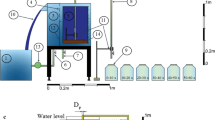
Abstract
Dam reservoir siltation is a worldwide problem that results in loss of storage capacity and blockage of drainage outlets. Previous sediment removal techniques include flushing, excavation, dredging, and sluicing. In this study, sediment removal is investigated experimentally using image processing techniques, to assess the suction action of a syphon pipe. The syphon results in a scour hole that depends on several factors including the sediment mean diameter (d50), the applied suction head (Hw), the pipe diameter (dp), and the penetration depth (Zo). One soil type was used, poorly graded sand (d50 of 1 mm), to examine the interdependence of the other factors on the developed scour hole at equilibrium. Three heads (Hw) of 0.82 m, 1.04 m, and 1.22 m were applied and three pipe diameters (dp) of 6 mm, 9.5 mm, and 13.8 mm were used. Various Zo values that ranged between 0.0 and 7.0 cm were used. Measurements of the hole depth (hd), the hole diameter (D), and the removed soil mass were recorded. Non-dimensional characteristic relationships between the different factors were developed and a new non-dimensional design parameter (ϕ) is proposed to be used for estimating the scour hole dimensions. The design parameter ϕ depends on (Zo/Hw) and Reynolds number as input parameters. The results indicate a linear relation between (D/dp) and (hd/dp) with a regression coefficient (R2) ≈ 0.98, and a power-law relation between the normalized weight of the removed sediments (Ws/Fp) and (hd/dp) with R2 ≈ 0.95, where Fp is the suction pressure force.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asiaban P, Kouchakzadeh S, Asiaban S (2017) Enhanced hydro-suction performance for cohesive sediment removal in low-head reservoirs. Ain Shams Eng J 8:491–497
Bruk S (1985) Methods of computing sedimentation in lakes and reservoirs. UNESCO, Paris
Chen S-C, Wang S-C, Wu C-H (2010) Sediment removal efficiency of siphon dredging with wedge-type suction head and float tank. Int J Sediment Res 25:149–160
Dismuke CP, Randal RE, Yeh Po-H (2012) Laboratory measurements of the suction inlet flow field of a model cutter suction dredge. Proceedings, WEDA XXXII Technical Conference & TAMU 43 Dredging Seminar
Hannoyer J (1974) Nouvelle Method de Devasement des Barrages – Reservoirs. Ann Inst Technique Batiment Travaux Publics 314:146–153
Herbich JB (2000) Handbook of dredging engineering, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Jacobsen T (1997) Economic aspects of removal of sediment from reservoirs. Hydropower ’97, A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam
McFall BC, Bryant DB, Welp TL (2018) Literature review of dredging physical models. US Army Corps of Engineers, Engineer Research and Development Center, Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory Report. ERDC/CHL SR-18-1, Dredging Operations and Environmental Research (DOER) Program, Mississippi
Rehbinder G (1994) Sediment removal with a siphon at critical flux. J Hydraul Res IAHR 32(6): 845-860; published online in 2010. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221689409498694
Sedicon (2018) http://www.sedicon.no/ .Accessed December 2018
Thompson JR (2018) Ecological effects of offshore dredging and beach nourishment: a review. ISBN-13: 978-0364414286. Forgotten Books, London
Ullah SM (2003) Siphon removal of cohesionless materials. MASc. Dissertation, University of Windsor, Ontario, Canada
Ullah SM, Mazurek KA, Rajaratnam N (2005) Siphon removal of cohesionless materials. J Waterw Port Coast Ocean Eng 131(3):115–122
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1994) Assessment and remediation of contaminated sediments (ARCS) program. EPA/905/R-94/003, USEPA, Great Lakes National Program Office, Chicago
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Civil Engineering Department of King Saud University for allowing the use of its hydraulics laboratory, as well as the College of Engineering Research Centers at both King Saud University and Al-Imam Muhammad Ibn Saud Islamic University for providing technical support. The authors also thank Mr. John MacKenzie, who is a professional environmental engineer at AECOM Canada Ltd., for reviewing and editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Broder J. Merkel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elgamal, M., Fouli, H. Sediment removal from dam reservoirs using syphon suction action. Arab J Geosci 13, 943 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05955-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05955-x