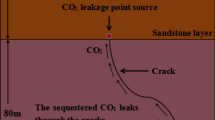
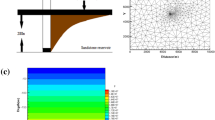
Abstract
This study focused on the target injection layers of deep saline aquifers in the Shiqianfeng Fm. in the Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) Demonstration Projects in the Ordos Basin, northwestern China. The study employed a combination method of experiments and numerical simulation to investigate the dissolution mechanism and impact factors of CO2 in these saline aquifers. The results showed (1) CO2 solubility in different types of water chemistry were shown in ascending order: MgCl2-type water < CaCl2-type water < Na2SO4-type water < NaCl-type water < Na2CO3-type water < distilled water. These results were consistent with the calculated results undertaken by TOUGHREACT with about 5% margin of error. CO2 solubility of Shiqianfeng Fm. saline was 1.05 mol/L; (2) compared with distilled water, the more complex the water’s chemical composition, the greater the increase in HCO3 −concentration. While the water’s composition was relatively simple, the tested water’s HCO3 −concentrations were in close accord with the calculated value undertaken by the TOUGHREACT code, and the more complex the water’s composition, the poorer the agreement was, probably due to the complex and unstable HCO3 − complicating matters when in an aqueous solution system including both tested HCO3 −concentration and calculated HCO3 −concentration; (3) the CO2 solubility in the saline at the temperature conditions of 55 °C and 70 °C were 1.17 and 1.02 mol/L. When compared with the calculated value of 1.20 and 1.05 mol/L, they were almost the same with only 1 and 3% margin of error; concentrations of HCO3 − were 402.73 mg/L (0.007 mol/L) and 385.65 mg/L (0.006 mol/L), while the simulation results were 132.16 mg/L (0.002 mol/L) and 128.52 mg/L (0.002 mol/L). From the contrast between the tested data and the calculated data undertaken by the TOUGHREACT code, it was shown that TOUGHRACT code could better simulate the interaction between saline and CO2 in the dissolution sequestration capacity. Therefore, TOUGHREACT code could be used for the inter-process prediction of CO2 long-term geological storage of CO2; (4) The Ca2+ concentration and SO4 2−concentration in saline water had less effect on the solubility of CO2 and HCO3 −concentration. In addition, TDS and pH values of saline affected not only the solubility of CO2, but also the conversion of CO2 to HCO3 − due to that they can affect the activity and acid-base balance. So in fact, we just need to consider that the TDS and pH values are main impact factors in the dissolution sequestration capacity of CO2 geological sequestration in deep saline aquifers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinfiev NN, Diamond LW (2010) Thermodynamic model of aqueous CO2–H2O–NaCl solutions from −22 to 100 °C and from 0.1 to 100 MPa. Fluid Phase Equilib 295:104–125
Bachu S (2015) Review of CO2 storage efficiency in deep saline aquifers. Int J Greenhouse Gas Contr 40(SI):188–202
Birkholzer JT, Oldenburg CM, Zhou QL (2015) CO2 migration and pressure evolution in deep saline aquifers. Int J Greenhouse Gas Contr 40(SI):203–220
Celia MA, Bachu S, Nordbotten JM, Bandilla KW (2015) Status of CO2 storage in deep saline aquifers with emphasis on modeling approaches and practical simulations. Water Resour Res 51:6846–6892
Crandell LE, Ellis BR, Peters CA (2010) Dissolution potential of SO2 co-injected with CO2 in geologic sequestration. Environ Sci Technol 44:349–355
Dowson GKW, Pearce JK, Biddle D, Golding SD (2015) Experimental mineral dissolution in Berea sandstone reacted with CO2 or SO2-CO2 in NaCl brine under CO2 sequestration conditions. Chem Geol 399:87–97
Du SH, Su XS, Xu W (2016) Assessment of CO2 geological storage capacity in oilfields of Songliao Basin, northeastern China. Geosci J 20:247–257
Duan ZH, Sun R (2003) An improved model calculating CO2 solubility in pure water and aqueous NaCl solutions from 257 to 533 K and from 0 to 2000 bar. Chem Geol 193:257–271
Duan ZH, MΦller N, Weare JH (1995) Equation of state for the NaCl–H2O–CO2 system: prediction of phase equilibria and volumetric properties. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:2869–2882
Duan ZH, Sun R, Zhu C, Chou IM (2006) An improved model for the calculation of CO2 solubility in aqueous solutions containing Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, and SO4 2−. Mar Chem 98:131–139
Emami-Meybodi H, Hassanzadeh H, Green CP, Ennis-King J (2015a) Convective dissolution of CO2 in saline aquifers: progress in modeling and experiments. Int J Greenhouse Gas Contr 40(SI):238–266
Emami-Meybodi H, Hassanzadeh H, Green CP, Ennis-King J (2015b) CO2 dissolution in the presence of background flow of deep saline aquifers. Water Resour Res 51:2595–2615
Ennis-King J, Paterson L (2005) Role of convective mixing in the long-term storage of carbon dioxide in deep saline formations. SPE Journal 10(3):349–356
Guo JQ, Wen DG, Zhang SQ, Xu TF, Li XF, Diao YJ, Jia XF (2015) Potential and suitability evaluation of CO geological storage in major sedimentary basin of China, and the demonstration project in Ordos Basin. Acta Geol Sinica 89(4):1319–1332
Hu JW, Duan ZH, Zhu C, Chou IM (2007) PVTx properties of the CO2–H2O and CO2–H2O–NaCl systems below 647 K: assessment of experimental data and thermodynamic models. Chem Geol 238:249–267
IPCC (2005) Carbon dioxide capture and storage. IPCC, Secretariat, Geneva, Switzerland
Li DD, Jiang X (2014) A numerical study of the impurity effects of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide on the solubility trapping of carbon dioxide geological storage. Appl Energy 128:60–74
Li Q, Fei WB, Liu XH, Wei XC, Jin M, Li XC (2014) Challenging combination of CO2 geological storage and coal mining in the Ordos basin, China. Greenh Gases-Sci Technol 4:452–467
Liu HJ, Hou ZM, Were P, Gou Y, Sun XL (2014) Simulation of CO2 plume movement in multilayered saline formations through multilayer injection technology in the Ordos Basin, China. Environ Earth Sci 71:4447–4462
Liu F, Song XF, Yang LH, Han DM, Zhang YH, Ma Y, Bu HM (2015a) The role of anthropogenic and natural factors in shaping the geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Subei Lake basin, Ordos energy base, northwestern Chian. Sci Total Environ 538:327–340
Liu HJ, Hou ZM, Were P, Gou Y, Xiong L, Sun XL (2015b) Modeling CO2-brine-rock interactions in the upper Paleozoic formations of Ordos Basin used for CO2 sequestration. Environ Earth Sci 73:2205–2222
Miri R, Aagaard P, Hellevang H (2014) Examination of CO2-SO2 solubility in water by SAFT1. Implications for CO2 transport and storage. J Phys Chem B 118:10214–10223
Moghaddam RN, Rostami B, Pourafshary P, Fallahzadeh Y (2012) Quantification of density-driven natural convection for dissolution mechanism in CO2 sequestration. Transp Porous Media 92:439–456
Mojtaba S, Behzad R, Rasoul NM, Mohammad R (2014) Experimental study of density-driven convection effects on CO2 dissolution rate in formation water for geological storage. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 21:600–607
Riaz A, Hesse M, Tchelepi HA, Orr FM Jr (2006) Onset of convection in a gravitationally unstable, diffusive boundary layer in porous media. J Fluid Mech 548:87–111
Spycher N, Pruess K (2005) CO2-H2O mixtures in the geological sequestration of CO2. II. Partitioning in chloride brines at 12-100 °C and up to 600 bar. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:3309–3320
Spycher N, Pruess K (2010) A phasepartitioning model for CO2-brine mixtures at elevated temperatures and pressures: application to CO2-enhanced geothermal systems. Transp Porous Media 82:173–196
Spycher N, Pruess K, Ennis-King J (2003) CO2-H2O mixtures in the geological sequestration of CO2. I. Assessment and calculation of mutual solubilities from 12 to 100 °C and up to 600 bar. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:3015–3031
Su XS, Xu W, Du SH (2013) Basin-scale storage capacity assessment of deep saline aquifers in the Songliao Basin, northeastern China. Greenh Gases: Sci Technol 3:266–280
Tan SP, Yao Y, Piri M (2013) Modeling the solubility of SO2 + CO2 mixtures in brine at elevated pressures and temperatures. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:10864–10872
Xie J, Zhang KN, Hu LT, Pavelic P, Wang YS, Chen MS (2015a) Field-based simulation of a demonstration site for carbon dioxide sequestration in low-permeability saline aquifers in the Ordos Basin, China. Hydrogeol J 23(7):1465–1480
Xie J, Zhang KN, Hu LT, Wang YS, Chen MS (2015b) Understanding the carbon dioxide sequestration in low-permeability saline aquifers in the Ordos Basin with numerical simulations. Greenh Gas: Sci Technol 5(5):558–576
Xu TF, Apps JA, Pruess K (2004) Numerical simulation of CO2 disposal by mineral trapping in deep aquifers. Appl Geochem 19:917–936
Xu TF, Apps JA, Pruess K (2007) Numerical modeling of injection and mineral trapping of CO2 with H2S and SO2 in a sandstone formation. Chem Geol 242:319–346
Xu T, Sonnenthal EL, Spycher N, Pruess K (2006) TOUGHREACT: a simulation program for nonisothermal multiphase reactive geochemical transport in variably saturated geologic media. Comput Geosci 32:145–165
Xu TF, Spycher N, Sonnenthal E, Zhang GX, Zheng LG, Pruess K (2011) TOUGHREACT version 2.0: a simulator for subsurface reactive transport under non-isothermal multiphase flow conditions. Comput Geosci 37:763–774
Zendehboudi S, Khan A, Carlisle S, Leonenko Y (2011) Ex situ dissolution of CO2: a new engineering methodology based on mass-transfer perspective for enhancement of CO2 sequestration. Energy Fuel 25:3323–3333
Zhang W (2013) Density-driven enhanced dissolution of injected CO2 during long-term CO2 geological storage. J Earth Syst Sci 122:1387–1397
Zhao RR, Cheng JM, Zhang K, Liu N, Xu FQ (2015) Numerical investigation of basin-scale storage of CO2 in saline aquifers of Songliao Basin, China. Greenh Gases: Sci Technol 5:180–197
Zheng LG, Apps JA, Zhang Y (2009) On mobilization of lead and arsenic in groundwater in response to CO2 leakage from deep geological storage. Chem Geol 268:281–297
Zheng LG, Apps JA, Spycher N (2012) Geochemical modeling of changes in shallow groundwater chemistry observed during the MSU-ZERT CO2 injection experiment. Int J Greenh Gas Control 7:202–217
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan (No. 20140520143JH) and the Multi-Subjects Research Program for Ph. D Student in Jilin University (2011 J012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Y., Du, S., Lin, G. et al. Dissolution sequestration mechanism of CO2 at the Shiqianfeng saline aquifer in the Ordos Basin, northwestern China. Arab J Geosci 10, 71 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2858-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2858-7