Abstracts
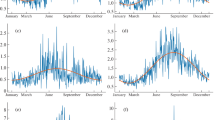
Harmonic techniques are used for computing solar irradiation for 14 stations in Saudi Arabia in order to map amplitudes (AMPs), percentages of variances (PVs), and phase angles (Φ) for six harmonics of solar irradiation. The annual cycle of solar irradiation is considered the main cycle prevailing over the semi-annual and seasonal cycles with first harmonic PVs of 96, 97, and 93% for north, east, and central regions, respectively. In the southwest region, at stations Abha and Albaha, there are some contributions of semi-annual cycle which reduce the PVs of the first harmonic to 60 and 55% at Abha and Albah, respectively. The low percentages at southwest stations are due to the wet summer monsoon. On the other hand, rainfall records at five stations are used in harmonic analysis in order to find the interrelationships between the two elements. It is found that the greater the amplitude of solar irradiations is the offset by the lack of rainfall and vice versa. Weak correlations between rainfall and solar irradiation in the majority of cities in all regions which are represented by Riyadh (− 0.23) for the central region, Tabuk (0.24) for the northern region, and Jazan (− 0.08) for southwest region, while there are three stations that are unique in exhibiting medium correlations among the stations of their regions; these are Taif (− 0.42), Abha (− 0.44), and Hail (− 0.56). These differences arise from, first the synoptic climatology, such as in Hail (weather system with respect to time and location), second the elevations of the station such as Abah and Taif. Finally, climatic rainfall indices are calculated to enrich the discussion on the interrelationships between rainfall and solar irradiation. The study shows that the stations of low amplitudes of solar irradiation are offset by an increase of both number of days where daily precipitation ≥ 20 mm (R20mm), and the annual sum of daily precipitation > 95th percentile (R95p) and vice versa, low amplitudes of solar irradiation with decreasing the number of consecutive dry day (CDD).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkhathlan K, Javid M (2015) Carbon emissions and oil consumption in Saudi Arabia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 48:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.03.072
Almazroui M (2010) Calibration of TRMM rainfall climatology over Saudi Arabia during 1998–2009. Atmos Res 99(3-4):400–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.11.006
Almazroui M (2011) Calibration of TRMM rainfall climatology over Saudi Arabia 1998-2009. Atmos Res 99(3-4):400–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.11.006
Burroughs W (1992) Weather cycles real or imaginary. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 175–177
Chisanga CB, Phiri E, Chinene VRN (2017) Trends of extreme events in precipitation and temperature during the 1963-2012 period at Mt Makulu, Zambia. J Sci Res Rep 15(4):1–19. https://doi.org/10.9734/JSRR/2017/34815
Dahamsheh A, Wedyan M, Alhasant MB (2018) Climate change impact assessment on rainwater in Jordan. Int J Adv Appl Sci 5(1):148–155. https://doi.org/10.21833/ijaas.2018.01.020
Davis JC (1986) Statistical and data analysis in geology. John Wiley, New York
Dorvlo AS, Ampratwum (2000) Harmonic analysis of global irradiation. Renew Energy 20(4):435–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-1481(99)00116-0
Duchon CE (1981) Time series Analysisworkshop. Sponsored by American Meteorology Society, Boston, pp 1–11
Fagbenle R, Karayiannis TG (1994) Harmonic analysis of monthly solar irradiation in Niegeria. Renw Energy 4(5):551–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-1481(94)90217-8
Gadiwala MS, Usman A, Akhtar M, Jamil K (2013) Empirical Models for the Estimation of Global Solar Radiation with Sunshine Hours on Horizontal Surface in Various Cities of Pakistan. Pak J Meteorol 9(8):43–49
Gana NN, Akpootu DO (2013) Angstrom type empirical correlation for estimating globalsolar radiation in north-Eastern Nigeria. Int J Eng Sci 2(11):58–78
Horn LH, Bryson RA (1960) Harmonic analysis of the annual march of precipitation over the United States. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 50(2):157–171. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8306.1960.tb00342.x
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: climate change impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 976
Jenkins MG, Watts D (1980) Spectral analysis and its applications. Holden-Day, London, pp 16–23
Kadioglu M, Ozturk N, Erdun H, Sen Z (1999) On the precipitation climatology on Turkey by harmonic analysis. Int J Climatol 19(15):1717–1728. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(199912)19:15<1717::AID-JOC470>3.0.CO;2-#
Matuszko D (2012) Influence of cloudiness on sunshine duration. Int J Climatol 32(10):1527–1536. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2370
McGee OS (1969) The use of the harmonic dial in rainfall climatology. S Afr Geogr J 51(1):65–72
Medvigy D, Beaulieu C (2012) Trends in daily solar radiation and precipitation coefficients of variation since. J Clim 25(4):1330–1339. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JCLI4115.1
Ogelman M, Ecevit A, Tasdemiroglu E (1984) A new method for estimating solar radiation from bright sunshine data. Sol Energy 33(6):619–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092X(84)90018-5
Palle E, Butler CJ (2002) Comparison of sunshine records and synoptic cloud observations: Acase study for Ireland. Phys Chem Earth 27(6-8):405–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-7065(02)00020-7
Panofsky HA, Brier GW (1958) Some applications of statistics to meteorology. Pennsylvania State University Press, Pennsylvania
Rahimi I, Bakhtiari B, Qaderi K (2012) Calibration of angstrom equation for estimating solar irradiation using meta-heuristic harmony search algorithm: case study Masshad east of Iran. Energy Procidia 18:644–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2012.05.078
Rehmana S (1998) Solar radiation over Saudi Arabia and comparisons with empirical models. Energy 23(12):1077–1082. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(98)00057-7
Sahin AD, Kadioglo M, Sen Z (2000) Monthly clearness index values of Turkey by harmonic analysis approach. Energy Convers Manag 42:933–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0196-8904(00)00116-3
Salima G, Chavula GM (2012) Determining angstrom constants for estimating solar radiation. Int J Geosci 3(02):391–397. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2012.32043
Shehadeh N (1991) The climate of Jordan. Albasheer press, Amman
Tarawneh Q (2013) Quantification of drought in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 5th International Conf. Water resources and Arid Environment, King Saud University, Riyadh, 7-9 Jan. 2013. Proceeding, pp 425–433
Tarawneh Q (2016) Harmonic analysis of precipitation climatology in Saudi Arabia. Theor Appl Climatol 124(1):205–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1408-z
Tarawneh Q, Kadioglu M (2002) An analysis of precipitation climatology in Jordan. Theor Appl Climatol 74:123–136
Tarawneh QY, Şahin AD (2008) Solar irradiance polygon concept and application for Jordan. Energy Sources Part A 30(10):932–941. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826070601082682
Wang Q, Qian Y (1996) Effects of land-sea distribution, topography and diurnal change on summer monsoon modeling. Adv Atmos Sci 13(2):253–259
Wu LG, Zong HJ, Liang J (2013) Observation analysis of tropical cyclone formation associated with monsoon gyres. J Atmos Sci 70(4):1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-12-0117.1
Zell E, Gasim S, Wilcox S, Katamoura S, Stoffel T, Shibli H, Engel-Cox J, Al-Subieb M (2015) Assessment of solar radiation resources in Saudi Arabia. Sol Energy 119:422–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2015.06.031
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to express his gratitude to the editor, the reviewers for their valuable comments, and assistance in revising the manuscript. This project was financially supported by the Vice Deanship of Research Chairs at King Saud University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarawneh, Q.Y. Harmonic analysis of solar irradiation and rainfall data in the context of various climatic indicators in Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 11, 75 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3414-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3414-9