Abstract
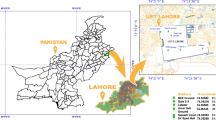
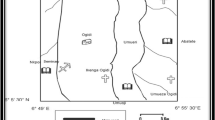
The current study is carried out for the determination of groundwater potential in District Rawalakot Azad Jammu and Kashmir (AJ&K) Pakistan by using electrical resistivity method and petrographic analysis of the area. The tape-compass-clinometers method was used in section measurement to understand the facies and depositional environment. The electrical resistivity survey was carried out in the project area in sub-Himalayan Siwaliks system of Pakistan to overcome water scarcity in a few regions. The area was chartered with the Schlumberger configuration up to the AB/2 depth of 150 m. The ABEM Terrameter SAS 4000 (Sweden) and accessories were used to acquire vertical electrical soundings in 24 locations. The results obtained through the 2D and 3D isoresistivity maps of apparent resistivity for 15, 45, and 130 m spacings, the 3D isoresistivity maps of transverse resistance and anisotropy, the VES curve types, and the measured stratigraphic section of surface rocks revealed the confined or semi-confined type aquifers within sedimentary formations. The petrographic analysis indicates the clues of the secondary porosity and fluid migrations through the rocks.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alile OM, Ujuanbi O, Evbuomwan IA (2011) Geoelectric investigation of groundwater in Obaretin -Iyanomon locality, Edo state, Nigeria. J Geol Mining Res 3(1):13–20
Balaji S, Rahmam K, Jeganathan R, Neelakantan R (2010) Demarcation of fresh/saline water Interface in Kavaratti Island of union territory of Lakshadweep island of India using electrical and electromagnatic methods. Int J Earth Sci Eng 3:62–72
Barseem M, El Tamamy A, Masoud M (2013) Hydrogeophyical evaluation of water occurrences in El Negila area, Northwestern coastal zone–Egypt. J Appl Sci Res 9:3244–3262
Bayewu OO, Oloruntola MO, Mosuro G (2014) Evaluation of resistivity anisotropy of P”WEtrfdgvb’abrts of Ijebu Igbo, southwestern, Nigeria using azimuthal resistivity survey (ARS) method. J Geogr Geol 6(4):140–152
Blair TC, McPherson M (1994) Alluvial fans and their natural distinction from rivers based on morphology, hydraulic processes, sedimentary processes and facie assemblage. J. Sediment Res A 64:450–489
Bloch S (1994) Secondary porosity in sandstones, significance, origin, relationship to subaerial unconformities, and effect on pre-drill reservoir quality prediction. SEPM short course 30:137–162
Choudhury K, Saha DK, Chakraborty P (2001) Geophysical study for saline water intrusion in a coastal alluvial terrain. J Appl Geophys 46:189–200
Compton R (1985) Geology in the field. John Wiley and Son, New York, p 398
DeLima OAL, Clennell MB, Nery GG, Niwas S (2005) A volumetric approach for the resistivity response of freshwater shaly sandstones. Geophysics 70:1–10
Dobrin MB (1988) Introduction to geophysical prospecting. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 867
Elizondo GM, Lofthouse V (2010) Towards a sustainable use of water at home: understanding how much, where and why? J Sustain Dev 3(1):3–10
Gile LH, Peterson FF, Grossman RB (1965) The K horizon—a master soil horizon of carbonate accumulation. Soil Sci 99:74–82
Gowd SS (2004) Electrical resistivity survey to delineate the groundwater potential aquifers in Peddavanka watershed, Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh. Environ Geol 46:118–131
Harms JC, Southhard JB, Walker RG, (1982) Structures and sequences in clastic rocks. SEPM ShortCourse 9.
Hisatomi K, Tanaka S (1994) Climatic and environmental changes at 9 and 7.5 Ma in the Churia (Siwalik) group, west-Central Nepal. Himal Geol 15:161–180
Hubbard SS, Rubin Y (2005) Introduction to hydrogeophysics. In Hydrogeophysics (pp. 3–21). Springer, Dordrecht
Joseph OC (2012) Vertical electrical sounding (VES) methods to delineate potential groundwater aquifers in Akobo area, Ibadan, south-western Nigeria. J Geol Min Res 4:35–42
Joshua EO, Odeyemi OO, Fawehinmi OO (2011) Geoelectric investigation of the groundwater potential of Moniya area, Ibadan. J Geol Min Res 3:54–62
Khaled M, Galal G (2012) Study of groundwater occurrence and the impact of salt water intrusion in east bitter lakes area. Northwest Sinai, Egypt, by using the geophysical techniques. Egypt Geophy Soc J 10:1–12
Khalil MH (2010) Hydro-geophysical configuration for the quaternary aquifer of Nuweiba alluvial fan. J Environ Eng Geophys 15:77–90
Khan IA, Bridge JS, Kappelman J, Wilson R (1997) Evolution of Miocene fluvial environment, eastern Potwar plateau, northern Pakistan. Sediment 44(2):349–368
Kraus MJ (1999) Paleosols in clastic sedimentary rocks: their geological applications. Earth Sci Rev 47:41–70
Lutgens FK, Tarbuck EJ, Tasa D, (2014) Essentials of geology. Pearson Higher Ed
Margat J, Van der Gun J (2013) Groundwater around the world. CRC Press/Balkema, Leiden
Martinelli E (1978) Groundwater exploration by geoelectrical methods in southern Africa. Bull Engin Geol 15:113–124
Maury S, Balaji S (2014) Geoelectrical method in the investigation of groundwater resource and related issues in ophiolite and flysch formations of Port Blair, Andaman Island, India. Environ Earth Sci 71:183–199
Nakajima T (1982) Sedimentology and uranium prospecting of the Siwaliks in western Nepal. Bull Geol Surv Jpn 33(12):593–617
Niaz A, Khan MR, Mustafa S, Hameed F (2016) Determination of aquifer properties and vulnerability mapping by using geoelectrical investigation of parts of sub-Himalayas, Bhimber, Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 49:36–46
Niaz A, Khan MR, Nisar UB, Khan S, Mustafa S, Hameed F, Mughal MS, Farooq M, Rizwan M (2017) The study of aquifers potential and contamination based on geoelectric technique and chemical analysis in Mirpur Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan. J Himal Earth Sci 50(2):60–73
Niwas S, Gupta PK, de Lima OA (2006) Nonlinear electrical response of saturated shaley sand reservoir and its asymptotic approximations. Geophysics 71:G129–G133
Nwanko C, Nwasu L, Emujakporue G (2011) Determination of Dar Zarouk parameters for assessment of groundwater potential: case study of Imo state, southeastern Nigeria. J Econ Sustain Dev 2:57–71
Okafor P, Mamah L (2012) Integration of geophysical techniques for groundwater potential investigation in Katsina-ala, Benue state, Nigeria. Pacific J Sci Technol 13:463–474
Olasehinde PI, Bayewu O (2011) Evaluation of electrical resistivity anisotropy in geological mapping: a case study of Odo Ara, west Central Nigeria. Afr J Environ Sci Tech 5:553–566
Orellana E, Mooney H M, (1966) Master Tables and Curves for Vertical Sounding Over Layered Structures. Madrid: Interciencia
Oseji J, Asokhia M, Okolie E (2006) Determination of groundwater potential in obiaruku and environs using surface geoelectric sounding. Environmental 26:301–308
Ozcep F, Tezel O, Asci M (2009) Correlation between electrical resistivity and soil-water content: Istanbul and Golcuk. Int J Phys Sci 6(4):362–365
Parasnis DS (1979) Principles of applied geophysics, 3rd edn. Chapman &Hall, London
Rustam MK, Hameed F, Mughal MS, Mustafa S (2016) Tectonic study of the sub-Himalayas based on geophysical data Azad Jammu and Kashmir and Nothern Pakistan. J Earth Sci 27:981–988
Sapkota B (2003) Hydrogeological conditions in the southern part of dang valley, mid-western Nepal. Him J. Sci 1(2):119–122
Searle MP, Pickering KT, Cooper DJW (1990) Restoration and evolution of intermontane Indus molasse basin, Ladakh Himalaya, India. Tectonophysics 174:301–314
Siebert S, Burke J, Faures JM, Frenken K, Hoogeveen J, Döll P, Portmann FT (2010) Groundwater use for irrigation—a global inventory. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 14:1863–1880
Sikandar P, Bakhsh A, Arshad M, Rana T (2010) The use of vertical electrical sounding resistivity method for the location of low salinity groundwater for irrigation in Chaj and Rachna doabs. Environ Earth Sci 60:1113–1129
Smith M, Cross K, Paden M, Laban P (2016) Spring—managing groundwater sustainably. IUCN, Gland, pp 17–20
Thakur V, Jayangondaperumal R, Malik M (2010) Redefining Medlicott–Wadia’s main boundary fault from Jhelum to Yamuna: an active fault strand of the main boundary thrust in northwest Himalaya. Tectonophysics 489:29–42
Ulak PD (2009) Lithostratigraphy and late Cenozoic fluvial styles of Siwalik group along Kankai River section, East Nepal Himalaya. Bull Dep Geol, Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Nepal 12:63–74
Ulak PD, Nakayama K (2001) Neogene fluvial systems in the Siwalik group along the Tinau Khola section, west-Central Nepal Himalaya. J Nepal Geol Soc 25:111–122
Willis B (1993) Evolution of Miocene fluvial systems in the Himalayan foredeep through a two kilometer-thick succession in northern Pakistan. Sediment Geol 88:77–121
Yungul SH (1996) Electrical methods in geophysical exploration of sedimentary basins. Chapman & Hill, London
Zaleha MJ (1997) Fluvial and lacustrine paleoenvironments of the Miocene Siwalik group, Khur area, northern Pakistan. Sedimentol 44(2):221–252
Funding
The Director Institute of Geology, University of Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Muzaffarabad provided the financial assistance to carry out the field work in the study area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niaz, A., Khan, M.R., Ijaz, U. et al. Determination of groundwater potential by using geoelectrical method and petrographic analysis in Rawalakot and adjacent areas of Azad Kashmir, sub-Himalayas, Pakistan. Arab J Geosci 11, 468 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3811-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3811-0