Abstract
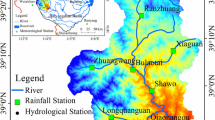
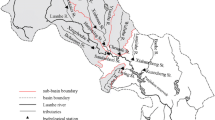
The Yuanshui River Basin is one of the most important river basins ensuring food production and livelihoods in the Hunan and Guizhou Provinces of China. Based on digital elevation model, land use, soil, and meteorological data, the soil and water assessment tool was used to analyze the response of water resources in the basin to climate change. Specifically, the monthly runoff from the Yuanshui River Basin was simulated. Runoff measurements from the 1961–1990 series were used to calibrate model parameters, and measurements from the 1991–2010 series were used for model validation. The Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient, correlation coefficient, and water balance error were used to evaluate the simulation results; the values obtained for these parameters were 0.925, 0.929, and 2.0%, respectively, indicating that the established model can be applied successfully to runoff simulations. To evaluate the effects of climate change and human activities on runoff, 24 different climate scenarios were modeled. By comparing the model simulation results with the baseline scenario, the effects of climate change were analyzed by year, during the dry season, and during extremely dry conditions. The results showed that runoff decreased with increasing air temperature and decreasing precipitation, and that the effects of rainfall on runoff were greater than those of air temperature. Under the same baseline conditions, the effects of climate change on runoff were most pronounced during extremely dry months.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, J.G., Neitsch, S.L., Kiniry, J.R., et al. Soil and water assessment tool. Theoretical documentation, version 2009, Agriculture Research Service US, 2009
Bajracharya AR, Bajrachary SR, Shrestha AB, Maharjan SB (2018) Climate change impact assessment on the hydrological regime of the Kaligandaki Basin, Nepal. Sci Total Environ 625:837–848
Chaplot V (2007) Water and soil resources response to rising levels of atmospheric CO2 concentration and to changes in precipitation and air temperature. J Hydrol 337(1):159–171
Chen Y, Youpeng X, Yin Y (2009) Impacts of land use change scenarios on storm-runoff generation in Xitiaoxi basin. China Quaternary Int 208:121–128
Chunshu S, Luo D (2006) Hydrological forecasting of Fengle River watershed based on SWAT model. Chinese agricultural Bulletin 22(9):493–498 (in Chinese)
Darren LF, Luo Y, Iris TS (2012) Development and application of a hydroclimatological stream temperature model within the soil and water assessment tool. Water Resour Res 48(1):1–16
Feng LI, Hu Tiesong, Huang Huajin. The principle, structure and application of the SWAT model. China rural water and hydropower,2008,(3):24–28. (in Chinese)
Ficklin DL, Luo Y, Luedeling E, Zhang M (2009) Climate change sensitivity assessment of a highly agricultural watershed using SWAT. J Hydrol 374(1):16–29
Hojat A, Saeed M, Majid D et al (2016) Using the SWAT model to assess the impacts of changing irrigation from surface to pressurized systems on water productivity and water saving in the Zarrineh Rud catchment. Agric Water Manag 175:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2015.10.026
Huaibin W, Zhanpang Z, Jinpeng Y (2007) Establishing method for soil database of SWAT model. Water Res Hydropower Engineering 38(6):15–18 (in Chinese)
Jingpeng Pang. Distributed simulation of non point source pollution: a case study of water resources protection in Miyun reservoir. Beijing: Beijing Normal University, 2007 (in Chinese)
Josh W, Christine A. S, Dillon C, Zach E. A comparison of a SWAT model for the Cannonsville watershed with and without variable source area hydrology. World Environmental and Water Resources Congress, 2009
Junxiang C, Ligang X, Jiahu J et al (2016) The research of runoff responses to climate change and human activities in the Dongting Lake catchment. J Agro-Environ Sci 35(11):2146–2153
Kim N, Lee J, Kim J (2012) Assessment of flow regulation effects by dams in the Han River, Korea, on the downstream flow regimes using SWAT. J Water Resour Plan Manag 138(1):24–35
Kliment Z, Kadlec J, Langhammer J (2008) Evaluation of suspended load changes using AnnAGNPS and SWAT semi-empirical erosion models. CATENA 73(3):286–299
Lin W, Xingwei C (2008) Review of study on watershed runoff simulation based on SWAT. J Huaqiao University: Nature Sci 29(1):6–10 (in Chinese)
Lin B, Chen X, Yao H, Chen Y, Liu M, Gao L, James A (2015) Analyses of landuse change impacts on catchment runoff using different time indicators based on SWAT model. Ecol Indic 58:55–63
Lirong S, Jianyun Z (2012) Hydrological response to climate change in Beijiang River Basin based on the SWAT model. Procedia Engineering 28:241–245
Maite Meaurio AZ, Jesus U, Raghavan S, Iñaki A (2015) Evaluation of SWAT models performance to simulate streamflow spatial origin—the case of a small forested watershed. J Hydrol 525:326–334
Navarro EM, Andersen HE, Nielsen A et al (2018) Quantifying the combined effects of land use and climate changes on stream flow and nutrient loads: a modelling approach in the Odense Fjord catchment (Denmark). Sci Total Environ 621:253–264
T Lotez, C Opp, X He. Factors of runoff generation in the Dongting Lake basin based on a SWAT model and implications of recent land cover change. Quaternary Internationa, 2017
Tao J, Yongqin C, Junhe C, Xi C (2000) Impact studies of future climate change on hydrological regimes and water resources in China. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni 39(2):151–157 (in Chinese)
Tongzhao H, Jinyu L (2009) Preliminary study for soil and water assessment tool. Res Soil Water Conservation 16(6):282–286 (in Chinese)
Tuan BL, Hatim OS (2015) Modeling the projected changes of river flow in Central Vietnam under different climate change scenarios. Water 7(7):3579–3598
Xi C, Buda SU, Tong J, Yafeng S (2003) Impacts of climate change on the streamflow in the Yuanjiang river basin. J Lake Sci 15(Suppl):115–122 (in Chinese)
Xiaofeng C (2009) Simulation study on runoff in Bailian River Basin based on SWAT model. Water Res Power 27(1):28–33 (in Chinese)
Xuan S, Chong W et al (2010) Application of SWAT model on reservior area. J Zhengzhou University (Engineering Sci) 31(6):35–38 (in Chinese)
Yuan J, Baoln S et al (2010) Runoff simulation in change reservoir catchment based on SWAT model. J Beijing Normal University (Nature Sci) 46(3):361–365 (in Chinese)
Zhang W, Chen X (2007) Runoff simulation in Xixi watershed of the Jinjiang Basin based on SWAT model. J Subtropical Res Environ 2(1):28–33 (in Chinese)
Zhihong X, Yuehua Z, Hongmei X (2009) Runoff simulation of Hanjiang River Basin based on SWAT model. Meterological 35(9):59–66 (in Chinese)
Zhu L, Wanchang Z (2005) Responses of water resources to climatic changes in the upper stream of the Hanjiang River basin based on rainfall-runoff simulations. Res Sci 27(2):16–22 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Liu, J., Yang, Z. et al. Effect of climate change on water resources in the Yuanshui River Basin: a SWAT model assessment. Arab J Geosci 11, 270 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3619-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3619-y