Abstracts
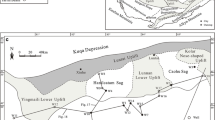
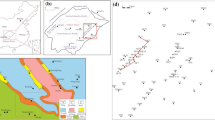
Detailed stratigraphic analysis of the second member of Shuangyang Formation of Y45 Block of the rift Yitong Basin in northeast China has revealed that the study area, previously interpreted as fan delta systems, actually originated mainly in relatively deep lacustrine setting with nearby line source. Two depositional systems have been recognized: slope apron and slump fan. The regional correlation of the lithofacies within the different depositional systems has led to a high-resolution stratigraphic framework of 20 small layers. Sequence boundary SB1 marks the top of the target interval and is characterized by thick and continuous mudstone overlying sand-rich lacustrine sediments. Sequence boundary SB2 marks the bottom of the target interval and is characterized by high-channel-ratio lacustrine deposits overlying stably distributed shales. Maximum flooding surface (MFS) marks the end of a transgressive tendency and the onset of a regressive tendency and is characterized by surrounding shale-rich zone. Two system tracts constitute the target interval together which is classified by SB1, SB2, and MFS. The base-level fluctuation has a strong tectonic component in accordance with the regional tectonic settings that during active subsidence stage, the base level rises rapidly and during relatively stable stage, the base level rises slowly and is usually overtaken by sediment supply rate.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouma AH (2000) Coarse-grained and fine-grained turbidite systems as end member models: applicability and dangers. Mar Petrol Geol 17(2):137–143
Catuneanu O (2002) Sequence stratigraphy of clastic systems: concepts, merits, and pitfalls. J Afr Earth Sci 35(1):1–43
Catuneanu O (2006) Principles of sequence stratigraphy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–3
Crevello PD, Harris PM (eds) (1985) Deep-water carbonates: buildups, turbidites, debris flows and chalks: a core workshop (No. 6). Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists
Cross TA, Baker MR, Chapin MA, Clark MS, Gardner MH, Hanson MS, Witter DN (1993) Applications of high-resolution sequence stratigraphy to reservoir analysis. Collect Colloque Sem Institut Franc Petrole 51:11–11
Eltom H, Abdullatif O, Makkawi M, Al-Ramadan K, Abdulraziq A (2014) Porosity evolution within high-resolution sequence stratigraphy and diagenesis framework: outcrop analog of the upper Jurassic Arab-D reservoir, Central Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1251-4
Embry AF (2002) Transgressive-regressive (TR) sequence stratigraphy. In: Gulf Coast SEPM Conference Proceedings, Houston, pp 151–172
Embry AF, Johannessen E, Owen D, Beauchamp B, Gianolla P (2007) Sequence stratigraphy as a “concrete” stratigraphic discipline. Report of the ISSC Task Group on sequence stratigraphy
Galloway WE (1989) Genetic stratigraphic sequences in basin analysis I: architecture and genesis of flooding-surface bounded depositional units. AAPG Bull 73(2):125–142
Holz M, Vieira PE, Kalkreuth W (2000) The early Permian coal-bearing succession of the Paraná Basin in southernmost Brazil: depositional model and sequence stratigraphy. Braz J Geol 30(3):424–426
Hou Q (2009) Evolution and oil & gas accumulation dynamics of Yitong Basin. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, pp 35–40. (In Chinese)
Li J (2013) High-resolution sequence stratigraphy of the 2nd member of Shuangyang Formation in Moliqing reservoir, Yitong Basin (Master’s thesis, OUC) (In Chinese)
Liu M (1993) Geological characteristics and evolution of Yitong-Yilan Graben. Geology Press, Beijing, (In Chinese)
Miall AD (1985) Architectural-element analysis: a new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits. Earth Sci Rev 22(4):261–308
Miall AD (1991) Stratigraphic sequences and their chronostratigraphic correlation. J Sediment Res 61(4):497–505
Mitchum Jr, RM (1985) Seismic stratigraphic expression of submarine fans: chapter 7
Pemberton SG (1992) Applications of ichnology to petroleum exploration: a core workshop: society for sedimentary geology. Tulsa, Oklahoma, core workshop
Posamentier HW, James DP (1993) An overview of sequence-stratigraphic concepts: uses and abuses. In: Posamentier HW, Summerhayes CP, Haq BU, Allen GP (eds) Sequence stratigraphy and facies associations, Blackwell Publishing Ltd., Oxford, UK
Sagoe KMO, Visher GS (1977) Population breaks in grain-size distributions of sand—a theoretical model. J Sediment Res 47(1):285–310
Shanley KW, McCabe PJ (1994) Perspectives on the sequence stratigraphy of continental strata. AAPG Bull 78(4):544–568
Srivastava AK, Mankar RS (2013) Lithofacies architecture and depositional environment of late Cretaceous Lameta Formation, Central India. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1192-y
Sun X, Long S, Zhang H, Liu X et al (2006) Recognition and formation of large reverse faults of Yitong-Jiamusi faults zone. Oil Gas Geol 27(5):637–643 (In Chinese)
Visher GS (1969) Grain size distributions and depositional processes. J Sediment Res 39(3):1074–1106
Zhang J, Xie J (2008) Reservoir sedimentary facies model. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, pp 8–15. (In Chinese)
Zhang J, Jiang Z, Li D, Sun J (2009) Sequence stratigraphic analysis of the first layer, upper second submember, Shahejie Formation in Pucheng oilfield. J Earth Sci 20:932–940
Acknowledgments
Financial support was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation (41172109) and Research Foundation for the Doctoral Program of higher education (20110003110014). We also acknowledge permission by PetroChina Jilin Oilfield Company to publish this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Li, J., Liu, S. et al. Sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy of the second member of Shuangyang Formation, Y45 Block, Moliqing oilfield, Yitong Basin, China. Arab J Geosci 8, 6697–6707 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1744-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1744-9