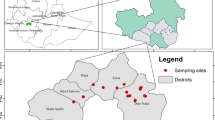
Abstract
The Chtouka-Massa area in Southern Morocco has shown an increase in water scarcity during the last decades, caused mainly by withdrawal of water resources aggravated by agricultural intensification and climate change impacts. To better understand the changes of groundwater quality, a sampling campaign was conducted in many wells during March 2015 and compared to historical chemical data from the hydraulic basin agency, as well as previous studies performed at Ibn Zohr University. All data were used to assess the spatial-temporal evolution of nitrate and salinity relevant to the recent sampling. This paper describes the current state of groundwater quality in the Chtouka-Massa zone with an overview of different sources of water mineralization and the nitrate evolution in an agricultural area. Our results indicate a general increase in mineralization from the north to the south, and from the east to the west. The plain, dominated by farms, shows a relatively high conductivity (up to 2000 μS/cm), while in both costal area and Anti-Atlas Mountain the water salinity shows a gradient increase from the north to the south. However, the highest electrical conductivity is observed along the Massa River. The water type is bicarbonate, chloride, and sodium for farm samples, while from the other parts, it is mostly dominated by chloride and sodium. The spatial-temporal analysis of nitrates generally shows an increasing trend. However, the levels remain overall lower than the limit. The temporal evolution of control points set by the hydraulic agency shows a decreasing trend decline that can be explained by the improvement of agriculture practices, including the conversion towards drip irrigation mode. Different chemical tracers highlighted some processes involving the changes of mineralization of groundwater (e.g., irrigation water return, marine intrusion, and water/rock interaction). The results will be used to improve water management in this area showing water quality degradation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABHSMD Agence Du Bassin Hydraulique De Souss-Massa-Draa (2006) Plan directeur d’aménagement intégré des ressources en eau (PDAIRE). Chapitre 3
ABHSMD Agence Du Bassin Hydraulique De Souss-Massa-Draa (2008) Plan directeur d’aménagement intégré des ressources en eau (PDAIRE). Chapitre 6
Aghzar N, Berdai H, Bellouti A, Soudi B (2002) Groundwater nitrate pollution in Tadla (Morocco). Rev Sci Eau 15:495–492
Ahkouk S, Hsissou Y, Bouchaou L, Krimissa M, Mania J (2003) Impact des fertilisants agricoles et du mode d’irrigation sur la qualité des eaux souterraines (cas de la nappe libre des Chtouka, bassin du Souss-Massa, Maroc). Afr Geosci Rev 9:355–364
Ahkouk S. (2004) Impact des fertilisants agricoles et du mode d’irrigation sur la qualité des eaux souterraines en zones irriguées sous climat semi-aride: cas de la plaine des Chtouka, bassin du Souss-Massa, Maroc. Thèse Doctorat 3ème Cycle, Université Ibn Zohr, Agadir, Maroc
Belghiti M.L, Chahlaoui A, Bengoumi D, El Moustaine R (2013) Etude de la qualité physico-chimique et bactériologique des eaux souterraines de la nappe plio-quaternaire dans la région de Meknes. Larhyss J, ISSN 1112–3680, pp. 21–36.
Bernert, G. (1968) Etude Hydrogéologique des Chtouka Nord. Exploitation des ressources disponibles
Bouchaou L, Michelot JL, Vengosh A, Hsissou Y, Gaye CB, Bullen TD, Zuppi GM, Qurtobi M (2008) Application of multiple isotopic and geochemical tracers for investigation of recharge, salinization, and residence time of water in the Souss–Massa aquifer, southwest of Morocco. J Hydrol 352:267–287
Boutaleb S, Bouchaou L, Mudry J, Hsissou Y, Chauve P (2000) Effects of lithology on quality of water resources. The case of oued Issen (Western Upper Atlas, Morocco). Hydrogeol J 8:230–238.
C.A.G. (1964) Compagnie Africaine de Géophysique : Etude par prospection électrique dans la plaine du Souss et dans la région de Tiznit. Rapp. Inédit. DRPE, Rabat 54 p.
Choubert G (1963) Histoire du précambrien de l’Anti-Atlas. Tome 1. Note et Mém. Serv. Géol. Maroc. n° 162, 352p
Cosserat M, Decau J, Patacq-Crontzet H, Pujol B (1990) Fertigation in coarse-textured soil. Consequences on production and nitrate pollution. In: Calvet R (ed) Nitrate-agriculture-eau. INRA, Paris, pp. 257–262.
Dindane K, Bouchaou L, Hsissou Y, Krimissa M (2003) Groundwater in the Souss upstream basin, southwestern Morocco: evidences to its chemical evolution and origin. J Afr Earth Sci 36:315–327.
Fakir Y, Zerouali A, Aboufirassi M et Bouabdelli M. (2001) Exploitation et salinité des aquifères de la Chaouia côtière, littoral atlantique, Maroc. J Afr Earth Sci Vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 791–801.
Fedrigoni L, Krimissa M, Zouari K, Maliki A and Zuppi G.M. (2001) Origine de la minéralisation et comportement hydrogéochimique d’une nappe phréatique soumise à des contraintes naturelles et anthropiques sévères : exemple de la nappe de Djebeniana (Tunisie). C R Acad Sci Paris, Sci Terre Planètes / Earth Planet Sci 332 : 665–671
Ghazali D, Zaid A (2013) Etude de la qualité physico-chimique et bactériologique des eaux de la source Ain SALAMA-JERRI (Région de MEKNES, Maroc) Larhyss J ISSN 1112–3680, pp. 25–36
Grassi S, Cortecci G (2004) Hydrogeology and geochemistry of the multilayered confined aquifer of the Pisa plain (Tuscany–central Italy). Appl Geochem 20:41–54.
Haut-Commissariat Au Plan (2013) Annuaire statistique de la région de SOUSS-MASSA-DRAA. 173:86–90.
Hsissou Y, Mudry J, Bouchaou L, Chauve P, Mania J (2002) Use of chemical tracy to study acquisition modality of mineralization and behaviour of unconfined groundwater under semi-arid climate: the case study of the Souss plain (Morocco). Environ Geol 42:672–680.
Hsissou Y, Mudry J, Mania J, Bouchaou L and Chauve P (1997) Dynamique et salinité de la nappe côtière d’Agadir (Maroc). Influence du biseau salé et des faciès évaporitiques. I.A.H.S. publication, n° 244, p 73–82.
Hsissou Y, Mudry J, Mania J, Bouchaou L, Chauve P (1999) Utilisation du rapport Br/Cl pour déterminer l'origine de la salinité des eaux souterraines: exemple de la Plaine du Souss (Maroc). C R Acad Sci Paris 328:381–386.
Hsissou, Y., (1999) Impact de l’environnement naturel et anthropique sur la qualité des eaux alluviales en zone semi-aride: cas de la plaine du Souss (Maroc). Thèse Doct. d’Etat. Univ. Ibn Zohr. Agadir (Maroc). 226 p.
Jalali M (2008) Geochemistry characterization of groundwater in an agricultural area of Razan, Hamadan, Iran. Environ Geol (2009) 56:1479–1488
Kim J.G, Chon C-M, Lee J-S (2004) Effect of structure and texture on infiltration flow pattern during flood irrigation. Environ Geol, 46: 962–969.
Kouzana L, Ben Mammou A, Sfar Felfoul M (2009) Seawater intrusion and associated processes: case of the Korba aquifer (Cap-Bon, Tunisia). Compt Rendus Geosci 341:21–35.
Krimissa S (2005) Nappe superficielles en zone semi-aride : origine des eaux et de la salinité, Renouvellement. Exemple des nappes Massa et Souss. Thèse Doctorat 3ème Cycle, Université Ibn Zohr, Agadir, Maroc.
Krimissa S, Michelot JL, Bouchaou L, Mudry J, Hsissou Y (2004) Sur l’origine par altération du substratum schisteux de la minéralisation des eaux d’une nappe côtière sous climat semi-aride (Chtouka Massa, Maroc). Compt Rendus Geosci 336:1363–1369.
Lgourna Z, Warner N, Bouchaou L, Boutaleb S, Tagma T, Hsaissoune M, Ettayfi N, Vengosh A (2013) Investigation of groundwater salinity in the Ziz Basin, southeastern Morocco, by using hydrochemical and isotopic tools. Mineral Mag 77(5):1594.
Martos FS, Bosch PA, Sanchez LM, Vallejos-Izquierdo A (2001) Identification of the origin of salinization in groundwater using minor ions Lower Andarax, Southeast Spain. Sci Total Environ 297:43–58.
Morsli B (2007) Étude de l’intrusion marine et de ses répercussions sur la dégradation des sols : cas des zones côtières d’Alger Est: Actes des JSIRAUF, Hanoi.
Olobaniyi SB, Owoyemi FB (2006) Characterization by factor analysis of the chemical facies of groundwater in the deltaic plain sands aquifer of Warri, western Niger Delta, Nigeria. AJST Sci Eng Ser 7:73–81.
Pixie AH, Dennis RH (1995) Effects of agriculture on groundwater quality in five regions of the United States. Ground Water 33:217–226.
Schoeller, H., 1964. La classification géochimique des eaux. TASH Publication, iahs. Info, pp. 16–24.
Smiler R (2005) Diagram. Avignon University, France, Laboratory of Hydrogeology.
Tagma T, Hsissou Y, Bouchaou L, Bouragba L, Boutaleb S (2009) Groundwater nitrate pollution in Souss-Massa basin (South-West Morocco). Afr J Environ Sci Technol 3:301–309
Trabelsi R, Zaïri M, Smida H, Ben Dhia H (2005) Salinisation des nappes côtières: cas de la nappe nord du Sahel de Sfax, Tunisie. Compt Rendus Geosci 337:515–524.
Warner N, Lgourna Z, Bouchaou L, Boutaleb S, Tagma T, Hsaissoune M, Vengosh A (2013) Integration of geochemical and isotopic tracers for elucidating water sources and salinization of shallow aquifers in the sub-Saharan Draa Basin, Morocco. Appl Geochem 34:140–151.
WHO, (2006) World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking-water quality—Volume 1: Recommendations. 3rd edition, incorporating first and second addenda. Available from: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/gdwq3rev/en/
Zocovic D (1965) Sur le rapport de la solubilité des calcaires et des dolomies. Colloque sur l’hydrologie de roches fissurées. Paris, 10 septembre 1965
Acknowledgments
We thank the Hydraulic Basin Agency of Souss-Massa-Draa for their support and cooperation in providing all necessary data. Our gratitude to the University of Bonn, Germany, for their contribution to the sampling campaign and chemical analysis. We also thank the project GLOBAQUA and WASA for the financial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Water Resources in Arid Areas
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mouna, M., Redouane, CA., Lhoussaine, B. et al. Evolution of groundwater quality in intensive agricultural zone: case of Chtouka-Massa Aquifer, Morocco. Arab J Geosci 9, 566 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2592-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2592-6