Abstract
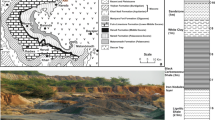
This paper is concerned with the study of paleoclimate and paleoenvironmental changes of Hussaynia township which is located in Karbala at the center of the Mesopotamian plain during Holocene. Ten soil samples were examined to determine their content of pollens, spores, and marine organisms (dinoflagellates). These palynomorphs include: Graminidites, Palmaepollenites, Chenopodiaceae, Composita, Cyperaceae, Sphaginum sporites, Pinus pollenites, Convovolus, Artimesia, Laevigatosporites, Quercus, dinoflagellates, and fungi. The study revealed climatic and environmental changes in the area during Holocene and four climatic zones were determined in the studied sequence and correlated with other areas in and outside of Iraq. The climate was pluvial with intervening dry periods in the 10000 years bp. The study indicated as well, some marine effects on the studied area on the commencement of Holocene due to the global transgression. This is based on the presence of marine organisms, dinoflagellate.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud IA (1999) Quaternary paleoclimate and palaeohydrology of Wadi Mugat Basin, Al-Badia, NE Jordan. Ph.D. Thesis (unpublished), College of Science, University of Baghdad, 146 p
Al-Ameri TK, Jassim SY (2007) Recent environmental changes in wetlands South Iraq. The Arabian Sea International Conference on Science and Technology of Aquaculture, Fisheries and Oceanography. 10–13 February. Kuwait (Abstract)
Al-Dulaimy AS (1999) Late Quaternary paleoclimate and paleovegetation of Euphrates flood plain sediments from Al-Qaim to Ramadi, Iraq. Ph.D. thesis (unpublished), College of Science, University of Baghdad, 117 p
Ali MO (2005) Palaeoenvironment and palaeoclimate of Holocene sediment at Babylon district. M.Sc. Thesis. (Unpublished), College of Science, University of Baghdad, 103 p
Al-Tawash BS (1996) The Pleistocene history of Razzaza and Tharthar depressions in Central Iraq. Ph.D. Thesis (unpublished), College of Science, University of Baghdad, 124p
Aqrawi AA (1993) Recent sediments of the Tigris–Euphrates delta. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis. University of London, 332 p
Bars MS, Williams GL (1977) Palynology and nannofossil processing techniques. Geol Surv Canada 73:25–26, Paper
Benni TJ (2001) Sedimentology and palaeoclimate record of Bahr Al-Najaf depression during Late Quaternary. M.Sc. Thesis (unpublished), College of Science, University of Baghdad, 148 p
Buday T, Jassim SZ (1987) The regional geology of Iraq. Vol. 2: Tectonism, magmatism and metamorphism. S.E. Geol Surv Mine Inves, Baghdad, 352 p
El-Muslimany AP (1986) Ecology and late quaternary history of the Kurdo-Zagrosian Oak forest near lake Zeribar, Western Iraq. Vegetation 68:55–63
El-Muslimany AP (1987) The Late Pliestoicene climates of Zeribar region (Kurdsatan–Western Iran) deduced from ecology and pollens production of the arboreal vegetation. Vegetation 72:131–139
El-Muslimany AP (1990) Ecological significance of common nonarboreal pollen: examples from dry lands of the Middle East. Rev Palaeobot Palynol 64:343–350
El-Muslimany AP (1994) Evidence of Early Holocene summer precipitation in the continental Middle East. In: Yousif O, Kra RS (eds) Late quaternary chronology and palaeoclimate of the Eastern Mediterranean, radiocarbon. pp. 1–10
Euphrates Center for Irrigation Studies and Designations (1995) Lower the levels of ground water in the Karbala city, pp. 10–38
Harrison SP, Digerfeldt G (1993) European lakes as palaehydrological and palaeoclimatical indicators. Quat Sci Rev 12:233–248
Jassim SZ, Goff GC (2006) Geology of Iraq. Dloin, Prague and Moravian Museum, Brno. Czech Republic, 341 p
Jassim RZ, Al-Rawi YT, Habib HR (2007) Holocene aridification in central Iraq. GEOSURV, Baghdad 3(1):1–9
McClure H (1984) Late Quaternary geology of the Rub Al-Khali. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis. University of London, 240 p
Van Ziest W, Bottema S (1977) Palynological investigation in western Iran. Palaeohistoria 19:19–85
Yan Z, Petit-Maire N (1994) The last 140 ka in the Afro-Asian arid/semi-arid transition zone. Palaegeogr Palaeoclimate Palaeoecol 110:217–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M.O. Palynological evidences on paleoclimate and paleoenvironmental changes during Holocene of Al-Hussaynia District, Central Iraq. Arab J Geosci 7, 589–595 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0801-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0801-5