Abstract
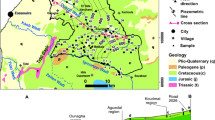
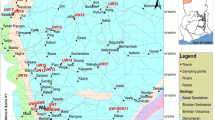
The paper evaluates the quality of groundwater for agricultural use in Tierra Nueva, San Luis Potosi, Mexico, where the agricultural productivity zone presents problems of salinity soil. Twenty groundwater samples and 11 soil samples at 2 depths at each point were collected and analyzed. In this type of water quality study, Wilcox classification diagram and the method of Salinity Laboratory United States for the quality of agricultural land were used. However, in some cases, these rankings do not reflect the actual condition, as in the case of Tierra Nueva, where the soil is classified as normal while water is classified at intermediate good. To analyze the real conditions of soil and water quality indicators of water for agricultural use risk of salinization, sodium adsorption ratio, adsorption ratio magnesium, permeability index, sodium percentage, soluble sodium percentage, residual sodium carbonate, and Kelly ratio were used. Sodicity rates including sodium adsorption ratio indicate no problem in soil extract. However, 25% of water samples are dangerous, with levels ranging from medium to high. For indexes of sodium percentage, residual sodium carbonate, and Kelly ratio, a distribution of classes ranging from questionable to inadequate was applied. Salinity levels show that effective salinity has good classification; potential salinity (PS) is conditional and therefore not recommended; and osmotic potential and electrical conductivity are classified as high in saline water, which is an increasingly important problem. The combination of different indices emphasized serious problems of salinity conditions, particularly sodicity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera M, Martínez R (1996) Relaciones Agua Suelo Planta Atmósfera, 4th edn. Departamento de Irrigación. Universidad Autónoma Chapingo, México, p. 256
Aher KR, Deshpande SM (2011) Assessment of water quality of the Maniyad reservoir of Parala Village, district Aurangabad: suitability for multipurpose usage. Int J Re Trends Sci Technol 1:91–95
Almeida C, Quintar S, González P, Mallea M (2008) Assessment of irrigation water quality: a proposal of a quality profile quality: a proposal of a quality profile. Environ Monit Assess 142(1–3):149–152
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Ayers S, Westcot D (1985) Water quality for agriculture. Rome (Vol. 29). Rome: FAO: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Roma, Italia. 163–174
Barrios-Castillo I (2014) Calidad de aguas naturales y residuales en el sistema hidrográfico del Valle del Mezquital, Hidalgo, México. Tesis de Maestría, Colegio de Posgraduados. Montecillo, México. p 155
De Pascale S, Barbieri G (1995) Effects of soil salinity from long-term irrigation with saline-sodic water on yield and quality of winter vegetable crops. Sci Hortic 64(3):145–157
Deshpande SM, Aher KR (2012) Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agriculture use in parts of Vaijapur, district Aurangabad, MS. India Res J Chem Sci 1:25–31
Doneen LD (1964) Notes on water quality in agriculture. Department of Water Science and Engineering. University of California, Davis
Eaton FM (1950) Significance of carbonates in irrigation water. Soil Sci 69:123–133
Essien OE, Ubit F (2013) Investigation of Ikpa river water quality with consideration for domestic and agricultural uses. Wudpecker J Agric Res 2:315–323
Grattan SR, Oster JD (2003) Use and reuse of saline-sodic waters for irrigation of crops. J C Prod 7:131–162
Hamdy A, Abdel-Dayem S, Abu-Zeid M (1993) Saline water management for optimum crop production. Agric Water Manag 24:189–203
Hinrichsen D, Robey B and Upadhyay UD (1998) Solutions for a water-short world. Population Reports. Series M: Special Topics (14): 1–31
Ishaku JM, Ahmed AS, Abubakar MA (2011) Assessment of groundwater quality using chemical indices and GIS mapping in Jada area. Northeastern Nigeria J Earth Sci Geotechn Eng 1:35–60
Joshi N, Chauhan A, Joshi PC (2009) Impactos de los contaminantes del aire industriales sobre algunos parámetros bioquímicos y de rendimiento en plantas de trigo y mostaza. Ecologista 29:98–104
Kelly WP (1940) Permissible composition and concentration of irrigated waters. Proceedings of the A.S.C.F, In, p. 607
Mancilla O (2012) Índices de Salinidad y Calidad de las aguas superficiales de Tlaxcala, Puebla y Veracruz. Tesis de Doctorado, Colegio de Posgraduados. Montecillo, México. p 263
Mateo-Sagasta J, Burke J (2012) Agriculture and water quality interactions: a global overview. SOLAW Background Thematic Report—TR08. FAO, Italy
MGS, Servicio Geológico Mexicano (1999) Carta geológico-minera Tierra Nueva F14-C25
Miguez-Macho G, Fan Y (2012) The role of groundwater in the Amazon water cycle: 2. Influence on seasonal soil moisture and evapotranspiration. J Geophys Res 117:D15114. doi:10.1029/2012JD017540
Nag SK, Ghosh P (2013) Variation in groundwater levels and water quality in Chhatna block, Bankura District, West Bengal—a GIS approach. J Geol Soc India 81:261–280
Obiefuna GI, Sheriff A (2011) Assessment of shallow ground water quality of Pindiga Gombe area, Yola area, NE. Nigeria Irrig Domest Purposes Res J Environ Earth Sci 2:31–141
Palacios O, Aceves E (1970) Instructivo para el registro, muestreo e interpretación de datos de calidad del agua para riego. Colegio de Posgraduados. Serie de Apuntes No. 15. Chapingo, México. p 49
Paliwal KV (1967) Effect of gypsum application on the quality of irrigation waters. Turkish J Eng Environ Sci 30:203–219
Peinado H, Green C, Herrera J, Escolero O, Delgado O, Belmonte S, Ladrón M (2011) Calidad y aptitud de uso agrícola y doméstico del agua del acuífero del río Sinaloa, porción costera. Hidrobiológica 1:63–76
Pérez C, Martínez M, Sánchez J (2003) Efecto del riego con agua de mala calidad sobre la desertificación de zonas semi-áridas en Murcia. España Geoderma 113:109–125
Porta J, López-Acevedo M, Poch R (2010) Introducción a la Edafología: uso y protección de suelos, 2a edn. Mundi-Prensa, Madrid, España, p. 607
Pulido-Madrigal L, Simuta-Champo R, González-Meraz J, Saucedo H (2012) Producción Agrícola Sustentable en Condiciones de Sobreexplotación de Agua Subterránea. Terra latinoamericana 30(4):303–313
Raghunath HM (1987) Ground water: hydrogeology, ground water survey and pumping tests, rural water supply and irrigation systems. New Age International
Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Soil Sci 78(2):154
Rifat AW, Aabid HM, Aasimah T, Arshid J, Yousuf AR (2014) Preliminary study on irrigational quality of some ground water sources of Kashmir, India. Int J Sci Eng Res 5(2):318–323 ISSN 2229-5518
Rodríguez M, D’Urso C, Rodríguez G, Sales A (2008) Evaluación de la Calidad de Aguas para Riego de la Cuenca del Río Calera, Tucumán, Argentina. Ciencia 7:15–28
Romero J (2009) Calidad del agua, 3rd edn. Editorial Escuela colombiana de Ingeniería, Bogotá Colombia, p. 484
Rosas-Palafox A (2014) Caracterización geoeléctrica de la cuenca hidrológica de Tierra Nueva. S. L. P. Tesis de licenciatura. Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla, Puebla, México, p. 59
Ruda E, Mongiello A, Acosta A, Ocampo E, Contini L (2005) Calidad del agua subterránea con fines de riego suplementario en Argiudoles del Centro de Santa Fe. Argentina Agric Téc 4:411–420
Sharma DP, Rao KVGK (1998) Strategy for long term use of saline drainage water for irrigation in semi-arid regions. Soil Tillage Res 4:287–295
Sims JL and Patrick WH (1978) Micronutrient cations in soil under varying redox potential and pH. Soil Sci Soc Am J. 42
Stevenson FJ and Ardakani MS (1972) Organic matter reactions involving micronutrients in soils, p. 79–114. In J.J. Mortvdt et al. (ed) Micronutrients in agriculture. Soil Sci. Soc. of Am. Madison
Thien SJ (1979) A flow diagram for teaching texture by feel analysis. J Agronomic Education 8:54–55
Todd DK, Mays L (1980) Groundwater hydrology, 3rd edn. Wiley International Edition, New York, p. 656
Tristán MG (1987) Cartografía geológica “Hoja Tierra Nueva”, S. L. P. escala 1:50000. Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí, Folleto Técnico 109FAO/UNESCO 2001
Urbano Terrón, P. (2002) Fitotecnia: ingeniería de la producción vegetal. Ediciones Mundi- Prensa (Madrid). p 528
Wilcox LV (1955) Circular 969. Classification and use of irrigation waters. United States Deparment of Agriculture, Washington, D. C, p. 19
Acknowledgements
We are also grateful to the two reviewers for their help in the general improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramos-Leal, J.A., López-Álvarez, B., Santacruz-De León, G. et al. Quality indices of groundwater for agricultural use in the region of Tierra Nueva, San Luis Potosi, Mexico. Arab J Geosci 9, 736 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2758-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2758-2