Abstract
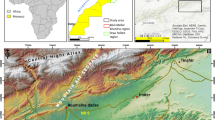
The study of structural lineaments is important for mineral exploration, geotectonic and geotechnical studies, and for the mitigation of geologic hazards. The present work deals with the extraction of lineaments from satellite imageries of different spatial resolutions as well as the analysis of these extracted lineaments. Wadi Bani Malik area located to the east of Jeddah city on the Red Sea coastal plain is chosen for such a study. Six types of digital satellite imagery data were used in the present study. These comprise satellite imagery of low spatial resolution (LSR) including Landsat MSS of 80-m resolution, Landsat TM of 30-m resolution, and Landsat TM of 25-m resolution; satellite imagery of moderate spatial resolution (MSR) including Landsat ETM+ panchromatic of 15-m resolution and SPOT panchromatic of 10-m resolution; and satellite imagery of high spatial resolution (HSR) including the Indian Remote Sensing satellite IRS data of 5-m resolution. As expected, the analysis of the extracted lineaments from different data sets shows that the imagery data of HSR of the Indian IRS data give the highest frequency of the extracted structural lineaments (N = 3,235), while the imagery data of LSR of the Landsat MSS data give the lowest frequency of the extracted lineaments (N = 89). The imagery data of MSR give moderate frequency (N = 1,643) in average. Due to the present study, it is recommended to use the imagery data of HSR and MSR for the extraction of structural lineaments for detailed and regional studies, respectively. The imagery data of LSR are not recommended for such studies due to the fact that most of the real structural lineaments framework cannot be extracted; accordingly, it is not useful in the analyses of lineaments for geological purposes.
Abstract
إنَّ دراسة السِّمَات الخَطِّيَّة البنائية مُهمة في الاستكشاف المعدني، وفي الدراسات البنائية والجيوتقنية، ومُهمة كذلك في الحَدِّ من المخاطر الجيولوجية. وتقوم الدراسة الحالية على استخلاص وتحليل السِّمَات الخَطِّيَّة من صور الأقمار الاصطناعية، مختلفة الدقة المكانية، وتَمَّ تطيبق هذه التقنية على منطقة وادي بني مالك، الواقعة إلى الشَّرق من مدينة جِدَّة على ساحل البحر الأحمر. واستُخْدِمَتْ ستة أنواع من البيانات الرقمية لصور الأقمار الاصطناعية التي تتضمن (1) صُور أقمار اصطناعية ذات بُعد مكاني مُنخفض LSR، وتشمل صُور لاندسات مُتعددة الأطياف MSS (80م)، ولاندسات الراسم الثيماتيكي TM (30م)، ولاندسات الراسم الثيماتيكي (25م)؛ (2) صُور أقمار اصطناعية ذات بُعد مكاني مُتوسط MSR، وتشمل صور لاندسات الراسم الثيماتيكي المُحَسَّنة ETM+ أحادية الطيف (15م)، وصُور أحادية الطيف للقمر الاصطناعي الفرنسي "سبوت" SPOT (10 م)؛ (3) صور أقمار اصطناعية ذات بُعد مكانيٍّ عالٍ HSR، وتشمل صُورة للقمر الاصطناعي الهندي IRS (5م). وكما كان مُتوقعًا، فإن تحليل هذه السِّمَات الخَطِّيَّة المُستخلصة من صُور الأقمار الاصطناعية المختلفة قد أكدت بأنَّ بيانات صُور HSR للقمر الاصطناعي الهندي نتج عنها أكبر عدد تكراري للسِّمَات الخَطِّيَّة البنائية ( 3235 سِمَّة خَطِّيَّة)، على عكس صور LSR للقمر الاصطناعي لاندسات مُتعدد الأطياف، والتي استخلص منها أقل عدد من السِّمات الخطية (89 سِمَّة خَطِّيَّة). أما بيانات صور MSR فقد استخلص منها قيمة متوسطة (1643 سِمَّة خَطِّيَّة). وخَلُصَتْ الدراسةُ إلى أنَّ استخدام بيانات صور HSR مُفِيدةٌ أَيَّمَا إفادة في الدراسات التفصيلية، أما صُور MSR فَيُوصَى باستخدامها في الدراسات الإقليمية لتتبع السِّمَات البنائية. ولا يُوصى باستخدام صور LSR في مثل تلك الدراسات؛ لصعوبة استخلاص البنيويات (التراكيب) الحقيقية منها، وهذه البنيويات غايةٌ في الأهمية في الأغراض الجُيولُوجيَّة.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arlegui LE, Soriano MA (1998) Characterizing lineaments from satellite images and field studies in the central Ebro basin (NE Spain). Int J Remote Sens 19(16):3169–3185
Casas AM, Cortes AL, Maestro A, Soriano MA, Riaguas A, Bernal J (2000) A program for lineament length and density analysis. Comput Geosci 26(9/10):1011–1022
Chang Y, Song G, HSU S (1998) Automatic extraction of ridge and valley axes using the profile recognition and polygon-breaking algorithm. Comput Geosci 24(1):83–93
Cortes AL, Soriano MA, Maestro A, Casas AM (2003) The role of tectonic inheritance in the development of recent fracture systems, Duero Basin, Spain. Int J Remote Sens 24(22):4325–4345
Costa RD, Starkey J (2001) Photo Lin: a program to identify and analyze linear structures in aerial photographs, satellite images and maps. Comput Geosci 27(5):527–534
Koike K, Nagano S, Ohmi M (1995) Lineament analysis of satellite images using a segment tracing algorithm (STA). Comput Geosci 21(9):1091–1104
Koike K, Nagano S, Kawaba K (1998) Constraction and analysis of interpreted fracture planes through combination of satellite-image derived lineaments and digital elevation model data. Comput Geosci 24(6):573–583
Leech DP, Treloar PJ, Lucas NS, Grocott J (2003) Landsat TM analysis of fracture patterns: a case study from the Coastal Cordillera of northern Chile. Int J Remote Sens 24(19):3709–3726
Mah A, Taylor GR, Lennox P, Balia L (1995) Lineament analysis of Landsat thematic mapper images, Northern Territory, Australia. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 61(6):761–773
Majumdar TJ, Bhattacharya BB (1998) Application of the Haar transform forextraction of linear and anomalous over part of Cambay Basin, India. Int J Remote Sens 9(12):1937–1942
Mostafa ME, Bishta AZ (2005) Significance of lineament patterns in rock unit classification and designation: a pilot study on the Gharib-Dara area, northern Eastern Desert, Egypt. Int J Remote Sens 26(7):1463–1475
Mostafa ME, Qari MYHT (1995) An exact technique of counting lineaments. Eng Geol 39:5–16
Mostafa ME, Zakir FA (1996) New enhancement techniques for azimuthal analysis of lineaments for detecting tectonic trends in and around the Afro-Arabian Shield. Int J Remote Sens 17(15):2923–2943
Nama EE (2004) Lineament detection on Mount Cameroon during the 1999 volcanic eruptions using Landsat ETM. Int J Remote Sens 25(3):501–510
O’Leary DW, Friedman JD, Pohn HA (1976) Lineament, linear, lineation: some proposed new standards for old terms. Geol Soc Am Bull 87:1463–1469
PCI (1997) Using PCI software, vol. 2, version 6.2. Richmond Hill, Ontario, Canada
PCI (1998) PCI GeoAnalyst, version 6.3. Richmond Hill, Ontario, Canada
PCI (2004) PCI Geomatica-9, version 9.1. Richmond Hill, Ontario, Canada
Qari MYHT (1991) Application of Landsat TM data to geological studies, Al-Khabt area, southern Arabian Shield. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 57(4):421–429
Qari MYHT, Şen Z (1994) Remotely sensed fracture patterns in southwestern Saudi Arabia and qualitative analysis. Bull Int Assoc Eng Geol, France 49:63–72
Rowan LC, Lathram EH (1980) Mineral exploration, chapter 17. In: Siegal BS, Gillespie AR (eds) Remote sensing in geology. Wiley, New York, pp 553–605
Sadagah BH, Qari MYHT (1993) Regional rock quality designation (RRQD) of the west central part of the Arabian Shield. Bull Assoc Eng Geol USA 30(4):455–467
Stefouli M, Angellopoulos A, Perantonis S, Vassilas N, Ambazis N, Charou E (1996) Integrated analysis and use of remotely sensed data for the seismic risk assessment of the southwest Peloponessus Greece. First Congress of the Balkan Geophysical Society, 23–27 September, Athens, Greece
Süzen ML, Toprak V (1998) Filtering of satellite images in geological lineament analyses: an application to a fault zone in Central Turkey. Int J Remote Sens 19(6):1101–1114
Vassilas N, Perantonis S, Charou E, Tsenoglou T, Stefouli M, Varoufakis S (2002) Delineation of lineaments from satellite data based on efficient neural network and pattern recognition techniques. 2nd Hellenic Conference on AI, SETN-2002, 11–12 April 2002, Thessaloniki, Greece, Proceedings Companion Volume, pp 355–366
Wang, Jinfei, Howarth, Philip J (1990) Use of the Hough transform in automated lineament detection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 28(4):561–566
Zakir FA, Qari MHT, Mostafa ME (1999) A new optimizing technique for preparing lineament density maps. Int J Remote Sens 20(6):1073–1085
Zlatopolsky AA (1992) Program LESSA (lineament extraction and stripe statistical analysis) automated linear image features analysis experimental results. Comput Geosci 18(9):1121–1126
Zlatopolsky AA (1997) Description of texture orientation in remote sensing data using computer program LESSA. Comput Geosci 23(1):45–62
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Prof. Adel Zein Bishta for helping during the progress of this work and King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for providing the images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qari, M.H.T. Lineament extraction from multi-resolution satellite imagery: a pilot study on Wadi Bani Malik, Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 4, 1363–1371 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0116-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0116-3