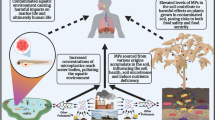
Abstract
The city of Fallujah, Iraq experienced extensive bombardment during recent military conflicts. However, limited environmental sampling has occurred to assess potential contamination. This study aimed to measure soil concentrations of heavy metals across Fallujah to determine the current levels of environmental pollution. We collected 117 surface soil samples in a grid pattern across Fallujah. Samples were analyzed using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) to quantify the levels of 13 elements. Geographic information systems (GIS) mapping visualized the spatial distribution of metals. Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) identified contaminant groupings. Multiple heavy metals were detected at concerning levels, including uranium, thorium, lead, and arsenic. Uranium and thorium were elevated in several areas, indicating potential contamination from depleted uranium munitions. FA results pointed to two primary exposure sources: burn pits in central Fallujah and industrial activity in the east. This study revealed heavy metal contamination in Fallujah soil, likely arising from military activity and industrial sources. The presence of toxic metals like uranium and lead raises concerns about potential health risks for residents. Further environmental sampling and health screening are urgently needed to fully characterize exposures and consequences. Remediation and prevention strategies should address the complex environmental legacy of conflict in the region.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Agency for toxic substances and disease registry (US). Health effects. In: Toxicological profile for thorium [Internet]. 2019 [Cited 2023 Nov 9]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK591331/
Ahmid K, Specht A, Morikawa L, Ceballos D, Wylie S (2022) Lead and other toxic metals in plastic play foods: results from testing citizen science, lead detection tools in childcare settings. J Environ Manage 321:115904
Al-Bassam KS, Yousif MA (2014) Geochemical distribution and background values of some minor and trace elements in iraqi soils and recent sediments. Iraqi Bull Geol Min 10(2):109–156
Al-Khuzaie MM, Maulud KNA (2022) Evaluation of soil pollution levels in Al-Qadisiyah Governorate, Iraq using contamination index and GIS. J Ecol Eng 23(3):206–213
Al-Sahlanee MHR, Ramli RM, Ali MAH, Tawfiq NF, Azman NZN, Rahman AA et al (2017) Trace of heavy metals in maternal and umbilical cord blood samples in association with birth outcomes in Baghdad, Iraq. EPJ Web Conf 156:00003
Alaani S, Al-Fallouji MAR, Busby C, Hamdan M (2012) Pilot study of congenital anomaly rates at birth in fallujah, Iraq, 2010. J IMA 44(1):44–41
Bhatia M, Specht AJ, Ramya V, Sulaiman D, Konda M, Balcom P et al (2021) Portable X-ray fluorescence as a rapid determination Tool to detect parts per million levels of Ni, Zn, As, Se, and Pb in human toenails: a South India case study. Environ Sci Technol 55(19):13113–13121
Bith-Melander P, Ratliff J, Poisson C, Jindal C, Ming Choi Y, Efird JT (2021) Slow burns: a qualitative study of burn pit and toxic exposures among military veterans serving in Afghanistan, Iraq and throughout the Middle East. Ann Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 4(1):1042
Busby C, Hamdan M, Ariabi E (2010) Cancer, infant mortality and birth sex-ratio in Fallujah, Iraq 2005–2009. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7(7):2828–2837
Cariccio VL, Samà A, Bramanti P, Mazzon E (2019) Mercury involvement in neuronal damage and in neurodegenerative diseases. Biol Trace Elem Res 187(2):341–356
Dickerson AS, Hansen J, Specht AJ, Gredal O, Weisskopf MG (2019) Population-based study of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and occupational lead exposure in Denmark. Occup Environ Med 76(4):208–214
Dinocourt C, Legrand M, Dublineau I, Lestaevel P (2015) The neurotoxicology of uranium. Toxicology 337:58–71
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN (2014) Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol 7(2):60–72
Johnson KM, Specht AJ, Hart JM, Salahuddin S, Erlinger AL, Hacker MR et al (2020) Lead exposure and association with angiogenic factors and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Pregnancy Hypertens 22:93–98
Lanphear BP, Hornung R, Khoury J, Yolton K, Baghurst P, Bellinger DC et al (2005) Low-level environmental lead exposure and children’s intellectual function: an international pooled analysis. Env Health Perspect 113(7):894–899
Lee MS, Eum KD, Golam M, Quamruzzaman Q, Kile ML, Mazumdar M et al (2021) Umbilical cord blood metal mixtures and birth size in Bangladeshi children. Environ Health Perspect 129(5):57006
Lin Y, Huang L, Xu J, Specht AJ, Yan C, Geng H et al (2019) Blood lead, bone lead and child attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-like behavior. Sci Total Environ 659:161–167
Liu J, Kang H, Tao W, Li H, He D, Ma L et al (2023) A spatial distribution—principal component analysis (SD-PCA) model to assess pollution of heavy metals in soil. Sci Total Environ 859:160112
Logan D (2018) Toxic violence: the politics of militarized toxicity in Iraq and Afghanistan. Cult Dyn 30(4):253–283
Masri S, LeBrón AMW, Logue MD, Valencia E, Ruiz A, Reyes A et al (2021) Risk assessment of soil heavy metal contamination at the census tract level in the city of Santa Ana, CA: implications for health and environmental justice. Environ Sci Process Impacts 23(6):812–830
Mordukhovich I, Wright RO, Hu H, Amarasiriwardena C, Baccarelli A, Litonjua A et al (2012) Associations of toenail arsenic, cadmium, mercury, manganese, and lead with blood pressure in the normative aging study. Env Health Perspect 120(1):98–104
Navas-Acien A, Guallar E, Silbergeld EK, Rothenberg SJ (2007) Lead exposure and cardiovascular disease—a systematic review. Env Health Perspect 115(3):472–482
Osuji LC, Adesiyan SO (2005) Extractable hydrocarbons, nickel and vanadium contents of Ogbodo-Isiokpo oil spill polluted soils in Niger Delta, Nigeria. Env Monit Assess 110(1–3):129–139
Rahaman S, Sinha AC, Pati R, Mukhopadhyay D (2013) Arsenic contamination: a potential hazard to the affected areas of West Bengal, India. Environ Geochem Health 35(1):119–132
Reis AP, Costa S, Santos I, Patinha C, Noack Y, Wragg J et al (2015) Investigating relationships between biomarkers of exposure and environmental copper and manganese levels in house dusts from a Portuguese industrial city. Env Geochem Health 37(4):725–744
Riccobono F, Perra G, Pisani A, Protano G (2011) Trace element distribution and 235U/238U ratios in Euphrates waters and in soils and tree barks of Dhi Qar province (southern Iraq). Sci Total Environ 409(19):3829–3838
Salah EA, Turki AM, Mahal SN (2015) Chemometric evaluation of the heavy metals in urban soil of Fallujah City, Iraq. J Environ Prot 6(11):1279–1292
Savabieasfahani M, Basher Ahamadani F, Mahdavi Damghani A (2020) Living near an active U.S. military base in Iraq is associated with significantly higher hair thorium and increased likelihood of congenital anomalies in infants and children. Environ Pollut Barking Essex 1987 256:113070
Shanshal M, Faris SS, Shihab OH (2020) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the soil of Fellujah City. J Univ Anbar Pure Sci 14(2):32–37
Skalny AV, Aschner M, Bobrovnitsky IP, Chen P, Tsatsakis A, Paoliello MMB et al (2021) Environmental and health hazards of military metal pollution. Environ Res 201:111568
Specht AJ, Weisskopf M, Nie LH (2014) Portable XRF technology to quantify Pb in bone in vivo. J Biomark 2014:9
Specht AJ, Lin Y, Weisskopf M, Yan C, Hu H, Xu J et al (2016) XRF-measured bone lead (Pb) as a biomarker for Pb exposure and toxicity among children diagnosed with Pb poisoning. Biomarkers 21(4):347–352
Specht AJ, Parish CN, Wallens EK, Watson RT, Nie LH, Weisskopf MG (2018a) Feasibility of a portable X-ray fluorescence device for bone lead measurements of condor bones. Sci Total Environ 615:398–403
Specht AJ, Kponee K, Nkpaa KW, Balcom PH, Weuve J, Nie LH et al (2018b) Validation of X-ray fluorescence measurements of metals in toenail clippings against inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in a Nigerian population(). Physiol Meas 39(8):085007
Specht AJ, Zhang X, Goodman BD, Maher E, Weisskopf MG, Nie LH (2019a) A dosimetry study of portable X-ray fluorescence in vivo metal measurements. Health Phys 116(5):590–598
Specht AJ, Kirchner KE, Weisskopf MG, Pokras MA (2019b) Lead exposure biomarkers in the common loon. Sci Total Environ 647:639–644
Specht AJ, Adesina KE, Read DE, Weisskopf MG (2024) Benchtop X-ray fluorescence to quantify elemental content in nails non-destructively. Sci Total Environ 918:170601
Suhl J, Conway KM, Rhoads A, Langlois PH, Feldkamp ML, Michalski AM et al (2023) Prepregnancy exposure to dietary arsenic and congenital heart defects. Birth Defects Res 115(1):79–87
Surdyk S, Itani M, Al-Lobaidy M, Kahale LA, Farha A, Dewachi O et al (2021) Weaponised uranium and adverse health outcomes in Iraq: a systematic review. BMJ Glob Health 6(2):e004166
Świercz A, Zajecka E (2017) Assessment of heavy metal content in the soils of industrial sites in Skarzysko-Kamienna and Kielce. Proc ECOpole 11(1):97–103
US EPA O (2015a) Ecological soil screening level metal contaminants [Internet] [Cited 2023 Aug 24]. https://www.epa.gov/chemical-research/ecological-soil-screening-level-metal-contaminants
US EPA O (2015b) SW-846 Test method 6200 field portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry for the determination of elemental concentrations in soil and sediment [Internet]. [Cited 2023 Nov 9]. https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-6200-field-portable-x-ray-fluorescence-spectrometry-determination
US EPA O (2015c) Regional screening levels (RSLs)-generic tables [Internet]. [Cited 2023 Nov 22]. https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-generic-tables
United States Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological profile for lead [Internet]. Atlanta, Ga.: U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, 2007. 1 online resource (528 p.). http://purl.fdlp.gov/GPO/gpo31474
Keith S, Faroon O, Roney N, Scinicariello F, Wilbur S, Ingerman L, Llados F, Plewak D, Wohlers D, Diamond G (2023) Uranium | Toxicological Profile | ATSDR [Internet]. [Cited 2023 Nov 9]. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=440&tid=77
Vellingiri B (2023) A deeper understanding about the role of uranium toxicity in neurodegeneration. Environ Res 233:116430
Weisskopf MG, Wright RO, Schwartz J, Spiro A, Sparrow D, Aro A et al (2004) Cumulative lead exposure and prospective change in cognition among elderly men: the VA normative aging study. Am J Epidemiol 160(12):1184–1193
Zhang P, Yang M, Lan J, Huang Y, Zhang J, Huang S et al (2023) Water quality degradation due to heavy metal contamination: health impacts and eco-friendly approaches for heavy metal remediation. Toxics 11(10):828
Acknowledgements
Dr. Specht was supported during the writing of this manuscript by NIOSH grant number K01OH012528.
Funding
This work was supported by National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (Grant No. K01OH012528).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Specht, A.J., Lindsay, I.C., Wells, E.M. et al. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils of Fallujah, Iraq. Expo Health (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-024-00645-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-024-00645-5