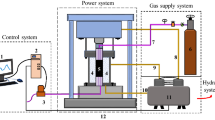
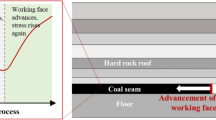
Abstract
It is of great significance for the analysis and prediction of coal-gas outburst disasters to understand the mechanical properties and permeability evolution of coal and rock under conditions of stope stress evolution. In this study, mechanical tests were conducted on gas-bearing coal under four stress paths, including conventional triaxial compression (CTC), phased variable speed triaxial compression (PVSTC), unloading confining pressure (UCP), and phased variable speed unloading confining pressure (PVSUCP), simultaneously measuring the permeability in mechanical tests. The mechanical properties and permeability evolutions in gas-bearing coal under four different stress paths were compared. The obtained results show that the deviatoric stress-strain curves of gas-bearing coal under four stress paths could be divided into five stages: compaction, linear elasticity, plastic deformation, stress drop, and residual stress stage. The permeability-strain curves under four stress paths could also be divided into five stages: fast drop, slow decrease, slow increase, sharp increase, and slowed growth. Compared to the CTC conditions, the peak strain and strength of coal under PVSTC conditions increased. Furthermore, the stress drop and energy release under PVSTC were more intense at the moment of instability failure. Compared to both loading paths, the coal was damaged more rapidly under unloading paths and the damage was stronger. Additionally, among both unloading paths, the time required for the failure of coal under PVSUCP was shorter than that under UCP, while the damage under PVSUCP was stronger. The strength characteristics of the gas-bearing coal under PVSTC and PVSUCP still met the Mohr–Coulomb criterion. This preliminary study has guiding significance for the understanding of the co-occurrence mechanisms of coal-gas outburst disasters.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTC:
-
Conventional triaxial compression
- PVSTC:
-
Phased variable speed triaxial compression
- UCP:
-
Unloading confining pressure
- PVSUCP:
-
Phased variable speed unloading confining pressure
References
Al-Ajmi AM, Zimmerman RW (2005) Relation between the Mogi and the Coulomb failure criteria. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 42:431–439
An FH, Cheng YP, Wang L, Li W (2013) A numerical model for outburst including the effect of adsorbed gas on coal deformation and mechanical properties. Comput Geotech 54:222–231
Aziz NI, Ming-Li W (1999) The effect of sorbed gas on the strength of coal-an experimental study. Geotech Geol Eng 17:387–402
Beamish BB, Crosdale PJ (1998) Instantaneous outbursts in underground coal mines: an overview and association with coal type. Int J Coal Geol 35:27–55
Chen HD, Cheng YP, Zhou HX, Li W (2013) Damage and permeability development in coal during unloading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46:1377–1390
Chen H, Cheng Y, Ren T, Zhou H, Liu Q (2014) Permeability distribution characteristics of protected coal seams during unloading of the coal body. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 71:105–116
Clarkson CR, Bustin RM (1999) The effect of pore structure and gas pressure upon the transport properties of coal: a laboratory and modeling study. 1. Isotherms and pore volume distributions. Fuel 78:1333–1344
Du F, Wang K, Wang G, Jiang YF, Xin CP, Zhang X (2018) Investigation on acoustic emission characteristics during deformation and failure of gas-bearing coal-rock combined bodies. J Loss Prevent Proc 55:253–266
Fairhurst CE, Hudson JA (1999) Draft ISRM suggested method for the complete stress-strain curve for intact rock in uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36:281–289
Gentzis T, Deisman N, Chalaturnyk RJ (2007) Geomechanical properties and permeability of coal from the foothills and mountain regions of western Canada. Int J Coal Geol 69:153–164
George JDS, Barakat MA (2001) The change in effective stress associated with shrinkage from gas desorption in coal. Int J Coal Geol 45:105–113
Goodman AL, Favors RN, Larsen JW (2006) Argonne coal structure rearrangement caused by sorption of CO2. Energy Fuel 20:2537–2543
Harpalani S, Chen G (1995) Estimation of changes in fracture porosity of coal with gas emission. Fuel 74:1491–1498
Hoek E, Brown ET (1982) Empirical strength criterion for rock masses. J Geotech Eng-Div 106:1013–1035
Hoek E, Wood D, Shah S (1992) Modified Hoek-Brown failure criterion for jointed rock masses. Proceedings of the international ISRM symposium on rock characterization. Chester, UK
Jaeger JC, Cook NGW (1979) Fundamentals of rock mechanics, third ed. John Wiley & Sons
Kasani HA, Chalaturnyk RJ (2017) Influence of high pressure and temperature on the mechanical behavior and permeability of a fractured coal. Energies 10(7):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10070854
Kumar H, Elsworth D, Liu J, Pone D, Mathews JP (2012) Optimizing enhanced coalbed methane recovery for unhindered production and CO2, injectivity. Int J Greenh Gas Con 11(6):86–97
Kumar H, Elsworth D, Liu J, Pone D, Mathews JP (2015) Permeability evolution of propped artificial fractures in coal on injection of CO2. J Pet Sci Eng 133:695–704
Kumar H, Elsworth D, Mathews JP, Marone C (2016) Permeability evolution in sorbing media: analogies between organic-rich shale and coal. Geofluids 16:43–55
Labuz JF, Zang A (2012) Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45:975–979
Lajtai EZ, Duncan EJS, Carter BJ (1991) The effect of strain rate on rock strength. Rock Mech Rock Eng 24:99–109
Li Z, Wang E, Ou J, Liu Z (2015) Hazard evaluation of coal and gas outbursts in a coal-mine roadway based on logistic regression model. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 80:185–195
Liu KD (2017) Mechanical properties of ram coal containing gas under high triaxial stress compression. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 36:380–393
Lu CP, Dou LM, Liu H, Liu HS, Liu B, Du BB (2012) Case study on microseismic effect of coal and gas outburst process. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 53:101–110
Masoudian MS, Airey DW, El-Zein A (2014) Experimental investigations on the effect of CO2 on mechanics of coal. Int J Coal Geol 12-23:s128–s129
Palmer I, Mansoori J (1996) How permeability depends on stress and pore pressure in coalbeds: a new model. SPE Reser Eval En 1:539–544
Siriwardane H, Haljasmaa I, Mclendon R, Irdi G, Soong Y, Bromhal G (2009) Influence of carbon dioxide on coal permeability determined by pressure transient methods. Int J Coal Geol 77:109–118
Somerton WH, Söylemezoḡlu IM, Dudle RC (1975) Effect of stress on permeability of coal. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 12:129–145
Viete DR, Ranjith PG (2007) The mechanical behaviour of coal with respect to CO 2 sequestration in deep coal seams. Fuel 86:2667–2671
Wang S, Elsworth D, Liu J (2011) Permeability evolution in fractured coal: the roles of fracture geometry and water-content. Int J Coal Geol 87:13–25
Wang K, Du F, Wang G (2017a) Investigation of gas pressure and temperature effects on the permeability and steady-state time of chinese anthracite coal: an experimental study. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 40:179–188
Wang K, Du F, Wang G (2017b) The influence of methane and CO2 adsorption on the functional groups of coal: insights from a Fourier transform infrared investigation. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 45:358–367
Wang K, Du F, Zhang X, Wang L, Xin C (2017c) Mechanical properties and permeability evolution in gas-bearing coal–rock combination body under triaxial conditions. Environ Earth Sci 76:815 1–19
Wold MB, Connell LD, Choi SK (2008) The role of spatial variability in coal seam parameters on gas outburst behaviour during coal mining. Int J Coal Geol 75:1–14
Xie G, Yin Z, Wang L, Hu Z, Zhu C (2017) Effects of gas pressure on the failure characteristics of coal. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50:1–13
Xue D, Zhou H, Wang Z, Ren W (2010) Failure mechanism and mining-induced mechanical properties of coal under different loading rates. J China Coal Soc 41:595–602
Xue Y, Ranjith PG, Gao F, Zhang D, Cheng H, Chong Z, Hou P, Xue Y, Ranjith PG, Gao F (2017) Mechanical behaviour and permeability evolution of gas-containing coal from unloading confining pressure tests. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 40:336–346
Yuan L (2016) Control of coal and gas outbursts in Huainan mines in China: a review. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 8:559–567
Yin G, Jiang C, Wang JG, Xu J (2015) Geomechanical and flow properties of coal from loading axial stress and unloading confining pressure tests. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 76:155–161
Zhang Q, Fan X, Liang Y, Li M, Li G, Ma T, Nie W (2017) Mechanical behavior and permeability evolution of reconstituted coal samples under various unloading confining pressures-implications for wellbore stability analysis. Energies 10(3):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10030292
Zhou X, Qian Q, Yang H (2010) Effect of loading rate on fracture characteristics of rock. J Cent South Univ Techno 17:150–155
Acknowledgments
This research is financially supported by the State Key Research Development Program of China (2016YFC0801402, 2016YFC0600708), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51474219, 51604153, 51874314), the Open Funds of Hebei State Key Laboratory of Mine Disaster Prevention (KJZH2017K02), the Joint Fund Project of Guizhou Science and Technology Department and Bijie Science and Technology Bureau and Institute of Circular Economy (LH[2017]7520), the Guizhou Science and Technology Support Program ([2017]2820), and the Yue Qi Distinguished Scholar Project, China University of Mining & Technology, Beijing. Feng Du would like to acknowledge the Fund of China Scholarship Council (CSC) for his study in Department of Civil Engineering and Engineering Mechanics, Columbia University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, C., Wang, K., Du, F. et al. Mechanical properties and permeability evolution of gas-bearing coal under phased variable speed loading and unloading. Arab J Geosci 11, 747 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4117-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4117-y