Abstract
Anthropogenic and natural emissions in the atmosphere directly affect the rainwater chemistry as its chemical speciation is representative of emission status in the surrounding area. A comprehensive assessment was carried out in 2008 for the wet precipitation in the context of chemical composition, in Karachi, a mega-city of Southeast Asia to delineate the urbanization impact on the local environment. Rainwater samples were analyzed for conductivity, pH, HCO3−, Mg2+, Ca2+, NO2−, NO3−, SO42−, Na+, NH4+, K+, F−, Cl−, HCOO−, CH3COO−, C2O42−, pyruvate, malonate, propionate, glyoxylate, and total organic carbon (TOC) levels. The ionic load in rainwater samples was found to be high in the densely populated sampling sites experiencing heavy traffic activity and located adjacent to industrial zones. Acidic content of rainwater had been neutralized by the local alkaline particulates and aerosols introducing alkalinity in rainwater of Karachi City. pH ranged from 3.30 to 7.91 having a mean value of 6.84 ± 0.93. The most dominant ionic species was Na+, followed by SO42−, Ca2+, Cl−, HCO3−, K+, NH4+, Mg2+, NO3−, CH3COO−, and HCOO− in sequence. HCOO− and CH3COO− were the dominant carboxylic acids found in this region, and their mean concentrations were 4.9 ± 7.3 and 9.4 ± 16.0 μeq/L, respectively. These organic acids together contributed 7% to the TOC in precipitation. The formate/acetate ratio was 0.52. Combustion and vehicular exhaust generated acetate may contribute to elevated levels of these organic acids. Statistical tools and source apportionment analysis confirmed the strong impact of anthropogenic pollution on wet precipitation of the mega-city.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khashman OA (2005) Ionic composition of wet precipitation in the Petra Region, Jordan. Atmos Res 78:1–12
Al-Khashman OA (2009) Chemical characteristics of rainwater collected at western site of Jordan. Atmos Res 91:53–61
Avery GB, Tang Y, Kieber RJ, Willey JD (2001) Impact of recent urbanization on formic and acetic acid concentrations in coastal North Carolina rainwater. Atmos Environ 35:3353–3359
Avila A, Alarcón M (1999) Relationship between precipitation chemistry and meteorological situations at a rural site in NE Spain. Atmos Environ 33:1663–1677
Báez A, Belmont R, García R, Padilla H, Torres MC (2007) Chemical composition of rainwater collected at a southwest site of Mexico City, Mexico. Atmos Res 86:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2007.03.005
Balachandran S, Khillare P (2001) Occurrence of acid rain over Delhi. Environ Monit Assess 71:165–176
Balasubramanian R, Victor T, Chun N (2001) Chemical and statistical analysis of precipitation in Singapore. Water Air Soil Pollut 130:451–456
Bayraktar H, Turalioglu FS (2005) Composition of wet and bulk deposition in Erzurum, Turkey. Chemosphere 59:1537–1546
Biswas KF, Ghauri BM, Husain L (2008) Gaseous and aerosol pollutants during fog and clear episodes in South Asian urban atmosphere. Atmos Environ 42:7775–7785
Bosco M, Varrica D, Dongarra G (2005) Case study: inorganic pollutants associated with particulate matter from an area near a petrochemical plant. Environ Res 99:18–30
Cerqueira MRF, Pinto MF, Derossi IN, Esteves WT, Santos MDR, Matos MAC, Matos RC et al (2014) Chemical characteristics of rainwater at a southeastern site of Brazil. Atmos Poll Res 5:253–261
Celle-Jeanton H, Travi Y, Loÿe-Pilot MD, Huneau F, Bertrand G (2009) Rainwater chemistry at a Mediterranean inland station (Avignon, France): local contribution versus long-range supply. Atmos Res 91:118–126
Charlson R, Rodhe H (1982) Factors controlling the acidity of natural rainwater. Nature 295:683–685
Das N, Das R, Chaudhury GR, Das SN (2010) Chemical composition of precipitation at background level. Atmos Res 95:108–113
Demirak ABA, Karaoglu H, Tosmur B (2006) Chemical characteristics of rainwater at urban site of south western Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 123:271–283
Downing C, Vincent K, Campbell G, Fowler D, Smith R (1995) Trends in wet and dry deposition of sulphur in the United Kingdom. Water Air Soil Pollut 85:659–664
Draxler RR, Rolph G (2003) HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) model access via NOAA ARL READY website (http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.html). NOAA Air Resources Laboratory, Silver Spring, MD.
Falkovich A, Graber E, Schkolnik G, Rudich Y, Maenhaut W, Artaxo P (2005) Low molecular weight organic acids in aerosol particles from Rondonia, Brazil, during the biomass-burning, transition and wet periods. Atmos Chem Phys 5:781–797
Bermudez GMA, Pla RJR, Pignata ML (2012) Heavy metals and trace elements in atmopsheric fall-out: their relationship with top soil and wheat element composition. J Hazard Mater 213-214:447–456
Galloway J, Gaudry A (1984) The composition of precipitation on Amsterdam island, Indian Ocean. Atmos Environ 18:2649–2656
Galloway J, Keene W, Artz R, Miller JM, Church T, Knap A (1989) Processes controlling the concentrations of SO4 2−, NO3 −, NH4 +, H+, HCOO− and CH3COO− in precipitation on Bermuda. Tellus B 41:427–443
Galloway JN, Keene WC, Likens GE (1996) Processes controlling the composition of precipitation at a remote southern hemispheric location: Torres del Paine National Park, Chile. J Geophys Res-Atmos 101(D3):6883–6897
Galloway JN, Likens GE (1976) Calibration of collection procedures for the determination of precipitation chemistry. Water Air Soil Pollut 6:241–258
Galloway JN, Likens GE, Keene WC, Miller JM (1982) The composition of precipitation in remote areas of the world. J Geophys Res Oceans 87(C11):8771–8786
Garcia R, Deltorresma C, Padilla H, Belmont R, Azpra E, Arcegacabrera F et al (2006) Measurement of chemical elements in rain from Rancho Viejo, a rural wooded area in the State of Mexico, Mexico. Atmos Environ 40:6088–6100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.048
Gillett R, Ayers G, Noller B (1990) Rainwater acidity at Jabiru, Australia, in the wet season of 1983/84. Sci Total Environ 92:129–144
Grosjean D (1989) Organic acids in southern California air: ambient concentrations, mobile source emissions, in situ formation and removal processes. Environ Sci Technol 23:1506–1514
Halstead MJ, Cunninghame RG, Hunter KA (2000) Wet deposition of trace metals to a remote site in Fiordland, New Zealand. Atmos Environ 34:665–676
Hasan A, Raza M (2015) Karachi: the transport crisis. Urban Resource Center, Karachi
Herrera J, Rodríguez S, Baéz AP (2009) Chemical composition of bulk precipitation in the metropolitan area of Costa Rica, Central America. Atmos Res 94:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2009.05.004
Hontoria C, Saa A, Almorox J, Cuadra L, Sánchez A, Gascó JM (2003) The chemical composition of precipitation in Madrid. Water Air Soil Pollut 146:35–54. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023964610330.
Hu G, Balasubramanian R, Wu C (2003) Chemical characterization of rainwater at Singapore. Chemosphere 51:747–755
Huang K, Zhuang G, Xu C, Wang Y, Tang A (2008) The chemistry of the severe acidic precipitation in Shanghai, China. Atmos Res 89:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2008.01.006
Huang XF, Li X, He LY, Feng N, Hu M, Niu YW, Zeng LW (2010) 5-Year study of rainwater chemistry in a coastal mega-city in South China. Atmos Res 97:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.03.027
Ito M, Mitchell MJ, Driscoll CT (2002) Spatial patterns of precipitation quantity and chemistry and air temperature in the Adirondack region of New York. Atmos Environ 36:1051–1062
Kawamura K, Ng LL, Kaplan IR (1985) Determination of organic acids (C1-C10) in the atmosphere, motor exhausts, and engine oils. Environ Sci Technol 19:1082–1086
Keene WC, Galloway JN (1984) Organic acidity in precipitation of North America. Atmospheric Environment (1967) 18:2491–2497
Keene WC, Galloway JN (1986) Considerations regarding sources for formic and acetic acids in the troposphere. J Geophys Res-Atmos 91(D13):14466–14474
Khwaja HA, Brudnoy S, Husain L (1995) Chemical characterization of three summer cloud episodes at Whiteface Mountain. Chemosphere 31:3357–3381
Khwaja HA, Fatmi Z, Malashock D, Aminov Z, Kazi A, Siddique A, Qureshi J, Carpenter DO (2013) Effect of air pollution on daily morbidity in Karachi, Pakistan. J Local Global Health Sci 3:1–13
Khwaja HA, Husain L (1990) Chemical characterization of acid precipitation in Albany, New York. Atmos Environ 24:1869–1882
Kulshrestha U, Kulshrestha MJ, Sekar R, Sastry G, Vairamani M (2003) Chemical characteristics of rainwater at an urban site of south-central India. Atmos Environ 37:3019–3026
Kumar N, Kulshreshta U, Saxena A, Kumari K, Srivastava S (1993) Effect of anthropogenic activity on formate and acetate levels in precipitation at four sites in Agra, India. Atmos Environ Part B Urban Atmos 27:87–91
Kus B, Kandasamy J, Vigneswaran S, Shon H (2011) Water quality in rainwater tanks in rural and metropolitan areas of New South Wales, Australia. J Water Sustain 1:33–43
Lee BK, Hong SH, Lee DS (2000) Chemical composition of precipitation and wet deposition of major ions on the Korean peninsula. Atmos Environ 34:563–575
Menz FC, Seip HM (2004) Acid rain in Europe and the United States: an update. Environ Sci Pol 7:253–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2004.05.005
Migliavacca D, Teixeira E, Wiegand F, Machado A, Sanchez J (2005) Atmospheric precipitation and chemical composition of an urban site, Guaiba hydrographic basin, Brazil. Atmos Environ 39:1829–1844
Morales JA, de Graterol LS, Velasquez H, de Nava MG, de Borrego BS (1998) Determination by ion chromatography of selected organic and inorganic acids in rainwater at Maracaibo, Venezuela. J Chromatogr A 804:289–294
Munger JW, Eisenreich SJ (1983) Continental-scale variations in precipitation chemistry: ion concentrations are dominated by land use and proximity to man-made emissions. Environ Sci Technol 17:32–42
Nilles MA, Conley BE (2001) Changes in the chemistry of precipitation in the United States, 1981–1998. Water Air Soil Pollut 130:409–414
Okuda T, Iwase T, Ueda H, Suda Y, Tanaka S, Dokiya Y, Fushimi K, Hosoe M (2005) Long-term trend of chemical constituents in precipitation in Tokyo metropolitan area, Japan, from 1990 to 2002. Sci Total Environ 339:127–141
Parekh PP, Khwaja HA, Khan AR, Naqvi RR, Malik A, Shah SA, Khan K, Hussain G (2001) Ambient air quality of two metropolitan cities of Pakistan and its health implications. Atmos Environ 35:5971–5978
Park SM, Seo BK, Lee G, Kahng SH, Jang YW (2015) Chemical composition of water soluble inorganic species in precipitation at Shihwa Basin, Korea. Atmosphere 6:732–750
Possanzini M, Buttini P, Di Palo V (1988) Characterization of a rural area in terms of dry and wet deposition. Sci Total Environ 74:111–120
Pszenny AA, MacIntyre F, Duce RA (1982) Sea-salt and the acidity of marine rain on the windward Coast of Samoa. Geophys Res Lett 9:751–754
Rastogi N, Sarin M (2005) Chemical characteristics of individual rain events from a semi-arid region in India: three-year study. Atmos Environ 39:3313–3323
Rasul G, Sixiong Z, Qingcun Z, Linlin QI, Gaoying Z (2005) A diagnostic study of heavy rainfall in Karachi due to merging of a mesoscale low and a diffused tropical depression during South Asian summer monsoon. Adv Atmos Sci 22:375–391
Safai P, Rao P, Momin G, Ali K, Chate D, Praveen P (2004) Chemical composition of precipitation during 1984–2002 at Pune, India. Atmos Environ 38:1705–1714
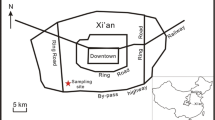
Saied S, Masood SS, Siddique A, Khwaja HA, Khan MK, Hussain MM (2015) Effect of cyclone on the composition of rainfall at Karachi City. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 11:81–89
Sakugawa H, Kaplan IR, Shepard LS (1993) Measurements of H2O2, aldehydes and organic acids in Los Angeles rainwater: their sources and deposition rates. Atmospheric Environment Part B Urban Atmosphere 27:203–219
Senthilnathan T (2008) Measurements of urban ambient air quality of Chennai City. Indian J Air Poll Control VIII(I March):35–47
Seto S, Oohara M, Ikeda Y (2000) Analysis of precipitation chemistry at a rural site in Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. Atmos Environ 34:621–628
Singh S, Khare P, Satsangi G, Lakhani A, Kumari KM, Srivastava S (2001) Rainwater composition at a regional representative site of a semi-arid region of India. Water Air Soil Pollut 127:93–108
Smirnioudi V, Siskos P (1992) Chemical composition of wet and dust deposition in Athens, Greece. Atmos Environ Part B Urban Atmos 26:483–490
Song F, Gao Y (2009) Chemical characteristics of precipitation at metropolitan Newark in the US East Coast. Atmos Environ 43:4903–4913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.07.024
Sorooshian A, Shingler T, Harpold A, Feagles C, Meixner T, Brooks P (2013) Aerosol and precipitation chemistry in the southwestern United States: spatiotemporal trends and interrelationships. Atmos Chem Phys 13:7361–7379
Staelens J, De Schrijver A, Van Avermaet P, Genouw G, Verhoest N (2005) A comparison of bulk and wet-only deposition at two adjacent sites in Melle (Belgium). Atmos Environ 39:7–15
Talbot R, Beecher K, Harriss R, Cofer W (1988) Atmospheric geochemistry of formic and acetic acids at a mid-latitude temperate site. J Geophys Res-Atmos 93:1638–1652
Tang J, Xue H, Yu X, Cheng H, Xu X, Zhang X et al (2000) The preliminary study on chemical characteristics of precipitation at Mt. Waliguan. Acta Sci Circumst 20:420–425
Tanner P, Law P (2003) Organic acids in the atmosphere and bulk deposition of Hong Kong. Water Air Soil Pollut 142:279–297
Taylor S (1964) Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: a new table. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 28:1273–1285
Topçu S, Incecik S, Atimtay AT (2002) Chemical composition of rainwater at EMEP station in Ankara, Turkey. Atmos Res 65:77–92
Tsakovski SL, Simeonov VD (1998) Chemometric study of atmospheric wet and dry precipitates from an urban region. Toxicol Environ Chem 65:203–216
Wai K, Wang S, Tanner P, Lin N (2007) A dual site study of the rainwater chemistry within the Western Pacific region. J Atmos Chem 57:85–103
Yamasoe MA, Artaxo P, Miguel AH, Allen AG (2000) Chemical composition of aerosol particles from direct emissions of vegetation fires in the Amazon Basin: water-soluble species and trace elements. Atmos Environ 34:1641–1653
Zhang M, Wang S, Wu F, Yuan X, Zhang Y (2007) Chemical compositions of wet precipitation and anthropogenic influences at a developing urban site in southeastern China. Atmos Res 84:311–322
Zhang Y, Lee X, Cao F (2011) Chemical characteristics and sources of organic acids in precipitation at a semi-urban site in Southwest China. Atmos Environ 45:413–419
Funding
The authors are deeply thankful to the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan (HEC) for giving the opportunity and financial support to perform the current research under the umbrella of Indigenous Scholarship Program for Ph.D. Scholars conducting in different Universities. The support provided by the Wadsworth Center is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masood, S.S., Saied, S., Siddique, A. et al. Influence of urban–coastal activities on organic acids and major ion chemistry of wet precipitation at a metropolis in Pakistan. Arab J Geosci 11, 802 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4118-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4118-x