Abstract
The Mazafran wadi is characterized by a strong connection of the solids flow in kilograms per second to the liquid flow in cubic meters per second. However, high solids flow can also be associated to low liquid flow after severe summer storms. We also note that high water flows generate low solids transport; this is probably because of the groundwater draining after major floods. The relation between the daily solids flow and the average daily liquid flow varies from 50 to 600 m3 s−1. It is represented as follows: Qs = 2.03 Qmj2.626. The correlation of suspended matter and liquid flow concentrations follows the Serrat model which is presented as a second-degree logarithmic-based polynomial equation. Both equations show that the Total Suspended Solid (TSS) increases with the downstream and upstream flow. The suspended solids transport occurs mainly in the winter and to a less extent in the spring and autumn.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminot-Suchet P, Probst JL (1995) A global model for present-day atmospheric soil CO2 consumption by chemical erosion of continental rocks (GEM-CO2). Tellus 47B:273–280
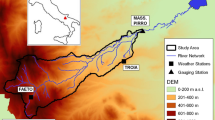
ANRH n.d.. Agence Nationale des Ressources Hydrauliques de Blida: Liquid and solid flow old and 2005–2006 MES data
Bouanani A (2004) Hydrology, solid transportation, and modeling. Study of some sub-basins of the Tafna River (NW - Algeria). State Thesis. Abu Bakr Belkaid Tlemcen University. 250 p
Boudjadja A, Messahel M, Pauc H (2003) Water resources in Northern Algeria. Revue des Sciences de l’Eau 16/3 pp 285–304
Bourouba M (2002) Comparison of the suspended solid charge in Algerian wadis: synthesis test. Bulletin Reseau Erosion 21, IRD Montpellier (France). pp 358–374
Bourrin F (2007) Variability and fate of sedimentary inputs by coastal rivers: the case of the Têt-Littoral Roussillonnais system in the Gulf of Lion. Doctoral thesis. The University of Perpignan. 305 pages
Foudil Bouras A E (2012) A geochemical approach of an Algerian coastal hydro system: organic matter transfer from the Mazafran wadi to Bou Ismail Bay. Ph.D. thesis. USTHB. 188 pages
Garcia-Esteve J, Ludwig W (2003) Suspended matter and particulate carbon transfer in the Têt basin (South of France). IAHS Publishing No. 278 pp. 442–447
Lespinas F (2008) Impact of climate change on the hydrology of coastal rivers in the Languedoc-Roussillon region. The Ph.D. thesis University of Perpignan. 339 pages
Linsley RK, Franzini JB (1979) Water Resources Engineering, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Messaoud Nacer N, Remini B, Hadj Kadour B, Habi M (2006) Water pollution problems. Methodological and legislative aspects. The case of surface waters of the Mazafran plain (Mitidja, Algeria). TSM number 5:89–97
Meybeck M (1985) Time variability in the chemical composition of rivers and their solution and suspension transportation. Revue Française des Sciences de l’Eau Vol. 4 pp 93-121
Pauc H (2005) Formation of the Aude, Orb and Herault prodeltas and their characterization using physicochemical and sedimentological parameters. Mar Geol 222–223:335–343
Probst JL (1992) Geochemistry and hydrology of continental erosion. Mechanisms, current global balance sheet and fluctuations over the last 500 million years. Geol science, Memo, Strasbourg 94:161
Serrat P (1998) Spatial analysis of the erodibility of a watershed through the integration of multi-source data, in 17 Réunion des Sciences de la Terre, BRGM Brest, 194
Serrat P (1999) Current sediment dynamics of a Mediterranean river system: the Agly (France). CR Acad Sci 329:189–196
Serrat P, Ludwig W, Navarro B, Blazi JL (2001) Spatio-temporal variability of suspended matter flows in a Mediterranean coastal river: the Têt (France). CR Acad Sci Paris, Sciences de la Terre et des Planètes 333:389–397
Terfous A, Megnounif A, Bouanani A (2001) Study of solid transport in suspension in the Mouilah wadi (North West Algeria). Revue des Sciences de l’eau 14:173–185
Acknowledgments
The authors especially thank the heads of the National Agency for Blida Hydraulic Resources (ANRH) Messrs Tabet and Imessoudene who have made numerous hydrological and chemical data available to us and who have also well wanted to analyze the samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Current Advances in Geology of North Africa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouras, A.E.F., Nacer, N.M., Buscail, R. et al. Supplies of suspended matter by surface water of the Mazafran drainage basin (western Algiers, Algeria). Arab J Geosci 13, 900 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05862-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05862-1