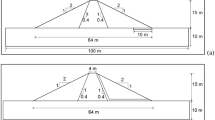
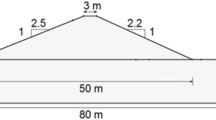
Abstract
Slope stability analysis during rapid drawdown is an important consideration in the design of embankment dams. During rapid drawdown, the stabilizing effect of the water on the upstream face is lost, but the pore water pressures within the embankment may remain high. As a result, the stability of the upstream face of the dam can be much reduced. Installing horizontal drains is a very efficient and cost-effective method for reducing the pore water pressure and increasing the stability of the upstream slope. The theory of horizontal drains in the upstream shell of earth dams is well established, but there seems to be limited resources available for the design of this type of horizontal drains. Hence, this study is focused on the performance of horizontal drains in the upstream shell of the slope of earth dams on the upstream slope stability during rapid drawdown conditions. The parametric study has been conducted on the variation of horizontal drain parameters such as the number of drains, their length, and their location. In this study, ten scenarios were analyzed based on different drainage configurations and the performance of each scenario is investigated on the seepage and the upstream slope stability during rapid drawdown conditions using finite element and limit equilibrium methods. The results demonstrated that the stability of the upstream slope during rapid drawdown conditions increases by increasing the number of drains. The length of drains extending further from its intersection with the critical failure surface does not provide any significant change in the factor of safety. Finally, the study also found that installing drains in the lower region of the upstream shell of earth dams gives more stability than those installed in higher elevations.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berilgen M (2007) Investigation of stability of slopes under drawdown conditions. Comput Geotech 2:81–91
Craig DJ, Gray I (1985) Groundwater lowering by horizontal drains. GCO publication no.: 2/85. Geotechnical Control Office Engineering Development Department, Hong Kong, p 123
Geo-Slope (2007a) SEEP/W version 7.1.0 User’s manual. GEOSLOPE International. Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Geo-Slope (2007b) SLOPE/W version 7.1.0 User’s manual. GEOSLOPE International. Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Lau KC, Kenney TC (1984) Horizontal drains to stabilize clay slopes. Can Geotech J 21(2):241–249
Martin RP, Siu KL, Premchitt J (1994). Performance of horizontal drains in Hong Kong. Special Project Report, SPR 11/94, Geotechnical Engineering Office, Civil Engineering Department, Hong Kong.
Rahardjo H, Hritzuk KJ, Leong EC, Rezaur RB (2002) Effectiveness of horizontal drains for slope stability. Eng Geol 69:295–308
Royster DL (1980) Horizontal drains and horizontal drilling: an overview. Transp Res Rec 783:16–25
Reddi LN (2003) Seepage in soils principles and applications. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Spencer E (1967) A method of analysis of the stability of embankments assuming parallel interslice forces. Geotechnique 17:11–26
Tran TX (2004) Stability problems of an earthfill dam in rapid drawdown condition. Doctoral dissertation. Slovak University of Technology, Bratislava, Slovak Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moharrami, A., Hassanzadeh, Y., Salmasi, F. et al. Performance of the horizontal drains in upstream shell of earth dams on the upstream slope stability during rapid drawdown conditions. Arab J Geosci 7, 1957–1964 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0872-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0872-y