Abstract
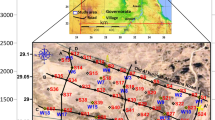
Water seepage to ground surface at a limestone quarry located at Wadi Garawy about 20 km south-east of Helwan city in Egypt posed a real threat to the mining activity at the quarry. The quarry area is known to be very dry for decades and away from water utilities and infrastructures that may cause water leaks to the quarry. Geophysical investigation including 1D Vertical Electrical Sounding (VES), 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) and 1D Transient Electromagnetic (TEM) surveys were conducted to characterize the rock sequence and locate what could be a possible source of water seepage to the quarry. The resistivity profiles generated from the VES and TEM surveys mapped the rock units in the area down to depths exceeded 100 m. The ERT profiles acquired from the quarrying zone close to the water seepage spot have imaged the top of groundwater level at few meters below the ground surface at the quarry open pit. The spot of groundwater seepage seemed to occur at an area of limestone dissolution that were filled by finer sediments. The finer sediments acted as a hydrological conduit that allowed an upward seepage of groundwater to ground surface under the capillary action effect.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Carpenter PJ (2003) Geophysical response of filled sinkholes, soil pipes and associated bedrock fractures in thinly mantled karst, east-central Illinois. Environ Geol 44:705–716
Annan AP, Cosway SW, Redman JD (1991) Water table detection with ground-penetrating radar. Soc Explor Geophys (Annual International Meeting Program with Abstracts) 494–497. doi:10.1190/1.1888793
Ballard, RF (1983) Cavity detection and delineation research. Report 5, Electromagnetic (radar) techniques applied to cavity detection. Technical Report GL, 83–1, 90 P
Cook JC (1965) Seismic mapping of underground cavities using reflection amplitudes. Geophysics 30(4):527–538
Egyptian Geological Survey (EGS (2007) Detailed geological studies to evaluate rock quality at Wadi Garawy, southeast of Helwan city. Internal Report, Egypt
Griffiths DH, Barker RD (1993) Two-dimensional resistivity imaging and modelling in areas of complex geology. J Appl Geophys 29:211–226
Ismail A, Anderson N (2007) Near surface characterization of a geotechnical site north east Missouri using shear wave velocity measurements. Near surface Geophysics Journal, European Association of Geoscientists & Engineering 6:331–336
Labuda ZT, Baxter CA (2001) Mapping karst conditions using 2D and 3D resistivity imaging methods. In: Powers M (ed). Proceedings of the Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems, Environmental and Engineering Geophysical Society, Paper GTV-1
Loke MH (1994) The inversion of two-dimensional resistivity data. PhD thesis, University of Birmingham
Loke MH (1999) Electrical imaging surveys for environmental and engineering studies: a practical guide to 2D and 3D surveys, 63 P
Loke MH, Barker RD (1996a) Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudo-sections by a quasi-Newton method. Geophys Prospect 44:131–152
Reynolds JM (1997) An introduction to applied and environmental geophysics. John Wiley and Sons Ltd., England
Roth MJS, Mackey JR, Mackey C, Nyquist JE (1999) A case study of the reliability of multi-electrode earth resistivity testing for geotechnical investigations in karst terrains. Proceedings of the 7 Multidisciplinary Conference on Sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst, Balkema 247–252
Steeples DW, Miller RD (1987) Direct detection of subsurface voids using high-resolution seismic reflection techniques. In: Bek, B. F., Wilson, W. L., Balkema, A. A. (eds) Karst Hydrogeology: Engineering and Environmental Applications 179–183
TEMIXL XL V4 (1996) Temix V.4 user's manual, Interprex, 468 P
Vander V (1988) Resist, a computer program for the interpretation of resistivity sounding curves. An ITCD M. Sc. Research Project. ITCD, Delft, the Netherlands
Zhou W, Beck BF, Adams AL (2002) Effective electrode array in mapping karst hazards in electrical resistivity tomography. Environ Geol 42:922–928
Zohdy A (1989) The use of Schlumberger and equatorial sounding in groundwater investigations near El-Paso, Texas. Geophysics 34:713–728
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mesbah, H.S., Ismail, A., Taha, A.I. et al. Electrical and electromagnetic surveys to locate possible causes of water seepage to ground surface at a quarry open pit near Helwan city, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 10, 230 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2997-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2997-x