Abstract
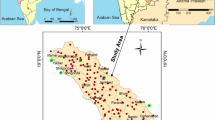
Groundwater resources management in arid regions needs a special considerations, where each stage is affected by a wide variety of technical, social, and economic considerations, and therefore, in an integrated analysis, the foundation stone is the strategic planning, which should include ingredients of basic field data and their simple interpretations, identification of relevant parameters, sub-regions of water priority, and risk assessments. In arid regions, Quaternary deposit aquifer potentiality within any catchment (wadi) is partitioned into subdivisions for strategic planning according to rainfall pattern, morphology, geology, recharge features, and water quality. The climatologic, hydrologic, morphologic, geophysical, and hydrogeological factors combined together lead to a proper assessment of the water availability, abstractability, and recharge possibility in the area. In this paper, rather than deterministic classical approaches, uncertainty in the nature of different factors is explored during the assessment through simple risk concepts. Hence, each key factor (storativity, transmissivity porosity, saturation, and unsaturation thicknesses) is attached with respective risk values leading to groundwater volume calculations. The scenarios of possible strategic groundwater resources management are given on the human population and time bases. The application is presented for one of the major wadis, Wadi Na’man, in the central western part of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitcheson J, Brown JAC (1957) The lognormal distribution with special reference to its uses in economics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 176 pp
Al-Sayari SS, Zotl JH (1978) Quaternary Period in Saudi Arabia. Springer-Verlag, Wien 334p
Al-Sefry S, Şen Z, Al-Ghamdi SA, Al-Ashi W, Al-Baradi W (2004) Strategic ground water storage of Wadi Fatimah—Makkah region Saudi Arabia. Saudi Geological Survey, Hydrogeology project team, final report
Al-Yamani MS, Şen Z (1993) Regional variations of monthly rainfall amounts in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. Fac. Arts and Humanities, (Earth Sciences Division) King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia 6:113–133
Benjamin AC, Cornell CE (1970) Probability, statistics and decision making in civil engineering. Mc-Graw Hill, New York
Bouwer H (1978) Groundwater hydrology. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York 480p
Butler DR, Malanson GP (1993) An unusual early-winter flood and its varying geomorphic impact along a subalpine river in the Rocky Mountains of Montana. USA: Zeitschrifft für Geomorphologie 37:145–155
Chapman RE (1981) Geology and water. An introduction to fluid mechanics for geologists. Dr. W. Junk Publishers, The Hague 228 pp
Davis SN (1969) Porosity and permeability of natural materials. In: DeWeist RJH (ed) Flow through porous media. Academic Press, New York, pp 54–89
Es-Saeed M, Şen Z, Basamad A, Dahlawi A (2004) Strategic groundwater storage of Wadi Na’man—Makkah region, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Geological Survey, Hydrogeology Team Work, Final Report
Freeze AR, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall Book Co., Englewood Cliffs 604 pp
Gheorghe A (1978) Processing and synthesis of hydrogeological data. Abacus Press, Kent 390 pp
Kazakis N, Voudouris KS (2015) Groundwater vulnerability and pollution risk assessment of porous aquifers to nitrate: modifying the DRASTIC method using quantitative parameters. J Hydrol 525:13–25
Krumbein WC, Graybill FA (1965) An introduction to statistical models in geology. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York 475 pp
Larsson I (1972) Ground water in granite rocks and techtonic models. Nord Hydrol 3:111–129
Lloyd JW, Heathcote JA (1985) Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Miller AJ (1990) Flood hydrology and geomorphic effectiveness in the central Appalachians: earth surf. Proc Land forms 15:119–134
Rushton KR (2003) Groundwater hydrology. Conceptual and computational models. John Wiley, New York 416 pp
Seabear PR, Hollyday EF (1966) Statistical analysis of regional aquifers. Amer. Geophys. Union Meeting, San Francisco
Şen Z (1978) Risk and reliability analysis in hydrologic design. Int. Sym. on Risk and Reliability in Water Resources, University of Waterloo, 2:364–375
Şen Z (1986) Determination of aquifer parameters by the slope matching method. Ground Water 24(2):217–223
Şen Z (1999) Simple probabilistic and statistical risk calculations in an aquifer. Ground Water 37(5):748–754
Şen Z (2012) Groundwater risk management assessment in arid regions. Water Resour Manag 26(5): 4510–4524
Şen Z (2014) Practical and applied hydrogeology. Elsevier, New York 406 pp
Şen Z, Baradi A (1991) Sample functions as indicators of aquifer heterogeneities. J. Nord Hydrol 22:37–48
Şen Z, Wagdani E (2007) Statistical evaluation of parameters in heterogeneous aquifers. J Hydrol Eng 18(5):576–581
Shirazi SM, Imran HM et al (2012) GIS-based DRASTIC method for groundwater vulnerability assessment: a review. Journal of Risk Research 15(8):991–1011
Todd DK (1980) Groundwater hydrology. John Wiley and Sons, New York 535pp
Way JH (1968) Bed thickness analysis of some carboniferous fluvial sedimentary rocks near Joggin, Nova Scotia. J Sedimentary Petrology 83:424–435
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şen, Z., As-Sefry, S. & Al-Harithy, S. Strategic management of groundwater resources in the Arabian Peninsula: Wadi Na’man case. Arab J Geosci 10, 50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2824-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2824-9