Abstract
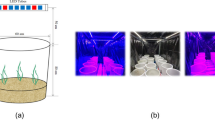
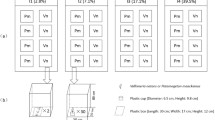
This study investigated the effects of light intensity on growth and biomass production of three submerged macrophyte species including Hydrilla verticillata, Vallisneria natans, and Ceratophyllum demersum in different water strata. For this purpose, water was classified into six strata designed: 5 cm, 30 cm, 60 cm, 90 cm, 120 cm, and 150 cm in the field under natural conditions. Results revealed that very high and very low heat intensity affected the growth of submerged macrophyte species differently. The growth of macrophytes was inhibited because of the high light intensity at 5 cm water strata. However, at 150-cm water strata, the macrophytes were died due to low light penetration. Among macrophyte species, the biomass production of Hydrilla verticillata and Ceratophyllum demersum was highest in the water strata at 90 cm, while Vallisneria natans were died in water strata of 120 cm due insufficient illumination. Furthermore, Hydrilla verticillata and Ceratophyllum demersum showed resilience and grown normally in later stages. The highest height of Vallisneria natans (35.3 cm), including Hydrilla verticillata (45.8 cm) and Ceratophyllum demersum (28.2 cm), was observed in water strata at 30, 60, and 60 cm. This study revealed that high and low light intensity affects the chlorophyll contents of macrophytes that results an impact on their growth and biomass production.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1
Bakker E, Van Donk E, Declerck S, Helmsing N, Hidding B, Nolet B (2010) Effect of macrophyte community composition and nutrient enrichment on plant biomass and algal blooms. Basic Appl Ecol 11:432–439
Bunluesin S, Kruatrachue M, Pokethitiyook P, Upatham S, Lanza GR (2007) Batch and continuous packed column studies of cadmium biosorption by Hydrilla verticillata biomass. J Biosci Bioeng 103:509–513
Canfield DE, Hodgson L (1983) Prediction of Secchi disc depths in Florida lakes: impact of algal biomass and organic color. Hydrobiologia 99:51–60
Cao J-j, Wang Y, Zhu Z-L (2012) Growth response of the submerged macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum to sediment nutrient levels and water-level fluctuations. Aquat Biol 17:295–303
Chen J, Liu Z, Xiao S, Chen R, Luo C, Zhu T, Zhang M (2020) Effects of benthivorous fish disturbance on chlorophyll a contents in water and the growth of two submersed macrophytes with different growth forms under two light regimes. Sci Total Environ 704:135269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135269
Collier C, Waycott M, McKenzie L (2012) Light thresholds derived from seagrass loss in the coastal zone of the northern Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Ecol Indic 23:211–219
Dong B, Qin B, Gao G, Cai X (2014) Submerged macrophyte communities and the controlling factors in large, shallow Lake Taihu (China): sediment distribution and water depth. J Great Lakes Res 40:646–655
Garg, N., & Kaur, H. (2013). Response of Antioxidant Enzymes, Phytochelatins and Glutathione Production Towards C d and Z n Stresses in C ajanus cajan (L.) M illsp. Genotypes Colonized by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 199(2), 118-133.
Gu J, Jin H, He H, Ning X, Tan B, Jeppesen E, Li K (2016) Effects of small-sized crucian carp (Carassius carassius) on the growth of submerged macrophytes: implications for shallow lake restoration. Ecol Eng 95:567–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.118
Hilt S, Gross EM (2008) Can allelopathically active submerged macrophytes stabilise clear-water states in shallow lakes? Basic Appl Ecol 9:422–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2007.04.003
Jadoon S, Hilal Z, Ali M, Muhammad S (2019) Potentially toxic elements in drinking water and associated health risk assessment in Abbottabad city, northern Pakistan. Desalin Water Treat 151:392–402
Johnson RE, Kong Y, Zheng Y (2020) Elongation growth mediated by blue light varies with light intensities and plant species: a comparison with red light in arugula and mustard seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 169:103898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.103898
Khan SA, Abeer N, Hussain SZ, Muhammad S, Jawad F, Khan T (2019) Potentially toxic elements contamination in water and evaluation for risk assessment in the Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Desalin Water Treat 159:327–337
Li L, Bonser SP, Lan Z, Xu L, Chen J, Song Z (2017) Water depth affects reproductive allocation and reproductive allometry in the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans. Sci Rep 7:16842. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16719-1
Liang S, Guo J, Wu P, Feng Y, Wang X, Wang G, Xu W (2020) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of surface water and groundwater in the Qinghai Lake catchment (China). Arab J Geosci 13:135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5103-8
Liu H, Zheng L, Wu J, Liao Y (2020) Past and future ecosystem service trade-offs in Poyang Lake Basin under different land use policy scenarios. Arab J Geosci 13:46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-5004-x
Milne JM, Murphy KJ, Thomaz S (2006) Morphological variation in Eichhornia azurea (Kunth) and Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms in relation to aquatic vegetation type and the environment in the floodplain of the Rio Paraná, Brazil. Hydrobiologia 570:19–25
Muhammad S, Ullah R, Jadoon IA (2019) Heavy metals contamination in soil and food and their evaluation for risk assessment in the Zhob and Loralai valleys, Baluchistan province, Pakistan Microchem J:103971
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters Analytica. Chim Acta 27:31–36
Nazeri Tahroudi M, Ramezani Y, Ahmadi F (2019) Investigating the trend and time of precipitation and river flow rate changes in Lake Urmia basin, Iran. Arab J Geosci 12:219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4373-5
Qin B (2013) A large-scale biological control experiment to improve water quality in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Lake Reservoir Manage 29:33–46
Qin B, Yang L, Chen F, Zhu G, Zhang L, Chen Y (2006) Mechanism and control of lake eutrophication. Chin Sci Bull 51:2401–2412
Sabir MA, Muhammad S, Umar M, Farooq M, Fardiullah NA (2017) Water quality assessment for drinking and irrigation purposes in upper Indus basin, northern Pakistan. Fresenius Environ Bull 26:4180–4186
Saleh HM, Moussa HR, Mahmoud HH, El-Saied FA, Dawoud M, Wahed RSA (2020) Potential of the submerged plant Myriophyllum spicatum for treatment of aquatic environments contaminated with stable or radioactive cobalt and cesium. Prog Nucl Energy 118:103147
Scheffer M (2004) The story of some shallow lakes. In: Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Springer, pp 1-19
Søndergaard M, Johansson LS, Lauridsen TL, Jørgensen TB, Liboriussen L, Jeppesen E (2010) Submerged macrophytes as indicators of the ecological quality of lakes. Freshw Biol 55:893–908
Spence DHN (1982) The zonation of plants in freshwater lakes. In: Advances in Ecological Research, vol 12. Elsevier, pp 37-125
Townsend SA, Webster IT, Burford MA, Schult J (2018) Effects of autotrophic biomass and composition on photosynthesis, respiration and light utilisation efficiency for a tropical savanna river. Mar Freshw Res 69:1279–1289
Vanderstukken M, Mazzeo N, Van Colen W, Declerck SA, Muylaert K (2011) Biological control of phytoplankton by the subtropical submerged macrophytes Egeria densa and Potamogeton illinoensis: a mesocosm study. Freshw Biol 56:1837–1849
Vanderstukken M, Declerck SA, Decaestecker E, Muylaert K (2014) Long-term allelopathic control of phytoplankton by the submerged macrophyte Elodea nuttallii. Freshw Biol 59:930–941
Wang C, Zhang SH, Wang PF, Hou J, Li W, Zhang WJ (2008) Metabolic adaptations to ammonia-induced oxidative stress in leaves of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Aqua Toxicol 87:88–98
Wollheim WM, Bernal S, Burns DA, Czuba J, Driscoll CT, Hansen A, Kaushal S (2018) River network saturation concept: factors influencing the balance of biogeochemical supply and demand of river networks. Biogeochemistry 141:503–521
Xu N-N, Tong X, Tsang P-KE, Deng H, Chen X-Y (2011) Effects of water depth on clonal characteristics and biomass allocation of Halophila ovalis (Hydrocharitaceae). J Plant Ecol 4:283–291
Zhang Q, Liu Y-P, Luo F-L, Dong B-C, Yu F-H (2019) Does species richness affect the growth and water quality of submerged macrophyte assemblages? Aquat Bot 153:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2018.11.006
Zhu G, Li W, Zhang M, Ni L, Wang S (2012) Adaptation of submerged macrophytes to both water depth and flood intensity as revealed by their mechanical resistance. Hydrobiologia 696:77–93
Zhu Z, Song S, Yan Y, Li P, Jeelani N, Wang P, Leng X (2018) Combined effects of light reduction and ammonia nitrogen enrichment on the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans. Mar Freshw Res 69:764–770
Funding
Financial support is provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Amjad Kallel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, S., Ibrahim, M., Muhammad, S. et al. Light intensity effects on the growth and biomass production of submerged macrophytes in different water strata. Arab J Geosci 13, 948 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05924-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05924-4