Abstract
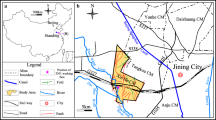
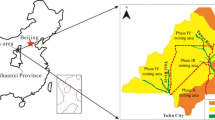
In North China coal basin, there is an accident: the water which comes from Ordovician system aquifer (O2) discharges into underground coal mines. The coal mining operations would be seriously threatened by this kind of accident. In order to solve this problem, the characteristics of various exploration methods have been discussed. A comprehensive approach involving hydrogeological analysis, geophysical prospecting, hydrogeological drilling, and hydrogeological field test was proposed to explore the groundwater recharge channel. A typical North China coal mine, Siwan coal mine, was taken as an example. The groundwater recharge channel on F8 fault was precisely explored and plugged. After the curtain grouting, the water discharge rate per unit of drawdown was dropped from 12.0 to 7.0 m3/(h m), and the water yield in coal mine was reduced by 600 m3/h. A much safer condition can be provided for Siwan coal mine, avoiding the waste of water resource.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burazer M, Žitko V, Radaković D, Parezanović M (2010) Using geophysical methods to define the attitude and extension of water-bearing strata in the Miocene sediments of the Pannonian Basin. J Appl Geophys 72:242–253
Cao H, Cowart JB, Osmond JK (1999) Uranium and strontium isotopic geochemistry of karst waters, Leon Sinks Geological Area, Leon County, Florida. Cave Karst Sci 26(3):101–106
Danielsen JE, Auken E, Jørgensen F, Søndergaard V, Sørensen KI (2003) The application of the transient electromagnetic method in hydrogeophysical surveys. J Appl Geophys 53:181–198
Dou H, Ma Z, Cao H, Liu F, Hu W, Li T (2011) Application of isotopic and hydro-geochemical methods in identifying sources of mine inrushing water. Min Sci Technol (China) 21:319–323
Fang X, Fu Y, Hua J, Wu T (2011) Modes and characteristics of karst groundwater system in north of China. J Hefei Univ Technol 34(2):286–291
Gao H, Lin Z (1985) Regional characteristics of mine-hydrogeological conditions of coal deposits in China. Hydrogeol Engg Geol 12:14–17
Giustiniani M, Accaino F, Picotti S, Tinivella U (2009) 3D seismic data for shallow aquifers characterisation. J Appl Geophys 68:394–403
Han D, Yang Q (1984) Coal geology of China, 2nd edn. Publishing House of China Coal Industry, Beijing
Han D, Li D, Shi X (2011) Effect of application of transient electromagnetic method in detection of water-inrushing structures in coal mines. Procedia Earth Planet Sci 3:455–462
Hatherly P (2013) Overview on the application of geophysics in coal mining. Int J Coal Geol 114:74–84
Huang P, Chen J (2012) Recharge sources and hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in the coal-mining district of Jiaozuo, China. Hydrogeol J 20:739–754
Jiang C, Lin J, Qin S, Li S, Duan Q (2012) Experiment on dam leakage detection with magnetic resonance sounding. J Jilin Univ 42(3):858–863
Kogovšek J, Šebela S (2004) Water tracing through the vadose zone above Postojnska Jama, Slovenia. Environ Geol 45(7):992–1001
Lapworth DJ, Gooddy D, Butcher A, Morris B (2008) Tracing groundwater flow and sources of organic carbon in sandstone aquifers using fluorescence properties of dissolved organic matter (DOM). Appl Geochem 23(12):3384–3390
Li X (2012) Evaluation of mine shaft water discharge prediction based on underground dewatering test. Coal Geol China 24(10):26–30
Lin Y, Wang G, Pan G (2010) A study of groundwater pollution mechanism by using stable isotopes and hydrochemistry. China Rural Water Hydropower 5:01–04
Liu S, Liu Z, Jang Z (2005) Application of TEM in hydrogeological prospecting of mining district. J China Univ Min Technol 34(4):414–417
Liu Y, Yamanaka T, Zhou X, Tian F, Ma W (2014) Combined use of tracer approach and numerical simulation to estimate groundwater recharge in an alluvial aquifer system: a case study of Nasunogahara area, central Japan. J Hydrol 519:833–847
Ma P (2005) Aquifer hydrogeological testing studies aimed at floor water bursting prevention. [J] Coal Geol China 17:61–64
Meigs LC, Beauheim RL (2001) Tracer tests in a fractured dolomite: 1. Experimental design and observed tracer recoveries. Water Resour Res 37:1113–1128
Pan G, Wang P (2011) The feasibility study on Cambrian limestone water discharging based on large dewatering test of group holes. J Henan Polytech Univ 30:674–678
Pan G, Xuan J, Yue B, Liu Z (2007) The large dewatering test and tracing experiment based on GSM water level remote sensing system. J Henan Polytech Univ 26:153–155
Pan G, Wu Y, Lin Y (2014) The evaluation and exploration of the coal mine water bursting accident. China coal industry publishing house, Beijing
Pu C, Zhang X, Yin W, Qu X (2001) Inundation in the North-China type coalfields and the status quo of its protection. Geol Rev 47:405–410
Sibanda T, Nonner JC, Uhlenbrook S (2009) Comparison of groundwater recharge estimation methods for the semi-arid Nyamandhlovu area, Zimbabwe. Hydrogeol J 17:1427–1441
Song S-H, Song Y, Kwon B-D (2005) Application of hydrogeological and geophysical methods to delineate leakage pathways in an earth fill dam. Explor Geophys 36(1):92–96
Sui W, Liu J, Yang S, Chen Z, Hu Y (2011) Hydrogeological analysis and salvage of a deep coalmine after a groundwater inrush. Environ Earth Sci 62:735–749
Thrailkill J, Sullivan SB, Gouzie DR (1991) Flow parameters in a shallow conduit-flow carbonate aquifer, Inner Bluegrass Karst Region, Kentucky, USA. J Hydrol 129:87–108
Van Paridon H, Brandimarte F (2012) Interburden mapping using 3D seismic attributes at an underground coal mine, Bowen Basin, Queensland. ASEG Ext Abstr 2012:1–4
Wang X, Pan J (2010) Location detection of concentrated-leakage passages in dam by groundwater temperature. Chin J Geotech Eng 32(11):1800–1805
Wu Q, Jin Y (1995) Deciding system of preventing and curing mine water in Northern China Coalfield. Publishing House of Coal Industry, Beijing
Wu Q, Wang M (2006) Characterization of water bursting and discharge into underground mines with multilayered groundwater flow systems in the North China coal basin. Hydrogeol J 14:882–893
Yin H, Wei J, Guo J, Guan Y, Liu R, Hu D (2012) Research on water quality characteristics in the process of dewatering test for Ordovician limestone aquifer. Procedia Environ Sci 13:2146–2153
Zhang C, Li Z (2009) The analysis about characteristics of Xujiazhuang limestone water in Bucun coalmine and corresponding prevention and control measures. J Shandong Univ Sci Technol 28(6):51–55
Zhang M, Zhang W, Sun G (2006) Evaluation technique of grouting effect and its application to engineering. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 25(2):3909–3918
Zhao P, Wu X (2005) How seismic has helped to change coal mining in China. First Break 23:31–34
Zhu S, Wang F, Zeng X (2007) Groundwater blockage by grouting curtain in Dahongshan mine and its evaluation. Metal Mine 9:79–83
Acknowledgments
The data were based on the reports of projects presided by the authors. This study was financially supported by the Doctor Foundation of Henan Polytechnic University (No. B2012-034). We thank for the helpful suggestions of Baoxiang Yue, Zhaoxia Liu, and Guojun Chen. We also thank the workers of Siwan coal mine and students of Henan Polytechnic University for their hardwork in the experiments. The constructive suggestions of all referees and editors on this paper were appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y., Wu, Y., Pan, G. et al. Determining and plugging the groundwater recharge channel with comprehensive approach in Siwan coal mine, North China coal basin. Arab J Geosci 8, 6759–6770 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1753-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1753-8