Abstract
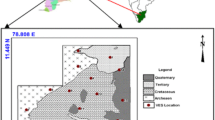
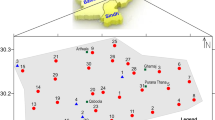
Rapidly depleting resources of surface water necessitate the exploration of groundwater reservoirs to cope with the water demand in Lahore and its periphery. For this purpose, a study was conducted to investigate groundwater depth, water quality, and subsurface lithology through Geo-electrical Resistivity Survey (ERS). Vertical electrical soundings (VES) at six (06) stations in the city of Lahore were performed using Schlumberger array. Apparent resistivity values were recorded at surface and processed with a computer software IPI2win to assess groundwater depth, quality, and subsurface formations. The VES resulted that the study area comprises of three layers. Top layer was determined as fill up to depth of 2 m followed by an unsaturated alluvium up to depth of 40 m, and the bottom layer was saturated alluvium up to the study depth of 100 m. The average water table depth was appeared to be at 39 m below the ground surface. The computed groundwater depths were also compared with the previous studies conducted in the proximity by different agencies in the past using destructive techniques and showed close resemblance. The study also shows that the groundwater up to depth of 100 m was having excess amount of total dissolved solids and was not drinkable as per quality standards set by the World Health Organization.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERS :
-
Geo-electrical Resistivity Survey
- VES :
-
Vertical electrical soundings
- TDS :
-
Total dissolved solids
- Pvt. :
-
Private limited
- Ltd. :
-
Limited
- ρa :
-
Apparent resistivity
- ρ :
-
Resistivity
- RMS :
-
Root mean square
- Ppm :
-
Parts per million
- Ωm :
-
Ohm-m
- WHO :
-
World Health Organization
- WASA :
-
Water and Sanitation Agency
- NESPAK :
-
National Engineering Services Pakistan
- UET :
-
University of Engineering and Technology
References
Adepelumi AA, Ako B, Ajayi T, Afolabi O, Omotoso E (2009) Delineation of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer of Lekki Peninsula, Lagos, Nigeria. Environ Geol 56:927–933
Anomohanran O (2013) Geophysical investigation of groundwater potential in Ukelegbe, Nigeria. J Appl Sci 13:119–125
Anomohanran O (2014) Assessment of groundwater potential in Ozoro, Delta state, Nigeria using the electrical resistivity method. Appl Phys Res 6:116
Anomohanran O (2015) Hydrogeophysical investigation of aquifer properties and lithological strata in Abraka, Nigeria. J Afr Earth Sci 102:247–253
Anomohanran O, Orhiunu ME (2018) Assessment of groundwater occurrence in Olomoro, Nigeria using borehole logging and electrical resistivity methods. Arab J Geosci 11:219
Batayneh AT (2006) Use of electrical resistivity methods for detecting subsurface fresh and saline water and delineating their interfacial configuration: a case study of the eastern Dead Sea coastal aquifers, Jordan. Hydrogeol J 14:1277–1283
Bhattacharya P, Patra H (1968) Direct current electrical sounding. Elseveir, Amsterdam
Bobachev C (2002) IPI2Win: a windows software for an automatic interpretation of resistivity sounding data. Moscow State University 320
Choudhury J, Kumar KL, Nagaiah E, Sonkamble S, Ahmed S, Kumar V (2017) Vertical electrical sounding to delineate the potential aquifer zones for drinking water in Niamey city, Niger, Africa. J Earth Syst Sci 126:91
Dakhnov F. (1953) Electrical prospecting for petroleum and gas deposits (in Russian): Moscow. Gostoptekhizdat,
Edet A, Okereke C (2014) Hydrogeologic framework of the shallow aquifers in the Ikom–Mamfe embayment, Nigeria using an integrated approach. J Afr Earth Sci 92:25–44
Edition F (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO chronicle 38:104–108
Frohlich RK, Barosh PJ, Boving T (2008) Investigating changes of electrical characteristics of the saturated zone affected by hazardous organic waste. J Appl Geophys 64:25–36
Gupta G, Erram VC, Kumar S (2012) Temporal geoelectric behaviour of dyke aquifers in northern Deccan Volcanic Province, India. J Earth Syst Sci 121:723–732
Hamzah U, Samsudin AR, Malim EP (2007) Groundwater investigation in Kuala Selangor using vertical electrical sounding (VES) surveys. Environ Geol 51:1349–1359
Huang Z., Mohammed E.E., Changchun Z., Zhenya C. (2014) An approach to evaluate groundwater salinity using electrical well logging data case study: sandstone aquifer in Daging oil field, China
Hussain Y, Ullah SF, Akhter G, Aslam AQ (2017) Groundwater quality evaluation by electrical resistivity method for optimized tubewell site selection in an ago-stressed Thal Doab Aquifer in Pakistan. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:15
Jha MK, Kumar S, Chowdhury A (2008) Vertical electrical sounding survey and resistivity inversion using genetic algorithm optimization technique. J Hydrol 359:71–87
Kalenov E (1957) Interpretation of vertical electrical sounding curves. Mascow, Gostoptekhiz at
Karlık G, Kaya MA (2001) Investigation of groundwater contamination using electric and electromagnetic methods at an open waste-disposal site: a case study from Isparta, Turkey. Environ Geol 40:725–731
Kayode J, Adelusi A, Nawawi M, Bawallah M, Olowolafe T (2016) Geo-electrical investigation of near surface conductive structures suitable for groundwater accumulation in a resistive crystalline basement environment: a case study of Isuada, southwestern Nigeria. J Afr Earth Sci 119:289–302
Keller GV, Frischknecht FC (1966) Electrical methods in geophysical prospecting
Khan GD, Waheedullah ASB (2013) Groundwater investigation by using resistivity survey in Peshawar, Pakistan. Journal of Resources Development and Management-An Open Access International Journal 2
Koefoed O, Patra H, Mallick K (1979) Geosounding principles, vol 2. Elsevier Science & Technology, Amsterdam
Kundu MC, Mandal B (2009) Assessment of potential hazards of fluoride contamination in drinking groundwater of an intensively cultivated district in West Bengal, India. Environ Monit Assess 152:97
Lima OALD, Sato HK, Porsani MJ (1995) Imaging industrial contaminant plumes with resistivity techniques
Mondal N, Singh V, Ahmed S (2013) Delineating shallow saline groundwater zones from southern India using geophysical indicators. Environ Monit Assess 185:4869–4886
Nespak NESP (2015) Geotechnical Investigation of at Orange Line Metro Train Project Lahore Package-II Borehole No 27
Panda KP, Sharma S, Jha MK (2018) Mapping lithological variations in a river basin of West Bengal, India using electrical resistivity survey: implications for artificial recharge. Environ Earth Sci 77:626
Park Y-H, Doh S-J, Yun S-T (2007) Geoelectric resistivity sounding of riverside alluvial aquifer in an agricultural area at Buyeo, Geum River watershed, Korea: an application to groundwater contamination study. Environ Geol 53:849–859
Ruggeri P, Gloaguen E, Lefebvre R, Irving J, Holliger K (2014) Integration of hydrological and geophysical data beyond the local scale: application of Bayesian sequential simulation to field data from the Saint-Lambert-de-Lauzon site, Québec, Canada. J Hydrol 514:271–280
Sikandar P, Bakhsh A, Ali T, Arshad M (2010) Vertical electrical sounding (VES) resistivity survey technique to explore low salinity groundwater for tubewell installation in Chaj doab. J Agric Res 03681157:48
Sonkamble S (2014) Electrical resistivity and hydrochemical indicators distinguishing chemical characteristics of subsurface pollution at Cuddalore coast, Tamil Nadu. J Geol Soc India 83:535-548
Statistics PBo. (2017) PROVISIONAL SUMMARY RESULTS OF 6TH POPULATION AND HOUSING CENSUS-2017 | Pakistan Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved November 10, 2017, from http://www.pbsgov.pk/content/provisional-summary-results-6th-population-and-housing-census-2017-0
Tizro AT, Voudouris K, Basami Y (2012) Estimation of porosity and specific yield by application of geoelectrical method–a case study in western Iran. J Hydrol 454:160–172
UET (2015) Geotechnical investigation report. Tube wells installation in main campus, UET Lahore
WASA (2014) Water issues of Lahore. Annual monitoring and Surveillance Report
Wattanasen K, Elming S-Å (2008) Direct and indirect methods for groundwater investigations: a case-study of MRS and VES in the southern part of Sweden. J Appl Geophys 66:104–117
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support provided by the University of Engineering and Technology (UET) Lahore, Pakistan, for providing the facilities as well as finance to accomplish the present study. Besides, we are grateful to Water and Sanitation Agency (WASA), Lahore, responsible for water supply and sanitation services in Lahore, and National Engineering Services Pakistan (NESPAK) Pvt. Ltd., in providing the requisite data for comparison of results with those of previously conducted studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Li Zhen Cheng
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehmood, Z., Khan, N.M., Sadiq, S. et al. Assessment of subsurface lithology, groundwater depth, and quality of UET Lahore, Pakistan, using electrical resistivity method. Arab J Geosci 13, 281 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5260-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5260-9