Abstract
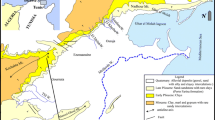
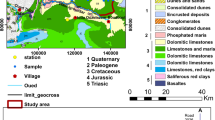
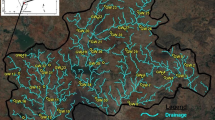
The major ion hydrochemistry, sodium absorption ratio (SAR), sodium percentage, and isotopic signatures of Hammamet-Nabeul groundwaters were used to identify the processes that control the mineralization, irrigation suitability, and origin of different water bodies. This investigation highlights that groundwater mineralization is mainly influenced by water-rock interaction and pollution by the return flow of irrigation water. The comparison of groundwater quality with irrigation suitability standards proves that most parts of groundwater are unacceptable for irrigation and this long-term practice may result in a significant increase of the salinity and alkalinity in the soils. Based on isotopic signatures, the shallow aquifer groundwater samples were classified into (i) waters with depleted δ18O and δ2H contents, highlighting recharge by modern precipitation, and (ii) waters with enriched stable isotope contents, reflecting the significance of recharge by contaminated water derived from the return flow of evaporated irrigation waters. The deep-aquifer groundwater samples were also classified into (i) waters with relatively enriched isotope contents derived from modern recharge and mixed with shallow-aquifer groundwater and (ii) waters with depleted stable isotope contents reflecting a paleoclimatic origin. Tritium data permit to identify three origins of recharge, i.e., contemporaneous, post-nuclear, and pre-nuclear. Carbon-14 activities demonstrate the existence of old paleoclimatic recharge related to the Holocene and Late Pleistocene humid periods.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams S, Tredoux G, Harris C, Titus R, Pietersen K (2001) Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the western Karoo, South Africa. J Hydrol 241:91–103
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (1993) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam
Baba SY M (2005) Recharge et paleorecharge du systeme aquifere du sahara septentrional. Thèse, université El Manar, 271p
Bakalowicz, M., Blavoux, B. and Mangin, A. 1974. Apports du tracage isotopique naturel a la connaissance du fonctionnement d’un systeme karstique-teneurs en oxygen-18 de trios systems des Pyrenees, France. Journal of Hydrology, 23:141–158
Barbieri M, Garone A, Neziri A (2015) First groundwater chemical status assessment of the Buna River-protected landscape (Albania). Environ Earth Sci 74:6325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4657-3
Bauder JW, Brock TA (2001) Irrigation water quality, soil amendment, and crop effects on sodium leaching. Arid Land Res Manag 15:101–113
Ben Moussa A (2011) étude hydrogéologique, hydrochimique et isotopique du système aquifère de hammametnabeul, Cap Bon, Tunisie nordorientale. Thèse, université de sfax, 147p
Ben Moussa A, Zouari K, Oueslati N (2011) Hydrochemical and isotope evidence of groundwater salinization processes on the coastal plain of Hammamet–Nabeul, north-eastern Tunisia. J Phys Chem Earth 36:167–178
Ben Moussa A, Bel Haj Salem S, Zouari K, Marc V, Jlassi F (2012) The hydrogeology of the deep groundwater system in the Hammamet–Nabeul regional basin, north-eastern Tunisia: a hydrochemical and isotopic approach. Carbonates Evaporites 26:327–338
Ben Salem H (1995) Evolution de la péninsule du cap Bon (Tunisie orientale) au cours du Néogène. Notes Serv Géol Tunisie 61:73–84
Beseme P., Kammoun Y. (1987) Les dépôts marins accompagnant l’épisode messinien préévaporitique (Formation Béni-Khiar) à Ksour Essaf (Sahel de Tunisie). 8e Congrès International de Sédimentologie, IAS, Tunis, 94
Bismuth H, Hooberghs HJF (1994) Foraminifères planctoniques et biostratigraphie de l’Oligocène et du Néogène dans le sondage Korba 1 (Cap Bon, Tunisie Nord-Orientale). Bull Cent Rech Expl Prod Elf Aquitaine 18:489–527
Burollet PF (1956) Contribution à l'étude stratigraphique de la Tunisie centrale. Ann Mines et Géol, Tunis, 18, 352p
Carol E, Kruse E, Mas-Pla J (2009) Hydrochemical and isotopical evidence of ground water salinization processes on the coastal plain of Samborombón Bay, Argentina. J Hydrol 365:335–345
Chadha DK (1999) A new diagram for geochemical classification of natural waters and interpretation of chemical data. Hydrogeol J 7:431e439
Clark I, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Coleman ML, Shepherd TJ, Durham JJ, Rouse JE, Moore GR (1982) Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis. Anal Chem 54:993–995
Colleuil B (1976) Etude stratigraphique et néotectonique des formations néogènes et quaternaires de la région de Hammamet-Nabeul (Cap Bon) Mémoire de DES, University of Nice
Dassi L (2004) Etude hydrogéologique, géochimique et isotopique du système aquifère du bassin de Sbeïtla (Tunisie Centrale). Thèse 3ème cycle, Univ. de Sfax, Tunisie
Dassi L, Tarki M (2014) Isotopic tracing for conceptual models of groundwater hydrodynamics in multilayer aquifer systems of central and southern Tunisia. Hydrol Sci J 59(6):1240–1258
Dassi L, Zouari K, Faye S (2005) Identifying sources of groundwater recharge in the Merguellil basin (Tunisia) using isotopic methods: implication of dam reservoir water accounting. Environ Geol 49:114–123
Elmejdoub N, Jedoui Y (2009) Pleistocene raised marine deposits of the Cap Bon peninsula (N-E Tunisia): records of sea-level highstands, climatic changes and coastal uplift. Geomorphology 112:179–189
Epstein S, Meyada TK (1953) Variations of 18O content of waters from natural sources. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 4:213–224
Garcia MG, Del Hidalgo M, Blesa MA (2001) Geochemistry of groundwater in the alluvial plain of Tucuman province, Argentina. J Hydrol 9:597–610
Gat JR, Issar A (1974) Desert isotope hydrology: water sources of the Sinai desert. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38:1117e1131
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanism controlling world water chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090
Hamed Y, Dassi L, Ahmadi R, Ben Dhia H (2008) Geochemical and isotopic study of the multilayer aquifer system in the Moulares-Redayef basin, southern Tunisia. Hydrol Sci J 53(5):1241–1252
Hanson BR, Grattan SR, Fulton A (2006) Agricultural salinity and drainage. Water Management Series Publication, pp 1–180
IAEA/WMO (1999) Global network of isotopes in precipitation. The GNIP database, station 7622500. Accessible at: http://isohis.iaea.org
Jeribi Derwich L, Zouari K, Michelot JL (2012) Recharge and paleorecharge of the deep groundwater aquifer system in the Zeroud Basin (Kairouan plain, Central Tunisia). Quat Int:56–63
Kaddachi S (2012) Gestion des aquifères côtiers et de l’eau souterraine. Le cadre juridique et institutionnel des aquifères côtiers en Tunisie. Sous-composante UNESCO-PHI, 55p
Kamel S, Dassi L, Zouari K (2006) Approche hydrogéologique et hydrochimique des échanges hydrodynamiques entre aquifères profond et superficiel du bassin du Djérid, Tunisie. Hydrol Sci J 51(4):713–730
Khayat, S., Möller, P Geyer, S., Marei, A., Siebert, C. and Hilo, F.A. 2008. Hydrochemical variation in the springs water between Jerusalem–Ramallah Mountains and Jericho Fault, Palestine. Environ Geol, 57:1739–1751
Lucas LL, Unterweger MP (2000) Comprehensive review and critical evaluation of the halflife of tritium. J Res NIST 105(4):541–549
Mc Lean W, Jankowski J, Lavitt N (2000) Groundwater quality and sustainability in alluvial aquifer, Australia. In: Sililoo Et (ed) Groundwater, past achievement and future challenges. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 567–573
Melanie JL, Marshall JD (2004) Palaeoclimate interpretation of stable isotope data from lake sediment archives. Quat Sci Rev 23:811–831
Mzali H (2010) Etude des déformations et des paléocontraintes dans les régions de Bouficha et Grombalia. Thèse, université de Tunis Elmanar
Mzali H, Zouari H (2006) Caractérisation géométrique et cinématique des structures lieés aux phases compressives de l’Eocène au Quaternaire inférieur en Tunisie: exemple de la Tunisie nord-orientale. Compt Rendus Geosci 338:742–749
Nishanthiny SC, Thushyanthy M, Barathithasan T, Saravanan S (2010) Irrigation water quality based on hydrochemical analysis, Jaffna, Sri Lanka. Am Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 7(1):100–102
Rightmire CT (1978) Seasonal variation in pCO2 and 13C content of soil atmosphere. Water Resour Res 14:691
Romanek CS, Grossman EL, Morse JW (1992) Carbon isotopic fractionation in synthetic aragonite and calcite: effects of temperature and precipitation rate. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56(1):419–430
Skrzypek G, Dogramaci S, Grierson PF (2013) Geochemical and hydrological processes controlling groundwater salinity of a large inland wetland of northwest Australia. Chem Geol 357(2013):164–177
Subba Rao N, Surya Rao P (2010) Major ion chemistry of groundwater in a river basin: a study from India. Environ Earth Sci 61:757–775
Tarki M, Dassi L, Hamed Y, Jedoui Y (2011) Geochemical and isotopic composition of groundwater in the complex terminal aquifer in southwestern Tunisia,with emphasis on the mixing by vertical leakage. Environ Earth Sci 64:85–95
Tarki M, Dassi L, Jedoui Y (2012) Groundwater composition and recharge origin in the shallow aquifer of the Djerid oases, southern Tunisia: implications of return flow. Hydrol Sci J 57(4):790–804
Tarki M., Ben Hammadi M., El Mejri H., Dassi L (2016) Assessment of hydrochemical processes and groundwater hydrodynamics in a multilayer aquifer system under long-term irrigation condition: A case study of Nefzaoua basin, southern Tunisia. Applied Radiation and Isotopes. 110:138–149
Vogel JC (1993) Variability of carbon isotope fractionation during photosynthesis. In: Ehleringer JR, Hall AE, Farquhar GD (eds) Stable isotopes and plant carbon–water relations. Academic press, San Diego, pp 29–46
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington, D.C, Circular 969, 19 p
Zouari K, Aranyossy JF, Mamou A, Fontes JCh (1985) Etude isotopique et géochimique des mouvements et de l’évolution des solutions de la zone aérée des sols sous climat semi-aride (Sudtunisien). In : Stable and radiactive isotopes in the study of the unsaturated soil zone. IAEATECDOC- 357, Vienna, p121–144
Zouari K, Aranyossy JF, Mamou A, Fontes JCh (1986) Etude isotopique et géochimique des mouvements et de l’évolution des solutions de la zone aérée des sols sous climat semi-aride (Sud tunisien). In: Stable and radioactive isotopes in the study of the unsaturated soil zone. IAEATECDOC-357, Vienna, p121–144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moussa, A.B., Salem, S.B.H., Zouari, K. et al. Hydrochemical and stable isotopic investigation of groundwater quality and its sustainability for irrigation in the Hammamet-Nabeul basin, northeastern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 10, 446 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3233-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3233-4