Abstract
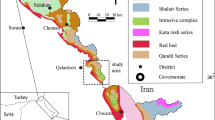
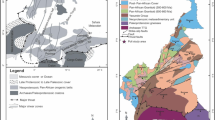
The Chodarchay area is located 50 km east of the city of Zanjan, within the Tarom-Hashtjin subzone, in the Western Alborz structural zone of NW Iran. Igneous rocks in the area include intrusive granitic (phases I and II), and volcanic rocks. Geochemical characteristics of the granitic rocks were determined using their trace and rare earth element (REE) compositions. The phase I intrusive rocks at Chodarchay include quartz monzonite and quartz syenite, while the phase II mainly consists of granite and alkali granite. These intrusive rocks have SiO2 contents ranging between 60.11 and 69.14 wt%, high K2O + Na2O (8.20 to 10.21 wt%) and K2O/Na2O ratios of 1.24 to 2.56. Petrological and geochemical studies indicate that the granitoids have high-K to shoshonitic affinity, they are metaluminous to mildly peraluminous and characterize as I-type granitoids. The investigated granitoids (phases I and II) have fractionated REE patterns characterized by enrichment in light REEs and varying degrees of depletion in heavy REEs. Large-ion lithophile element (LILE) enrichment, high-field strength element (HFSE) depletion, and distinct positive Pb anomaly in the primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns of the rocks imply subduction-related arc magmatic signatures. It is suggested that the granites formed in a volcanic arc to post-collision setting from a garnet spinel lherzolite source.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aftabi A, Atapour H (2000) Regional aspects of shoshonitic volcanism in Iran. Episodes 23:119–125
Aghazadeh M, Castro A, Badrzadeh Z, Vogt K (2011) Post-collisional polycyclic plutonism from the Zagros hinterland: the Shaivar Dagh plutonic complex, Alborz belt, Iran. Geol Mag 148:980–1008
Ahmadian J, Haschke M, McDonald I, Regelous M, Ghorbani MR, Emami MH, Murata M (2009) High magmatic flux during Alpine–Himalayan collision: constraints from the Kal-e-Kafi complex, Central Iran. Geol Soc Am Bull 121:857–868
Aldanmaz E, Pearce JA, Thirlwall MF, Mitchell JG (2000) Petrogenetic evolution of late Cenozoic, post-collision volcanism in western Anatolia, Turkey. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 102:67–95
Allen MB, Ghassemi MR, Shahrabi M, Qorashi M (2003) Accommodation of late Cenozoic shortening in the Alborz range, northern Iran. J Struct Geol 25:659–672
Asiabanha A, Foden J (2012) Post-collisional transition from an extensional volcanosedimentary basin to a continental arc in the Alborz ranges, N-Iran. Lithos 148:98–111
Beccaluva L, Bianchini G, Bonadiman C, Siena F, Vaccaro C (2004) Coexisting anorogenic and subduction-related metasomatism in the mantle xenoliths from the Betic Cordillera (southern Spain). Lithos 75:67–87
Berberian M (1983) The southern Caspian: a compressional depression floored by a trapped, modified oceanic crust. Can J Earth Sci 20:16–83
Berberian F, Berberian M (1981) Zagros-Hindu Kush-Himalaya Geodynamic Evolution. In: Gupta HK, Delany FM (eds) Tectono-plutonic episodes in Iran. AGU, Washington D.C., pp 5–32
Cameron BI, Walker JA, Carr MJ, Patino LC, Matias O, Feigenson MD (2003) Flux versus decompression melting at stratovolcanoes in southeastern Guatemala. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 119:21–50
Castro A, Aghazadeh M, Badrzadeh Z, Chichorro M (2013) Late Eocene–Oligocene post-collisional monzonitic intrusions from the Alborz magmatic belt, NW Iran: an example of monzonite magma generation from a metasomatized mantle source. Lithos 180-181:109–127
Chappell BW, White AJR (2001) Two contrasting granite types: 25 years later. Austral J Earth Sci 48:489–499
Cox KG, Bell JD, Pankhurst RJ (1979) The interpretation of igneous rocks. George Allen & Unwin, London
Elburg MA, Bergen MV, Hoogewerff J, Foden J, Vroon P, Zulkarnain I, Nasution A (2002) Geochemical trends across an arc-continent collision zone: magma sources and slab-wedge transfer processes below the Pantar Strait volcanoes, Indonesia. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:2771–2789
Emmermann R, Daieva L, Schneider J (1975) Petrologic significance of rare earths distribution in granites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 52:267–283
Floyd PA, Winchester JA (1975) Magma type and tectonic setting discrimination using immobile elements. Earth Planet Sci Lett 27:211–218
Foley SF, Wheller GE (1990) Parallels in the origin of the geochemical signatures of island arc volcanics and continental potassic igneous rocks: the role of residual titanites. Chem Geol 85:1–18
Förster HJ, Tischendorf G, Trumbull RB (1997) An evaluation of the Rb vs. (Y+Nb) discrimination diagram to infer tectonic setting of silicic igneous rocks. Lithos 40:261–293
Gill JB (1981) Orogenic andesites and plate tectonics. Springer-Verlag, Berlin 390 p
Guest B, Guest A, Axen G (2007) Late tertiary tectonic evolution of northern Iran: a case for simple crustal folding. J Global Planet Change 58:435–453
Ghorbani M (2013) The economic geology of Iran mineral deposits and natural resources. Springer:569 p
Hassanzadeh J, Ghazi AM, Axen G, Guest B (2002) Oligo–Miocene mafic alkaline magmatism north and northwest of Iran: evidence for the separation of the Alborz from the Urumieh–Dokhtar magmatic arc. Geol Soc Am Abst with Progr 34:331
Hastie AR, Kerr AC, Pearce JA, Mitchell SF (2007) Classification of altered volcanic island arc rocks using immobile trace elements: development of the Co–Th discrimination diagram. J Petrol 48:2341–2357
Hildreth W, Moorbath S (1988) Crustal contribution to arc magmatism in the Andes of southern Chile. Contrib Mineral Petr 98:455–489
Hirayama K, Samimi M, Zahedi M, Hushmand-zadeh A (1966) Geology of Taroum district, western part (Zanjan area north-west Iran). Geological Survey of Iran
Hofmann AW (1997) Mantle geochemistry: the message from oceanic volcanism. Nature 385:219–229
Hou T, Zhang ZC, Encarnacion J, Santosh M (2012) Petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Taihe gabbroic intrusion associated with Fe–Ti-oxide ores in the Panxi district, Emeishan large igneous province, Southwest China. Ore Geol Rev 49:109–127
Kepezhinskas PK, Defant MJ, Drummond MS (1996) Progressive enrichment of island arc mantle by melt-peridotite interaction inferred from Kamchatka xenoliths. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:1217–1229
Kleemann GJ, Twist D (1989) The compositionally-zoned sheet-like granite pluton of the Bushveld complex: evidence bearing on the nature of A-type magmatism. J Petrol 30:1383–1414
Li XH, Zhou HW, Liu Y, Le CY, Sun M, Chen ZH (2000) Shoshonitic intrusive suite in SE Guangxi: petrology and geochemistry. Chin Sci Bull 45:653–659
Lu YJ, Kerrich R, McCuaig TC, Li ZX, Hart CJR, Cawood PA, Hou Z-Q, Bagas L, Cliff J, Belousova EA, Tang SH (2013) Geochemical, Sr–Nd–Pb, and zircon Hf–O isotopic compositions of Eocene–Oligocene shoshonitic and potassic adakite-like felsic intrusions in western Yunnan, SW China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. J Petrol 54:309–1348
Maheshwaril A, Garhia SS, Sial AN, Ferreira VP, Dwivedil V, Chittora VK (2002) Geology and geochemistry of granites around Jaswantpura, Jalore district, southwestern Rajasthan, India. Gondwana Res 5:373–379
Maniar PD, Piccoli PM (1989) Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geol Soc Am Bull 101:635–643
McDonough WF, Sun SS (1995) The composition of the Earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253
Mirnejad H, Hassanzadeh J, Cousens BL, Taylor BE (2010) Geochemical evidence for deep mantle melting and lithospheric delamination as the origin of the inland Damavand volcanic rocks of northern Iran. J Volcanol Geoth Res 198:288–296
Moayyed M (2001) Geochemistry and petrology of volcano-plutonic bodies in Tarom area (Ph.D. thesis) University of Tabriz, Iran, in Persian with English abstract, 256 p
Morrison GW (1980) Characteristics and tectonic setting of the shoshonite rock association. Lithos 13:97–108
Muller D, Rock NMS, Groves DI (1992) Geochemical discrimination between shoshonitic and potassic volcanic rocks in different tectonic settings, a pilot study. Mineral Petrol 46:259–289
Müller D, Groves DI (1993) Direct and indirect associations between potassic igneous rocks, shoshonites and gold-copper deposits. Ore Geol Rev 8:386–406
Müller D, Groves DI (2000) Potassic igneous rocks and associated gold–copper mineralization, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (252 p)
Nabatian G, Ghaderi M, Daliran F, Rashidnejad-Omran N (2013) Sorkhe-Dizaj iron oxide-apatite ore deposit in the Cenozoic Alborz-Azarbaijan magmatic belt, NW Iran. Resour Geol 63:42–56
Nabatian G, Ghaderi M, Neubauer F, Honarmand M, Liu X, Dong Y, Jiang SY, Quadt AV, Bernroider M (2014) Petrogenesis of Tarom high-potassic granitoids in the Alborz-Azarbaijan belt, Iran: geochemical, U-Pb zircon and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic constraints. Lithos 184–187:324–345
Nabatian G, Jiang S-Y, Honarmand M, Neubauer F (2016) Zircon U–Pb ages, geochemical and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of the Tarom-Olya pluton, Alborz magmatic belt, NW Iran. Lithos 244:43–58
Nabavi MH (1976) An introduction to geology of Iran. Geological Survey of Iran, in Persian, 110 p
Nakamura N (1974) Determination of REE, Ba, Mg, Na and K in carbonaceous and ordinary chondrithes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38:757–775
Nazari H, Salamati R (1998) Roudbar 1:100,000 Geological map
Norman MD, Leeman WP, Mertzman SA (1992) Granites and rhyolites from the northern USA: temporal variation in magmatic processes and relations to tectonic setting. In: Brown PE and Chappell BW (eds.), Proc. I11 Hutton Symposium on the origin of granites and related rocks. Geol. SOC. Amer., Spec. Paper, 272:71–78
Obiora SC, Ukaegbu VU (2010) Preliminary investigation of the petrogenesis and geotectonic setting of the Precambrian basement complex rocks around northcentral Nigeria using trace and rare-earth elements geochemistry. J Mining Geol 46:127–137
Pang KN, Chung SL, Zarrinkoub MH, Lin YC, Lee HY, Ching-Hua Lo CH, Khatib MM (2013) Iranian ultrapotassic volcanism at ~11 Ma signifies the initiation of post-collisional magmatism in the Arabia–Eurasia collision zone. Terra Nova 25:405–413
Pearce JA (1982) Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries. In: Thorpe RS (ed.), Wiley, New York, 525–548
Pearce JA (1983) Role of the sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at active continental margins. In: Hawkesworth CJ, Norry NJ (eds) Continental basalts and mantle xenoliths. Shiva, Cheshire, UK, pp 230–249
Pearce JA (1996) A user’s guide to basaltic discrimination diagrams. In: Wyman DA (ed) Trace element geochemistry of volcanic rocks: applications for massive sulphide exploration, vol 12. Geological Association of Canada Short Course Notes, p 79–113
Peccerillo A, Taylor SR (1976) Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from Kastamonu area, northern Turkey. Contrib Mineral Petr 58:63–81
Peccerillo A (1992) Potassic and ultrapotassic magmatism: compositional characteristics, genesis and geologic significance. Episodes 15:243–251
Peyrovan H (1992) Petrographic, petrologic and geochemical studies of intrusive rocks north of Abhar and the association of plutonism in the area with mineralization. Tarbiat Moalem University, MSc thesis
Richards JP, Spell T, Rameh E, Razique A, Flectcher T (2012) High Sr/Y magmas reflect arc maturity, high magmatic water content, and porphyry Cu ± Mo ± Au potential: examples from the Tethyan arcs of central and eastern Iran and western Pakistan. Econ Geol 107:295–332
Rolland Y, Billo S, Corsini M, Sosson M, Galoyan G (2009) Blueschists of the Amassia-Stepanavan Suture Zone (Armenia): linking Tethys subduction history from E-Turkey to W-Iran. Int J Earth Sci 98:533–550
Stöcklin J (1974) Possible ancient continental margins in Iran. In: Burk CA, Drake CL (eds) The geology of continental margins. Springer, Berlin, pp 873–887
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD, Norry MJ (eds.), Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 42:313–435
Torabi G (2011) Middle Eocene volcanic shoshonites from western margin of Central-East Iranian Microcontinent CEIM, a mark of previously subducted CEIM-confining oceanic crust. Petrology 19(7):675–689
Torkamani E (1997) Petrologic study of intrusive rocks north of Abhar-Khoramdarreh. Shahid Beheshti University, MSc thesis
Turner S, Hawkesworth C, Liu J, Rogers N, Kelley S, Van Calsteren P (1993) Timing of Tibetan uplift constrained by analysis of volcanic rocks. Nature 364:50–54
Turner S, Arnaud N, Liu J, Rogers N, Hawkesworth C, Harris N, Kelley S, Van Calsteren P, Deng W (1996) Post-collision shoshonitic volcanism on the Tibetan plateau: implications for convective thinning of the lithosphere and the source of ocean island basalts. J Petrol 37:45–71
Wang Q, Xu JF, Jian P, Bao ZW, Zhao ZH, Li CF, Xiong XL, Ma JL (2006) Petrogenesis of cretaceous adakitic and shoshonitic igneous rocks in the Luzong area, Anhui Province (eastern China): implications for geodynamics and Cu–Au mineralization. Lithos 89:424–446
Wang K, Plank T, Walker JD, Smith EI (2002) A mantle melting profile across the basin and range, SWUSA. J Geophys Res 107:ECV 5-1–ECV 5-21. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000209
Whale JB, Currie KL, Chappell W (1987) A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contrib Mineral Petr 95:407–419
Whitney DL, Evans BW (2010) Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. Am Mineral 95:185–187
Yang JH, Sun JF, Chen FK, Wilde SA, Wu FY (2007) Sources and petrogenesis of late Triassic dolerite dikes in the Liaodong peninsula: implications for post-collisional lithosphere thinning of the eastern North China Craton. J Petrol 48:1973–1997
Yasami N, Ghaderi M, Madanipour S, Taghilou B (2017) Structural control on overprinting high-sulfidation epithermal on porphyry mineralization in the Chodarchay deposit, northwestern Iran. Ore Geol Rev 86:212–224
Zindler A, Hart SR (1986) Chemical geodynamics. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 14:493–571
Zonenshain LP, Lepichon X (1986) Deep basins of Black Sea and Caspian Sea as remnants of Mesozoic back-arc basin. Tectonophysics 123:181–211
Zhou MF, Robinson PT, Yan Wang C, Zhao JH, Yan DP, Gao JF, Malpas J (2012) Heterogeneous mantle source and magma differentiation of quaternary arc-like volcanic rocks from Tengchong, SE margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Contrib Mineral Petrol 163:841–860
Acknowledgements
This paper is a part of the first author’s Ph.D. thesis at Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran. Appreciation is extended to Madankaran Angouran Company for providing field survey facilities. We would like to thank Nematollah Rashidnejad-Omran and an anonymous reviewer for their constructive review on the manuscript. Abdullah Al-Amri and Yalcin Ersoy are also thanked for careful editorial handling of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasami, N., Ghaderi, M., Mokhtari, M.A.A. et al. Petrogenesis of the two phases of intrusive rocks at Chodarchay, NW Iran: using trace and rare earth elements. Arab J Geosci 11, 605 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3942-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3942-3