Abstract
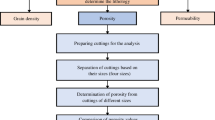
The Herron model does not consider the effect of organic matter and gas on total porosity. In this paper, the shale rock is equivalent to three parts: skeleton, organic matter, and pore. According to the volume model, a new total porosity model is established. The new model is applied to estimate the total porosity of a shale gas well in South Sichuan area from element capture logging and conventional logging data. The results show that in the formations with high gas content and organic matter, the total porosity calculated by the new model is smaller than that calculated by the Herron model. To verify the accuracy of the new model in evaluating the total porosity of shale, the advantages and disadvantages of Gas Research Institute (GRI) measurement method and helium injection measurement method for determining porosity are discussed in terms of theoretical analysis and experimental measurement. It is considered that the GRI porosity is closer to the total porosity of shale and it can be used to test the total porosity of logging evaluation. The total porosity of the ten shale samples calculated by the new model and the Herron model is compared with the GRI porosity. Results show that the average relative errors calculated by the Herron model and the new model are 61 and 10%, respectively. It indicates that the accuracy of the total porosity calculated by the new model is higher.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borjigin T, Shen BJ, Yu LJ, Yang YF, Zhang WT, Tao C, Xi BB, Zhang QZ, Bao F, Qin JZ (2017) Mechanisms of shale gas generation and accumulation in the Ordovician Wufeng-Longmaxi formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China. Petrol Explor Dev 44(1):69–78
Carpentier, B., Huc, A.Y., Bessereau, G., 1991. Wireline logging and source rocks-estimation of organic carbon content by the CARBOLOG method. Log Anal 279–297
Dong DZ, Gao SK, Huang Jl, Guan QZ, Wang SF, Wang YM (2014) A discussion on the shale gas exploration & development prospect in the Sichuan Basin. Natur Gas Indonesia 24(12):1–15
Guo TL (2016) Discovery and characteristic of the Fuling shale gas field and its enlightenment and thinking. Earth Sci Front. 23(1):029–043
Guo C, Zhang C, Zhu LQ (2017) Predicting the total porosity of shale gas reservoirs. Pet Sci Technol 42(2):1527–1534
He ZL, Nie HK, Zhang YY (2016) The main factors of shale gas enrichment of Ordovician Wufeng formation-Silurian Longmaxi formation in the Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas. Earth Sci Front 23(2):008–017
Herron, M.M., Herron, S.L., Grau JA, Seleznev NV, Phillips J, Sherif AE, 2002. Real-time petrophysical analysis in siliciclastics from the integration of spectroscopy and triple-combo logging: SPE Paper 77631 presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, Texas, September29–October 2, 1–7
Hou J, Zou CC, Yang YQ (2012) Well logging method in the analysis of the mineralogical composition of shale gas reservoirs. Chin J Eng Geophys 9(5):607–613
Jin ZJ, Hu ZQ, Gao B, Zhao JH (2016) Controlling factors on the enrichment and high productivity of shale gas in the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, southeastern Sichuan Basin. Earth Sci Front. 23(1):001–010
Kuila, U., Mccarty, D. K., Derkowski, A., Fischer, T. B., Topór, T., & Prasad, M. (2014) Nano-scale texture and porosity of organic matter and clay minerals in organic-rich mudrocks. Fuel, 135(6):359–373
Li J, Lu J, Li Z, Wu QZ, Nan Z (2014) ‘Four-pore’ modeling and its quantitative logging description of shale gas reservoir. Oil Gas Geol 35(2):266–271
Li J, Wu QZ, Lu J, Jin WJ (2017) Measurement and logging evaluation of total porosity and effective porosity of shale gas reservoirs: a case from the Silurian Longmaxi formation shale in the Sichuan Basin. Oil & gas. Geology 38(3):602–609
Luffel DL, Guidry FK, Curtis JB (1992) Evaluation of Devonian shale with new core and log analysis method. J Petrol Technol 44(11):1192–1197
Nie HK, Jin ZJ, Bian RK, Du W (2016) The “source-cap hydrocarbon-controling” enrichment of shale gas in upper Ordovician Wufeng formation-lower Silurian formation of Sichuan Basin and its periphery. Acta Petrol Sin 37(5):557–571
Passey QR, Moretti FJ, Kulla JB, Creaney S, Stroud JD (1990) A practical model for organic richness from porosity and resistivity logs. AAPG Bull 74:1777–1794
Passey QR, Bohacs KM, Esch WL, Klimentidis R, Sinha H (2010) From oil-prone source rock to gas-produ-cing shale reservoir-geologic and petrophysical characterization of unconventional shale gas reservoirs:SPE paper 131350 presented at the SPE International Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, Beijing, pp 1–29
Rick, L., David, I., Marc, P., 2004. New evaluation techniques for gas shale reservoirs. Reservioir Symposium Schlumberger
Sun JM, Dong X, Wang JJ, Douglas RS, Xu CL, Tariq M (2016) Measurement of total porosity for gas shales by gas injection. Fuel 186:694–707
Tissot BP, Welte DH (1984) Petroleum formation and occyrrence. 2nd edition: Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p. 699
Tomasz T, Arkadiusz D, Utpalendu K, Timothy BF, Doulas KM (2016) Dual liquid porosimeter: a porosity measurement technique for oil-and gas-bearing shales. Fuel 183:537–549
Xiao DS, Lu SF, Lu ZY, Zhang LH, Guo SQ, Gu MW (2016) Inversion method of shale oil reservoir mineral component content and its application in the fourth member of the Shahejie formation in the Damintun Sag, Liaohe depression. Oil Gas Geol 37(1):37–44
Zhang C, Guo C, Zhu LQ, Cheng Y, Yan W (2017) A loggong interpretation method for total porosity considering organic matter correction of shale gas reservoirs. J China Coal Soc 42(6):1527–1534
Zhao PQ, Mao ZQ, Huang ZH, Zhang C (2016) A new method for estimating total organic carbon content from well logs. AAPG Bull 100(8):1311–1327
Zhao PQ, Wang Z, Sun Z, Cai J, Wang L (2017) Investigation on the pore structure and multifractal characteristics of tight oil reservoirs using NMR measurements: Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin. Mar Pet Geol 86:1067–1081
Acknowledgements
We sincerely acknowledge the anonymous reviewers whose correlations and comments have greatly improved the manuscript.
Funding
This research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41404084), National Science and Technology major projects of China (2017ZX05032-003-005), and Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Exploration Technologies for Oil and Gas Resources (Yangtze University), Ministry of Education (No.K2017-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Wang, X. & Zhu, L. Estimation of total porosity in shale formations from element capture logging and conventional logging data. Arab J Geosci 11, 264 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3617-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3617-0