotopic signatures suggest important contributions from recycled gasoline, road dust and non-exhaust traffic sources for copper, zinc and lead in PM 10 in London, United Kingdom. Atmos Environ 165:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.06.020
Doronzo DM, Al-Dousari A, Folch A, Dagsson-Waldhauserova P (2016) Preface to the Dust Topical Collection. Arab J Geosci 9(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2504-9
Du Y, Gao B, Zhou H, Ju X, Hao H, Yin S (2013) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dusts in urban parks of Beijing, China. Procedia Environ Sci 18:299–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2013.04.039
Duan J, Tan J (2013) Atmospheric heavy metals and arsenic in China: situation, sources and control policies. Atmos Environ 74:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.03.031
Eqani S, Kanwal A, Bhowmik AK, Sohail M, Ullah R, Ali SM, Shen H (2016) Spatial distribution of dust-bound trace elements in Pakistan and their implications for human exposure. Environ Pollut 213(213-222). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.02.017
Ferreira-Baptista L, De Miguel E (2005) Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: a tropical urban environment. Atmos Environ 39(25):4501–4512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.03.026
Ghanavati N, Nazarpour A, Watts MJ (2019) Status, source, ecological and health risk assessment of toxic metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in street dust of Abadan, Iran. Catena 177:246–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.02.022
Gope M, Masto RE, George J, Hoque RR, Balachandran S (2017) Bioavailability and health risk of some potentially toxic elements (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in street dust of Asansol, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 138:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.008
Gope M, Masto RE, George J, Balachandran S (2018) Tracing source, distribution and health risk of potentially harmful elements (PHEs) in street dust of Durgapur, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 154:280–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.042
Goudarzi G, Daryanoosh SM, Godini H, Hopke PK, Sicard P, De Marco A, Omidi Khaniabadi Y (2017) Health risk assessment of exposure to the Middle-Eastern Dust storms in the Iranian megacity of Kermanshah. Public Health 148:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2017.03.009
Grigoratos T, Martini G (2015) Brake wear particle emissions: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(4):2491–2504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3696-8
Gunawardana C, Goonetilleke A, Egodawatta P, Dawes L, Kokot S (2012) Source characterisation of road dust based on chemical and mineralogical composition. Chemosphere 87(2):163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.012
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Huang M, Wang W, Chan CY, Cheung KC, Man YB, Wang X, Wong MH (2014) Contamination and risk assessment (based on bioaccessibility via ingestion and inhalation) of metal(loid)s in outdoor and indoor particles from urban centers of Guangzhou, China. Sci Total Environ 479-480:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.115
Karim Z, Qureshi BA, Mumtaz M, Qureshi S (2014) Heavy metal content in urban soils as an indicator of anthropogenic and natural influences on landscape of Karachi-A multivariate spatio-temporal analysis. Ecol Indic 42:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.07.020
Kováčik J, Dudas M, Hedbavny J, Martonfi P (2016) Dandelion Taraxacum linearisquameum does not reflect soil metal content in urban localities. Environ Pollut 218:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.030
Kurt-Karakus PB (2012) Determination of heavy metals in indoor dust from Istanbul, Turkey: estimation of the health risk. Environ Int 50:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2012.09.011
Li HH, Chen LJ, Yu L, Guo ZB, Shan CQ, Lin JQ, Cheng Z (2017) Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of human exposure to oral bioaccessibility of heavy metals via urban street dusts from different functional areas in Chengdu, China. Sci Total Environ 586:1076–1084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.092
Liu E, Wang X, Liu H, Liang M, Zhu Y, Li Z (2019) Chemical speciation, pollution and ecological risk of toxic metals in readily washed off road dust in a megacity (Nanjing), China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 173:381–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.019
Marcotte S, Estel L, Minchin S, Leboucher S, Le Meur S (2017) Monitoring of lead, arsenic and mercury in the indoor air and settled dust in the Natural History Museum of Rouen (France). Atmos Pollut Res 8(3):483–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2016.12.002
Men C, Liu R, Xu F, Wang Q, Guo L, Shen Z (2018) Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 612:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.123
Men C, Liu RM, Xu LB, Wang QR, Guo LJ, Miao YX et al (2020) Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 388:121763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121763
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. J Geol 2:108–118
Oliva SR, Espinosa AJF (2007) Monitoring of heavy metals in topsoils, atmospheric particles and plant leaves to identify possible contamination sources. Microchem J 86(1):131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2007.01.003
Pan H, Lu X, Lei K (2017) A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi’an, China: contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 609:1361–1369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.004
Phil-Eze P (2010) Variability of soil properties related to vegetation cover in a tropical rainforest landscape. J Geogr Reg Plann 3(7):177–184
Safiur Rahman M, Khan MDH, Jolly YN, Kabir J, Akter S, Salam A (2019) Assessing risk to human health for heavy metal contamination through street dust in the Southeast Asian Megacity: Dhaka, Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 660:1610–1622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.425
Škrbić BD, Buljovčić M, Jovanović G, Antić I (2018) Seasonal, spatial variations and risk assessment of heavy elements in street dust from Novi Sad, Serbia. Chemosphere 205:452–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.124
US EPA (1989) Risk assessment guidance for Superfund. Volume I: human health evaluation manual (Part A), Interim Final. 1989. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. In: Office of Emergency and Remedial Response (EPA/540/1-89/002)
US EPA (1996) Soil screening guidance: technical background document. EPA/540/r-95/128. Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response.
Wang ZX, Chen JQ, Chai LY, Yang ZH, Huang SH, Zheng Y (2011) Environmental impact and site-specific human health risks of chromium in the vicinity of a ferro-alloy manufactory, China. J Hazard Mater 190(1-3):980–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.039
Wei X, Gao B, Wang P, Zhou H, Lu J (2015) Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dusts from different functional areas in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.11.005
Yang J, Teng Y, Song L, Zuo R (2016) Tracing sources and contamination assessments of heavy metals in road and foliar dusts in a typical mining city, China. PLoS One 11(12):e0168528. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0168528
Yoshinaga J, Yamasaki K, Yonemura A, Ishibashi Y, Kaido T, Mizuno K, Tanaka A (2014) Lead and other elements in house dust of Japanese residences-source of lead and health risks due to metal exposure. Environ Pollut 189:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.03.003
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (41673109), National key R&D project (SQ2018YFC020021), and Sichuan science and technology support project (2017SZ0185).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Domenico M. Doronzo
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 87 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Huang, Y. & Cheng, X. Status, spatial distribution, and health risk assessment of potentially harmful element from road dust in steel industry city, China. Arab J Geosci 14, 318 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06556-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06556-y