Abstract
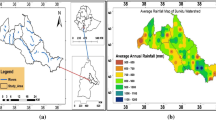
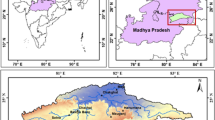
This paper presents spatio-temporal meteorological drought analysis of Pedda Vagu and Ookacheti Vagu watersheds of Mahabubnagar and Ranga Reddy Districts of Telangana state, South Central India. Rainfall anomaly index (RAI) and run analysis have been leveraged to assess drought characteristics at different stations in the basin. The study also presents the interpolation of RAI values using spline technique in a geographic information system (GIS) environment to map the spatial extent and variation of drought severity in different time steps. The study reveals that the occurrence, magnitude, and recurrence of drought varied among the stations in the basin during an observed time frame, i.e., 1986 to 2013. Significant variations in the occurrences of number of drought events are observed among the stations in the basin. The spline interpolated rainfall anomaly index maps illustrated that some regions experienced more severe drought while other regions were well-off. This uncertainty in rainfall essentially indicates that a finer scale of drought vulnerability assessment is highly necessary for better drought management practices. Furthermore, empirical relationships were developed between drought duration and magnitude to support decision-making during various agricultural practices and water management.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankegowda SJ, Kandiannan K, Venugopal MN (2010) Rainfall and temperature trends—a tool for crop planning. J Plant Crop 38(1):57–61
Biggs TW, Gaur A, Scott CA, Thenkabail P, Parthasaradhi G, Gumma MK, Acharya S, Turral H (2007) Closing of the Krishna Basin: stream flow depletion and macro scale hydrology. IWMI Research Report No. 111, Colombo
Gaur A, McCornick PG, Turral H, Acharya S (2007) Implications of drought and water regulation in the Krishna Basin, India. Int J Water Resour Dev 23(4):583–594
Hansel S, Matschullat J (2006) Drought in a changing climate, Saxon dry periods. Bioclimatological Conference 2006. Bioclimatology and water in the land. International scientific conference, 11–14 September 2006, Strecno
Hartkamp AD, De Beurs K, Stein A, White JW (1999) Interpolation techniques for climate variables. NRG-GIS Series 99–01. CIMMYT, Mexico
Hutchinson MF, Gessler PE (1994) Splines more than just a smooth interpolator. Geoderma 62:45–67
Iglesias A, Garrote L, Cancelliere A, Cubillo F, Wilhite AD (2009) Coping with drought risk in agriculture and water supply systems, drought management and policy development in the Mediterranean, Advances in Natural and Technological Hazards Research, Volume 26
Keyantash J, Dracup JA (2002) The quantification of drought: an evaluation of drought indices. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 1167–1180
Kwarteng AY, Dorvlo AS, Vijaya Kumar GT (2009) Analysis of a 27-year rainfall data (1977–2003) in the Sultanate of Oman. Int J Climatol 29(4):605–617
Loukas A, Vasiliades L, Dalezios N R (2003) Intercomparison of meteorological drought indices for drought assessment and monitoring in Greece. 8th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Lemnos island, Greece, 8–10, Sept, 2003
Mishra S S, Nagarajan R (2011) Drought assessment in tel watershed: an integrated approach using run analysis and SPI. Earthzine (IEEE)
Murali Krishna T, Ravikumar G, Krishnaveni M (2009) Remote sensing based agricultural drought assessment in Palar Basin of Tamil Nadu State, India. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 37:9–20
Oladipo EO (1985) A comparative performance analysis of three meteorological drought indices. J Climatol 5:655–664
Prabhakar SVRK, Shaw R (2008) Climate change adaptation implications for drought risk mitigation: a perspective for India. Climate Change 88:113–130
Rao B, Sreenivas Prasad P, Ahmed Iftekhar S (1998) Watershed management and consequential conservation/augmentation to groundwater resources. In Proceedings of International Conference on Watershed management and Conservation 259–268
Roshan G, Mirkatouli G, Ali S (2012) A new approach to technique for order-preference by similarity to ideal solution (TOPSIS) method for determining and ranking drought: a case study of Shiraz station. Int J Phys Sci 7(23):2994–3008. doi:10.5897/IJPS12.308
Saith N, Slingo J (2006) The role of the Midden-Julian Oscillation in the El Nino and Indian drought of 2002. Int J Climatol 26:1361–1378
Selvaraju R (2003) Impact of El Nino-Southern Oscillation on Indian foodgrain production. Int J Climatol 23:187–206
Sirdas S, Sen Z (2003) Spatio-temporal drought analysis in the Trakya region, Turkey. Hydrol Sci J 48(5)
Sreedhar G, Mishra S, Nagarajan R, Balaji V (2012) Micro-level drought vulnerability assessment in Peddavagu basin, a Tributary of Krishna River, Andhra Pradesh, India. Earthzine (IEEE)
Sreedhar G, Nagarajan R, Balaji V (2013) Village-level drought vulnerability assessment using geographic information systems (GIS). Int J Adv Res Comp Sci Softw Eng 3(3)
Srivastava SK, Upadhyay AP, Sahu AK, Dubey AK (2000) Rainfall characteristics and rainfall based cropping strategy for Jabalputr region. J Soil Conserv 28(3):204–211
Subudhi CR, Pradhan PC, Behara B, Senapati PC, Singh GS (1996) Rainfall characteristics at Phulani. Indian J Soil Conserv 24(1):41–43
Suresh R, Singh NK, Prasad P (1993) Rainfall analysis for drought study at Pusa, Bihar. Indian J Agric Eng 3(1–2):77–82
Thenkabail PS, Gamage MSDN, Smakhtin VU (2004) The use of remote sensing data for drought assessment and monitoring in south west Asia. Research report. 85. International Water Management Institute, Sri Lanka
Tilahun K (2006) Analysis of rainfall climate and evapo-transpiration in arid and semi-arid regions of Ethiopia using data over the last half a century. J Arid Environ 64:474–487
Valli M, Shanti Sree K, Murali Krishna IV (2013) Analysis of precipitation concentration index and rainfall prediction in various agro-climatic zones of Andhra Pradesh, India. Int Res J Environ Sci 2(5):53–61
van Rooy MP (1965) A rainfall anomaly index independent of time and space. Notos 14:43–48
Yevjevich V (1967) An objective approach to definition and investigation of continental hydrologic droughts. Colorado State Univ., Fort Collins, Colorado, USA. Hydrology Paper 23
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, for the support and encouragement. The authors are also grateful to District planning office, Mahabubnagar District, Regional agriculture research station, Hyderabad and Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Hyderabad for providing rainfall data. The authors are also thankful to the valuable suggestions provided by the two anonymous reviewers for the improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganapuram, S., Nagarajan, R., Sehkar, G.C. et al. Spatio-temporal analysis of droughts in the semi-arid Pedda Vagu and Ookacheti Vagu watersheds, Mahabubnagar District, India. Arab J Geosci 8, 6911–6929 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1696-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1696-0