Abstract
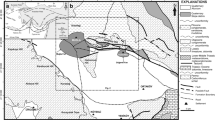
The aim of the present study is the recognition of the geological and sedimentological conditions which led in the formation of trapezoidal type fan deltas in linear extensional sub-basins located in the Mediterranean area and especially in Northern Africa and Southern Europe. For this purpose, two similar examples of such type of settings have been studied, in the Gulf of Suez (Egypt) and in Corinth Gulf (Greece), respectively. The development of these basins took place during Langhian (Suez Gulf) and Pleistocene (Gulf of Corinth) and was controlled by the presence of major marginal faults combined with transfer faults at the lateral extends of the basins. A critical factor for the sedimentation pattern into these basins is the presence of intrabasinal highs, trending parallel to the basin axis, which at the first stages of sedimentation acts as barriers, trapping the sediment and leading in the development of trapezoidal type fan deltas characterized by the absence of toe sets. Fine-grained sediment is transported outside the basin by strong currents, using transfer faults as pathways. In the Gulf of Corinth, the presence of intrabasinal highs and the limited space caused by this is the basic constraint for the development of trapezoidal type fan deltas, while in the Gulf of Suez, this has a secondary impact, as the main control factor is the viscosity and the bulk of sediment. Gradually, as the sediment accumulation is overstepping the intrabasinal high, more space is available for the evolution of the trapezoidal type fan delta to a Gilbert-type fan delta.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dorsey RJ, Umhoefer PJ, Renne PR (1995) Rapid subsidence and stacked Gilbert-type fan deltas, Pliocene Lorento Basin, Baja California Sur, Mexico. Sed Geol 98:181–204
Doutsos T, Piper DJW (1990) Listric faulting, sedimentation and morphological evolution of the Quaternary eastern Corinth rift, Greece: first stages of continental rifting. Geol Soc Am Bull 102:812–829
Evans L (1988) Neogene tectonic and stratigraphic events in the Gulf of Suez rift area, Egypt. Tectonophysics 153(1988):235–241
Poulimenos G (1993) Tectonics and sedimentation in the western Corinth, Greece, N. Jb. Geol. Palaont. Mh. 10, 670 – 630, Stuttgart
Poulimenos G, Albers G, Doutsos T (1989) Neotectonic evolution of the central section of Corinth Graben, Z. dt. Geol. Hannover. Ges 140:173–182
Poulimenos G, Zelilidis A, Kontopoulos N, Doutsos T (1993) Geometry of trapezoidal fan deltas and their relationship to extensional faulting along the southwestern active margins of the Corinth rift. Basin Res 5:179–192
Richardson M, Arthur MA (1988) The Gulf of Suez—northern Red Sea Neogene rift: a quantitative basin analysis. Mar Petrol Geol 5:247–270
Saudi AM (1992) Subsurface geology of Kareem Formation. Southern Gulf of Suez, Egypt. M.Sc. Thesis, Al Azhar University, p. 264
Sohn YK, Kim SB, Hwang IG, Bahk JJ, Choe MY, Choung SK (1997) Characteristics and depositional processes of large scale gravelly Gilbert type foresets in the Miocene Doumsan fan delta, Pohong basin, SE Korea. J Sed Res 67:130–141
Wescott WA (1988) A late Permian fan-delta system in the southern Morondava Basin, Madagascar. In: Nemec W, Steel RJ (eds) Fan deltas: sedimentology and tectonic settings. Blackie, London, pp 226–238
Young M, Gawthorpe R, Sharp I (2000) Sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy of a transfer zone coarse grained delta, Miocene Suez Rift, Egypt. Sedimentology 47:1081–1104
Zahran IM (2005) Petrology and Lithostratigraphy of the Miocene rocks, Amal field, Gulf of Suez, Egypt and its hydrocarbon potentiality. Unpublished PhD. Thesis, Zagazig University, p. 261
Zaid S (2012) Provenance, diagenesis, tectonic setting and geochemistry of Rudies sandstone (lower Miocene), Warda Field, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. J Afr Earth Sci 66–67(2012):56–71
Zelilidis A (2003) The geometry of fan deltas and related turbidites in narrow linear basins. Geol J 38:31–46
Zelilidis A, Kontopoulos N (1996) Significance of fan deltas without toe-sets within rift and piggy back basins: examples from the Corinth graben and the Mesohellenic trough, Central Greece. Sedimentology 43:253–262
Zelilidis A, Barkooky A, Darwish M, Tewfik N, Vakalas I (2002) Comparison between fan deltas formed in the Gulf of Suez in Egypt and in the Gulf of Corinth in Greece, Abstract volume a92, AAPG Meeting in Cairo, Egypt
Zelilidis A, Vakalas I, Barkooky A, Darwish M, Tewfik N (2008) Impact of transfer faults and intrabasinal highs in basin evolution and sedimentation processes: application to potential hydrocarbon fields development. Adv Sci Lett 1:1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vakalas, I., Zelilidis, A., Barkooky, A. et al. Comparison between fan deltas in the Gulf of Suez, Egypt, and in the Gulf of Corinth, Greece. Arab J Geosci 8, 3603–3613 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1457-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1457-0