Abstract
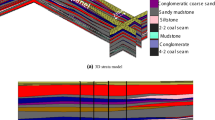
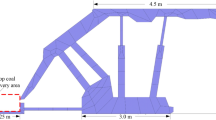
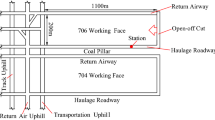
Roof strata movement and shield pressure are two important factors that affect the production and efficiency of longwall top coal caving (LTCC) method in extra-thick coal seams. The performances of these two aspects can be very different from one mine to another depending on the roof strata conditions. In this paper, the geological conditions of the LTCC 8202 panel at Tongxin Coal Mine of Datong Coal Field are investigated. Low working face pressure was observed in the 8202 panel when mining the 20.6-m-thick carboniferous coal seam. This paper examines the causes of low mining–induced pressure at the LTCC 8202 working face, with both numerical simulations and in situ measurements. A finite element-discrete element software called CDEM is used for two-dimensional modelling of the #3–5 coal seam extraction at the LTCC 8202 working face. The numerical model simulates progressive collapse of the roof strata and computes shield pressure and convergence of the shield legs as the coal face advances. It is shown that the numerical model reproduces the periodical weighting phenomenon observed at the working face, which is created by the successive formation of composite cantilever beams in the lower hard rock layers, while voussoir beams form in the upper hard rock layers. As the upper roof voussoir beams interlock, they will tend to support part of the overlying strata, which ultimately lessens the pressure on the shield. A simple analytical model is developed to calculate the shield pressure under the composite cantilever beam structure. Finally, comparison of numerical simulation and analytical model results with measured shield pressure data from the field shows good agreement.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Zhang H, Zhu Z, Yu B, Huo L (2014) Research on the law overburden movement and failure under the influence of double period coal seam mining. Chin J Geo Haz Cont 25(3):67–73
Feng C, Li S, Liu X (2011) Semi-spring contact model and its application to failure simulation of slope. Chin J Theo App Mech 43(1):184–192
Feng J, Zhou Y, Li H, Liu C (2016) Three kinds of basic structure of working face in near horizontal coal seam. J China Coal Soc 41(10):2576–2587
Habib A, Brett A (2010) Poulsen. Stress analysis of longwall top coal caving. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:30–41
Huang Q (2000) Study on roof structure and ground control of longwall mining in shallow coal seam. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou
Huang Z (2013) Study on laws of roof strata fracture of fully mechanized caving mining under goaf in ultra thick seam. Coal Sci Technol 41(7):60–62 66
Ju J, Xu J (2013) Structure characteristics of key strata and strata behavior of fully mechanized longwall face with 7.0 m height chocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 58:46–54
Kong L, Jiang F, Wang C (2010) Study of reasonable working resistance of support in fully-mechanized sublevel caving face in extra-thick coal seam. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 29(11):2312–2318
Lei W, Jun T, HEFNY A (2006) Numerical study on maximum rebound ratio in blasting wave propagation along radian direction normal to joints. J Central So Uni Tech (English Edition) 06:743–748
Li J (1996) Dynamic unloading test of hydraulically operated non-return valve. J China Coal Soc 21(3):325–330
Li S, Zhang Y, Feng C (2010) A spring system equivalent to continuum model[C] //Discrete Element Methods, Simulation of discontinue: theory and applications. Ed. By Antonio Munjiza. Queen Mary, University of London, London, pp 75–85
Li H, Jiang D, Li D (2014) Analysis of ground pressure and movement in fully-mechanized top coal caving with large mining height in ultra-thick seam. J China Coal Soc 39(10):1956–1960
Liu C, Yang J, Yu B, Yang P (2014) Destabilization regularity of hard thick roof group under the multi gob. J China Coal Soc 39(3):395–403
Liu C, Li H, Jiang D (2017a) Numerical simulation study on the relationship between mining heights and shield resistance in longwall panel. Int J Min Sci Technol 27(2):293–297
Liu C, Li H, Mitri H, Jiang D, Li H, Feng J (2017b) Voussoir beam model for lower strong roof strata movement in longwall mining – case study. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 09(6):1171–1176
Peng SS (2013) Coal mine ground control. China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou
Qian M, Shi P, Xu J (2010) Mining pressure and strata control. China Mining University Press, Xuzhou
Vakili A, Hebblewhite BK (2010) A new cavability assessment criterion for longwall top coal caving. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:1317–1329
Wang J, Wang L, Guo Y (2014) Determining the support capacity based on roof and coal wall control. J China Coal Soc 39(8):1619–1624
Yang J, Liu C, Yu B, Lu Y (2014) Strong strata pressure caused by hard roof group structure breaking and supporting strength determination. Univ Sci Technol Beijing 36(5):576–583
Yu B (2014) Study on strong pressure behavior mechanism and roof control of fully mechanized top coal caving in extra thickness seam [Ph.D. dissertation]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining & Technology
Yu B (2016) Behaviors of overlying strata in extra-thick coal seams using top-coal caving method. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 8(2):238–247
Yu B, Liu C, Yang J, Liu J (2013) Research on the fracture instability and its control technique of hard and thick roof. China Univ Min Technol 42(3):342–348
Yu B, Zhao J, Kuang T, Meng X (2015) In situ investigations into overburden failures of a super-thick coal seam for longwall top coal caving. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 78:155–162
Yu B, Zhu W, Gao R, Liu J (2016) Strata structure and its effect mechanism of large space stope for fully-mechanized sublevel caving mining of extremely thick coal seam. J China Coal Soc 41(3):571–580
Zhang Y, Feng C, Li S (2011) Feasibility study of wave method for detecting structure properties of soil-rock mixtures. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 30(9):1855–1863
Zhang J, Miao X, Huang Y, Li M (2014) Fracture mechanics model of fully mechanized top coal caving of shallow coal seams and its application. Int J Min Sci Technol 24(3):349–352
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the contributions of Associate Prof. GP Zhang, Mr. XH Zhang, Mr. QL Zhang, etc., during the set-up of the apparatus and the collection of field data.
Funding
This research is funded by the National key R&D Program of China 2018YFC0604502. The authors are grateful for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Abdullah M. Al-Amri
Highlights
• Analysis of roof structures in longwall top coal caving (LTCC)
• Influence of roof structure on ground pressure
• Calculation method for shield resistance at a specific working face
• Interpretation of observed low ground pressure at Tongxin Coal Mine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Li, H., Mitri, H. et al. Strata movement and shield pressure analysis at Tongxin longwall top coal caving working face with extra-thick coal seam. Arab J Geosci 12, 786 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4787-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4787-0