Abstract
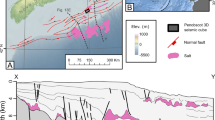
Most of hydrocarbon accumulations within the Gulf of Hammamet foreland basins in eastern Tunisia are reservoired within the Upper Miocene Birsa and Saouaf sandstones. It is the case of Birsa, Tazarka, Oudna, Baraka, Maamoura, Cosmos and Yasmine fields. These sandstones constitute oil and gas fields located on folded and faulted horst anticline highs and described as varying from shoreface to shallow marine and typically exhibit excellent reservoir quality of 30 to 35% porosity and good permeability from 500 to 1100 md. In addition, the fracturing of faults enhanced their reservoir quality potential. However, due to the lack of seismic stratigraphic studies to highlight depositional environment reservoir characterization and distribution, petroleum exploration faces structural and stratigraphic trap types and remains on targeting only high fold closures with limited reserve volumes of hydrocarbons. As an example of the Birsa concession case, syn-sedimentary tectonic structuring and geodynamic evolution during Middle to Upper Miocene Birsa reservoir sequences have guided the distribution of depositional environment of sandstone channel systems around horst and grabens by E-W, NE-SW and N-S strike slip flower faults controlling the subsidence distribution combined with the eustatic sea level variations. Seismic sequence stratigraphy study of Miocene Birsa reservoir horizons, based on the analysis and interpretations of E-W and N-S 3D selected regional lines that were compared and correlated to outcrops and calibrated by well data, permitted to highlight the basin configuration and sequence deposit nature and distribution. Sedimentary infilling of the basin from Langhian Ain Ghrab carbonate to Serravallian Tortonian Birsa and Saouaf sandstone and shale formations is organized in four third-order seismic sequences, limited by regional erosional toplap, onlap and downlap unconformity surfaces and by remarkable chronostratigraphic horizons of forced and normal erosive lowstand and highstand system tracts separated by transgressive and maximum flooding surfaces. Reconstructed sedimentary paleo-environment distribution vary from deltaic fluvial proximal deposits in the northern part of the high central Birsa horst to a delta front and prodelta coastal and shelf shore face and shore line channelized deposits in the surrounding borders of grabens. Distal deposits seem to be distributed from upper to lower slope fans and probably to the basin floor on the flanks of the subsiding grabens. Synthetic predictive paleogeographic depositional reservoir fairway map distribution of Lower, Middle and Upper Birsa sandstone reservoirs highlights four main domains of channelized superposed and shifted reservoirs to explore.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbès A, Polak M (1981) La formation Saouaf dans les synclinaux de la Dakhla (CapBon) et de Saouaf (Tunisienord-orientale). Notes Serv Geol Tun n°46:99–111
Abbès A (1983) Etude géologique et géophysique du Miocène de la Dakhla (Cap-Bon, Tunisie nord orientale): application à la prospection des couches lignitifères. Thèse 3 eme cycle, Fac. Sci. et Tech., Univ. Franche-Comte 199 p.
Bédir M, Tlig S (1992) Structuration des paraséquences miocènes le long des couloirs de coulissements de subsurface de la marge orientale de la Tunisie. 3ème Journées de l’exploration pétrolière. ETAP. Tunis 1992:8–9
Bédir M, Tlig S (1993) Les séquences turbiditiques miocènes du jebel Abderrahman eau Cap Bon, en Tunisie nord orientale. ème Meeting régional de sédimentologie. Marrakech. Maroc, 27–29 Avr. p.47.
Bédir M, (1995) Mécanismes géodynamiques des bassins associés aux couloirs de coulissements de la marge atlasique de la Tunisie, seismo-stratigraphie, seismo-tectonique et implications pétrolières. Thèse Doctorat d’Etat, Université de Tunis II, 412 p.
Bédir M, Tlig S, Bobier C, Aissaoui N (1996) Sequence stratigraphy, basin dynamics and petroleum geology of the Miocene from eastern Tunisia. A. A.P.G. Bulletin 80(1):63–81
Bédir M, Lachaal F, Chebbi MR, Gharsalli R, Khomsi S, Zouaghi T, Soussi M (2012) Geophysic and Geologic Deep Water Reservoir Characterization and Evaluation I Eastern Tunisia. American Water Resource Association Conference. 12–15 November, Jacksonville, Florida, USA.
Bédir M, Khomsi S, Houatmia F (2015) Basin dynamics and sedimentary in filling of Miocene sandstone reservoir systems in Eastern Tunisian African margin. European Geoscience Union General Assembly, 12–17 April 2015, Vienna.
Ben Brahim A (1991) Tunisia exploration review—Miocene Birsa Formation. ETAP – Schlumberger Conference. Tunis, pp. 95–107.
Ben Ferjani A, Burollet PF, Mejri F (1990) Petroleum geology of Tunisia. Mem. ETAP N°1. Tunis, 194 p.
Ben Ismail-Lattrache K (1981) Etude micropaléontologique et stratigraphique des séries paléogènes de l’anticlinal du jebel Abderrahmane (Cap Bon, Tunisie nord-orientale). Thèse 3eme cycle, Univ. Tunis II. Fac. Sci., 224 p.
Ben Salem H (1990) Carte géologiques de la Tunisie au 1/50000, feuille deTazoghrane, N°15, édition du Serv. Géol. de la Tunisie.
Ben Salem H (1992) Contribution à la connaissance de la géologie du Cap Bon: Stratigraphie, tectonique et sédimentologie. Thèse 3ème cycle, Univ. Tunis II. Fac. Sci., p. 203
Besème P, Blondel T (1989) Les séries à tendance transgressive marine du Miocène inférieur à moyen en Tunisie centrale. Données sédimentologiques, biostratigraphiques et paléoécologiques. Rev Paléobiol 8:187–207
Besème P, Kamoun Y (1988) Le Messinien marin de Ksour Essef (Sahel de la Tunisie orientale): une étude stratigraphique. In: sédimentologique et Paléontologique. Rev. Sci. De la, vol 8. Terre, Tunisie, pp. 129–142
Biely A, Rakus M, Robinson P, Salaj J (1972) Essai de corrélation des Formations miocènes au Sud de la dorsale Tunisienne. Notes Serv Geol Tunisie n° 26:73–92
Bismuth H (1984) Les unités lithostratigraphiques du Miocène en Tunisie orientale. Soc. Sci, De la Terre, Tunis, 2 p
Bobier C, Viguier C, Chaari A, Chine A (1991) The post-Triassic sedimentary cover of Tunisia: seismic sequences and structure. Tectonophysics 195:371–410
Bouaziz S, Barrier E, Soussi M, Turki MM, Zouari H (2002) Tectonic evolution of the northern African margin in Tunisia from paleostress data and sedimentary record. Tectonophysics 357:227–253
Bouma AH, Delery AM (2007) Fine grained Permian turbidites of south western South Africa:Tanqua Karoo and Laingsburg deep water basins In T. H. Nilsen, R. D. Shew GS, Steffens, JRJ, Stdlick, cds., Atlas of deep water outcrops: AAPG Studies in Geolog 56, CD ROM, 19 p.
Brehm JA (1993) The reservoir geology of the belli field (Marathon). ETAP –Fractured Reservoir Seminar:21–28
Burollet PF (1956) Contribution a l’étude stratigraphique de la Tunisie centrale. Anal Min Géol (Tun) n°18:350
Catuneanu O (2002) Sequence stratigraphy of clastic systems: concepts, merits, and pitfalls. J Afr Earth Sci 35(1):1–43
Catuneanu O (2003) Sequence stratigraphy of clastic systems. Geol Assoc Can, Short Course Notes 16:248
Catuneanu O (2006) Principles of sequence stratigraphy. First edition. Elsevier, The Netherlands, p 375
Chapin MA, Davies P, Gibson JL, Pettingill HS (1994) Reservoir architecture of turbidite sheet sandstones in laterally extensive outcrops, Ross formation, western Ireland. In: Weimer P, Bouma AH, Perkins BF (eds) Submarine fans and turbidite systems: Gulf Coast section SEPM foundation 15th. Annual research conference, pp. 53–68
Colleuil B (1976) Etude stratigraphique et néotectonique des Formations Néogènes et Quaternaires de la région de Nabeul-Hammamet (Cap-Bon, Tunisie). Diplôme d’Etudes Supérieures, Nice,France 93 p.
Craig AN (2010) Petroleum systems and Prospectivity of the Gulf of Hammamet. Report, Tunisia Cooper Energy, 14 p
ETAP (1998) Proceedings des Journées de l'exploration pétrolières de la Tunisie, Mem. 13
Fournié D (1978) Nomenclature lithostratigraphique des séries du Crétacé supérieur auTertiaireen Tunisie. Bull. Centres Rech. Pau-SNPA, pp. 97–148.
Gardner MH, Sonnenfeld MD (1996) Stratigraphic changes in facies architecture of thePermian BrushyCanyon formation in Guadalupe Mountain National Park. West Texas:Permian Basin Section-SEPM, publication 96-38:17–40
Gaaya A, Ghenima R (1998) Source rock and related petroleum systems in Tunisia. Revue Tunisienne de l’Energie: Special Exploration N°50, 3ème trimestre, pp.33–45.
Galloway WE (1989a) Genetic stratigraphic sequences in basin analysis: architecture and genesis of flooding-surface bounded depositional units. AAPG Bull 73(2):125–142
Galloway WE (1989b) Genetic stratigraphic sequences in basin analysis II: application to Northwest Gulf of Mexico Cenozoic Basin. AAPG Bull v. 73, n 2:pp. 143–154.
Gharsalli R (2006) Etude des séries miocènes et réservoirs associés dans le Cap Bon et le golfe d’Hammamet. Mémoire du Mastère, Université Tunis-El Manar, Tunisie, p 120
Gharsalli R, Zouaghi T, Soussi M, Chebbi R, Khomsi S, Bédir M (2013) Seismic sequence stratigraphy of Miocene deposits related to eustatic, tectonic and climatic events, Cap Bon peninsula, north- eastern Tunisia. In press, Comptes Rendus Geosciences, p 37
Haq BU, Hardenbol J, Vail PR (1987) The chronology of the fluctuating sea level since theTriassic. Science 235:1156–1167
Haq BU, Hardenbol LJ, Vail PR (1988) Mesozoic and Cenozoic chronostratigraphy and cycles of sea-level change. In: Wilgus CK, Hastings BS, Kendall, CG, Posamentier HW, Ross, CA, Van Wagoner, JC (eds.) Society of Economic Paleantologists and Mineralogists, SEPM, special publication, v. 42, pp. 71–108.
Hardenbol J, Thierry J, Farley MB, Jacquin T, de Graciansky PC, Vail PR (1998) Mesozoic and Cenozoic sequence chronostratigraphic framework of European basins. SEPM,Spec.Pub. 60, chart 6.
Homewood PW, Mauriaud P, Lafont, P (2002) Best Practicies in Sequence Stratigraphy for Explorationists and Reservoir Engineers. Total Fina Elf Publications. Pau 2002, p. 81.
Hooyberghs HJF (1995) Synthèse sur la stratigraphie de l’Oligocène, Miocène et Pliocène deTunisie. Notes Serv Geol Tun n°61:63–72
Hooyberghs HJF, Ben salem H (1999) Biostratigraphie des foraminifères planctoniques de la Formation Saouaf (Tortonien) dans le synclinal de Takelsa (CapBon, Tunisie). Notes ServGeol Tun n°66:13–124
Jeddi RS (2001) Oligocene-Miocene reservoirs and seals in the Gulf of Hammamet. Hydrocarbon Project Progress Report ETAP, 25 p.
Jeddi RS, Kharbachi S, El Maherssi L (2004) Miocene play in Eastern Tunisia. Field trip guide book. ETAP Mem. N°20. The 9th Tunisian Petroleum Exploration & Production Conference.
Khomsi S, Bédir M, Soussi M, Ben Jemia MG, Ben Ismail-Lattrache K (2006) Mise en évidence en subsurface d’événements compressifs Eocène moyen-supérieur en Tunisie orientale (Sahel): Généralité de la phase atlasique en Afrique du Nord. CR Géoscience 338(n° 1–2):41–49
Khomsi S, Ben Jemia MG, de Lamotte FD, Maherssi C, Echihi O, Mezni R (2009) An overview of the late cretaceous–Eocene positive inversions and Oligo- Miocene subsidence events in the foreland of the Tunisian atlas: structural style and implications for the tectonic agenda of the Maghrebian atlas system. Tectonophysics 475(1):38–582. doi:10.1016/j.tecto. 2009. 02.027
Klett TR (2000) Total Petroleum Systems of the Pelagian Province, Tunisia, Libya, Italy and Malta. The Bou Dabbous-Tertiary and Jurassic-Cretaceous Composite. USGS Geolgical Survey Bulletin D 2201
Lakin M (2013) Offshore Northern East Tunisia (Sicily Channel). Project synopsis 207 Report, ADX Ebergy, p 16
Mahaffie MJ (1994) Reservoir classification for turbidite intervals at the Mars discovery, Mississippi Canyon 807, Gulf of Mexico. In: Weimer P, Bouma AH, Perkins BF (eds) Submarine fans and turbidite systems, sequence stratigraphy, reservoir architecture and production characteristics: Gulf Coast section SEPM 15th annual research conference, pp. 233–244
Lundin (2005) Birsa Reservoir Study. Internal Report, 115 p.
Mahjoub M N, Khessibi M, Laridhi Ouazza L (1989) Découverte de conglomérats et galets granitiques dans les grés de groupe Oum Douil au Cap Bon. Proposition d’un modèle sédimentologique du Miocène moyen dans le NE de la Tunisie. Actes du 2ème j. de geol. tunisienne appliqué à la recherché des hydrocarbures, ETAP, pp. 369–394.
Mannai-Tayech B (2006) Les series silicoclastiques miocènes du Nord-Est au Sud-Ouest de laTunisie: une mise au point. Geobios 39:71–84
Mannai Tayech B (2009) The lithostratigraphy of Miocene series from Tunisia, revisited. J Afr Earth Sci 54:53–61
Mejri F, Burollet PF, Ben Ferjani A (2006) Petroleum geology of Tunisia, a renewed synthesis. Entrep Tunis Activ Petrol Mem (22):233
Melki F, Zouaghi T, Harrab S, Casas Sainz A, Bédir M, Zargouni F (2011) Structuring and evolution of Neogene transcurrent basins in the Tellian foreland domain, north-easternTunisia. J Geodyn. doi:10.1016/j.jog.2010.11.009
Méon H, Tayech B (1986) Étude palynologique dans le Miocène du Cap Bon (Tunisie). Essai d’établissement d’écozones et reconstitution paléogéographique Geobios 19:601–626
Mitchum RMJR, Vail PR, Sangree JB (1977) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level 6: stratigraphic interpretation of seismic reflection patterns in depositional sequences. Seismic stratigraphy- application exploration. A.A.P.G. Mém. 26:117–132
Mitchum RM Jr (1985) Seismic stratigraphic expression of submarine fans. Seismic stratigraphy II: an integrated approach to hydrocarbon exploration, pp. 117–138.
Patriat M, Ellouz N, Dey Z, Gaulier JM, Ben Kilani H (2003) The Hammamet, Gabes and Chotts basins (Tunisia): a review of the subsidence history. Sediment Geol 156:241–262
Richards M, Bowman M, Reading H (1998) Submarine-fan systems I: characterization and stratigraphic prediction. Mar Pet Geol 15:687–717
Robinson P (1971) The Beglia formation of Tunisia: Mémoire Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières. Vème Congrès Néogène en Méditerranée 78:235–237
Robinson P, Wiman S (1976) Are vision of the stratigraphie subdivision of the Miocène rock of sub-Dorsale Tunisia. Notes Serv Géol Dela Tunisie (n° 42):445–449
Saidi M, Acheche MH, Inoubli M, Belayouni H (1989) Identification et caractérisation des roches mères en Tunisie centrale. In: Actes des IIème Journées de Géologie Tunisienne Appliquée à la recherche des hydrocarbures. Mémoire ETAP, vol 3. Tunis, Tunisie, pp. 429–457
Salaj J, Stranik Z (1970) Contribution à l’étude stratigraphique du Miocène du synclinal de Saouaf (région du Jebel Fkirine, Tunisie orientale). Notes du Service Géologique de Tunisie (n°. 32):79–82
Sangree JB, Widmier JM (1977) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level, part 9: seismic interpretation of clastic depositional facies. Seismic stratigraphy application to hydrocarbon exploration. A.A.P.G. Mém 26:165–184
Sharnugam G (2003) Deep-marine tidal bottom currents and their reworked sands in modern and ancient submarine canyons. Mar Pet Geol 20(2003):471–491
Shew RD, Steffens GS, Studlick JRJ (2007) Deep-water exploration and production: a global overview, eds., atlas of deep-water outcrops. AAPG Stud Geol 56:28
Shell Exploration (1988) Internal Report. 52 p. Tunisia
Slatt RM, Minken J, Van Dyke SK, Pyles DR, Witten AJ, Young RA (2007) Scales of heterogeneity of an outcropping leveed-channel deep water system, Cretaceous Dad Sandstone Member, Lewis Shale,W yoming, USA,. H. Nilsen, R. D. Shew, G. S. Steffens, and J. R. J. Studlick, (eds.),29 p. Atlas of deep-water outcrops: AAPG Studies in Geology 56, 29 p.
Tayech B (1984) Etude palynologique dans le Néogène du Cap Bon(Tunisie).Thèse 3ème cycle, Univ. Paris VI, 266 p.
Touati MA, Brehm JA, Tenhave LE (1994) Tectonic development of the Belli field area. Mem. N°7 ETAP, pp. 365–378.
Vail PR, Mitchum RMJ, Todd RG, Widmier JW, Thomson S, Sangree JB, Bubb JM, Hatelid WG (1977) Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level, in: seismic stratigraphy, application to hydrocarbon exploration. AAPG, memory 26(49):49–212
Vail PR (1987) Seismic stratigraphy interpretation using stratigraphy, Part 1, Seismicstratigraphy interpretation procedure Atlas of Seismic Stratigraphy, AAPG studies in Geology, memory 27 1:1–10
Vail PR, Audemard E, Bowman S, Eisner PN, Pers Cruz C (1991) The stratigraphic signatures of tectonics, eustacy and sedimentology. An overview. In: Einsel G, Ricken W, Seilacher A et al (eds) Cycles andevents in stratigraphy. Spinger, Verlag, Berlin, pp. 617–659
Van Wagoner JC, Posamentier HW, Mitchum RM, Vail PR, Sarg JF, Loutit TS, Haedenbol J (1988) An overview on the fundamentals of sequence stratigraphy and key definitions. In: C.K Wilgusetal. (eds.), Sea level changes an integrated approach, SEPMS pec. Pub. 42:39–45
Weimer P, Henry S, Pettingill R (2007) Deep-water exploration and production A global overview, in Nilsen TH, Shew RD, Steffens GS, Studlick JRJ eds Atlas of deep-water outcrops: AAPG Studies in Geology, 56, CD-ROM, p 29
Zouaghi T, Melki F, Bédir M, Inoubli MH (2009) Structure, tectono-sedimentary events and geodynamic evolution of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic foreland basins, using 2D seismic data, northeastern Tunisia. 6th International Symposium on Geophysics, Tanta, Egypt, p 42
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Teico exploration company for the permission to publishing seismic lines and the well log data of Birsa concession. We are grateful to the two reviewers and especially Mira Rabineau for their efforts and suggestions that had improved considerably this final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Arabian Plate: Lithosphere Dynamics, Sedimentary Basins and Geohazards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bédir, M., Arbi, A., Khomsi, S. et al. Seismic tectono-stratigraphy of fluvio-deltaic to deep marine Miocene silicoclastic hydrocarbon reservoir systems in the Gulf of Hammamet, northeastern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 9, 726 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2745-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2745-7