Abstract
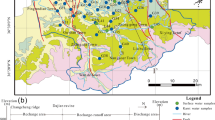
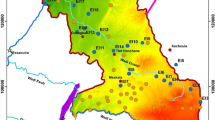
The salt chemical industrial base of Guyuan is located in the south of Ningxia, northwestern China. Guyuan had been not only an important but also a challenging area for the state’s poverty alleviation and development work for a long time. In addition, the overexploitation of groundwater for agriculture activities in recent decades had led to the decline of the water table and the degradation of the water quality. In this study, environmental isotope data for different water sources are presented and discussed to identify the hydrochemical character of the aquifer systems and to investigate the geochemical processes controlling groundwater mineralization. Piper trilinear diagrams indicate that shallow groundwater in the western mountainous area is characterized by three water types (i.e., SO4–HCO3, HCO3–SO4, and SO4) while deep groundwater is characterized by two water types (i.e., SO4 and SO4–Cl). Furthermore, hydrochemical tracers show that the groundwater in the Qingshuihe plain is of the (1) HCO3–SO4 and HCO3 types in the southern piedmont recharge zone, (2) SO4 type in the southwestern recharge zone, (3) SO4–HCO3 and HCO3–SO4 types in the midwestern recharge zone, (4) SO4–HCO3 and SO4–Cl–HCO3 types in the northwestern recharge zone, and (5) SO4–HCO3, HCO3–SO4, and SO4 types in the runoff and discharge zone. Dissolution of soluble salts is the principal contributor to the water geochemistry in the western mountainous area within the study region. However, water geochemistry in the Qingshuihe plain is primarily controlled by mixing processes and by the recharge of highly mineralized surface water and groundwater in the southwestern and northwestern piedmont areas. In the conventional δD and δ 18O diagram, the distribution of data points indicates that the groundwater is of meteoric origin and has been affected by evaporation before or during underground transit. The deep groundwater in the western mountainous area is recharged under conditions that are different from currently prevailing conditions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ako AA, Shimada J, Hosono T, Ichiyanagi K, Nkeng GE, Eyong GET, Roger NN (2012) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Mbanga, Njombe and Penja (Banana Plain)—Cameroon. J Afr Earth Sci 75:25–36
Allison GB (1983) The distribution of deuterium and 18O in dry soils. Exp J Hydrol 64:377–397
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric water. Science 133:1702–1703
Demlie M, Wohnlich S, Gizaw B, Stichler W (2007) Groundwater recharge in the Akaki catchment, central Ethiopia: evidence from environmental isotopes (delta O-18, delta H-2 and H-3) and chloride mass balance. Hydrol Process 21(6):807–818
Demlie M, Wohnlich S, Ayenew T (2008) Major ion hydrochemistry and environmental isotope signatures as a tool in assessing groundwater occurrence and its dynamics in a fractured volcanic aquifer system located within a heavily urbanized catchment, central Ethiopia. J Hydrol 353(1–2):175–188
Diaw M, Faye S, Stichler W, Maloszewski P (2012) Isotopic and geochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Senegal River delta aquifer: implication of recharge and flow regime. Environ Earth Sci 66(4):1011–1020
Dogramaci S, Skrzypek G, Dodson W, Grierson PF (2012) Stable isotope and hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in the semi-arid Hamersley Basin of subtropical northwest Australia. J Hydrol 475:281–293
Guo HM, Wang YX (2005) Geochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in Datong basin, northwestern China. J Geochem Explor 87(3):109–120
Han Y, Wang G, Hu W (2010) The geochemical evolution of deep Ordovician limestone groundwater in the coalfield of North China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74(12):A378–A378
Huntoon PW (1986) Incredible tale of Texasgulf well 7 and fracture permeability, Paradox Basin, Utah. Ground Water 24:643–653
Jalali M (2005) Major ion chemistry of groundwaters in the Bahar area, Hamadan, western Iran. Environ Geol 47:763–772
Li X, Yu Q, Hou X, Zhang L (2006) A study of the characteristics of groundwater circulation and the formation of bitter and saline groundwater in the Qingshuihe Basin in the southern Ningxia. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 1:46–51 (in Chinese)
Negrel P, Lemiere B, de Grammont HM, Billaud P, Sengupta B (2007) Hydrogeochemical processes, mixing and isotope tracing in hard rock aquifers and surface waters from the Subarnarekha River Basin, (east Singhbhum District, Jharkhand State, India). Hydrogeol J 15(8):1535–1552
Peng T-R, Huang C-C, Wang C-H, Liu T-K, Lu W-C, Chen K-Y (2012) Using oxygen, hydrogen, and tritium isotopes to assess pond water’s contribution to groundwater and local precipitation in the piedmont tableland areas of northwestern Taiwan. J Hydrol 450:105–116
Pu T, He Y, Zhang T, Wu J, Zhu G, Chang L (2013) Isotopic and geochemical evolution of ground and river waters in a karst dominated geological setting: a case study from Lijiang basin, South-Asia monsoon region. Appl Geochem 33:199–212
Qian H, Xu W, Dou Y (2008) The control factors of chemistry of Karst groundwater in southern Ningxia. 2008 Proceedings of Information Technology and Environmental System Sciences: Itess 2008, vol 2
Rao NS, Rao PS, Reddy GV, Nagamani M, Vidyasagar G, Satyanarayana NLVV (2012) Chemical characteristics of groundwater and assessment of groundwater quality in Varaha River Basin, Visakhapatnam District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 184(8):5189–5214
Tarki M, Dassi L, Hamed Y, Jedoui Y (2011) Geochemical and isotopic composition of groundwater in the complex terminal aquifer in southwestern Tunisia, with emphasis on the mixing by vertical leakage. Environ Earth Sci 64(1):85–95
Trabelsi R, Abid K, Zouari K (2012) Geochemistry processes of the Djeffara palaeogroundwater (Southeastern Tunisia). Quat Int 257:43–55
Wen XH, Wu YQ, Wu J (2008) Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Zhangye Basin, northwestern China. Environ Geol 55(8):1713–1724
Yang Y, Xiao H, Wei Y, Zhao L, Zou S, Yang Q, Yin Z (2012) Hydrological processes in the different landscape zones of alpine cold regions in the wet season, combining isotopic and hydrochemical tracers. Hydrol Process 26(10):1457–1466
Yu Y, Yu Q, Xue Z, Yin B, Guo Y (2005) Research on the evolution of groundwater hydrochemical and isotope characteristics in Qingshuihe Plain, South of Ningxia. Site Investig Sci Technol 4:42–44 (in Chinese)
Zhai YZ, Wang JS, Teng YG, Wang XN (2011) Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of springs in Beijing and their implications. Geol Bull China 30(9):1442–1449
Zhai Y, Wang J, Teng Y, Zuo R (2013) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence of groundwater evolution and recharge in aquifers in Beijing plain, China. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2167–2177
Zhang FW, Chen L, Yu QS, Xue ZQ (2006) Research on the forming mechanism of the ground water quality in the Southern Ningxia Autonoumous Region. Geol Rev 52(6):810–814 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by special funds for scientific research projects of the Ministry of Land and Resources of China (201111006). The authors thank Wang Xinhe and Dr. XueZhongqi from the Ningxia Institute of Geo-engineering and Reconnaissance for their assistance with the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Hu, F.S., Xue, Z.Q. et al. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in the salt chemical industrial base of Guyuan City, northwestern China. Arab J Geosci 8, 3427–3440 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1442-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1442-7