Abstract
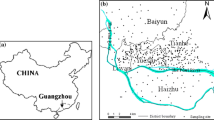
The source identification of trace elements in peri-urban soils has not been fully explored, especially for the areas in eastern China. Here, 80 soil samples, including 40 from cropland, 11 from orchards and 29 from forests, were collected in a typical peri-urban catchment, Ningbo, eastern China. The concentrations of arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn), Pb isotopes and basic soil properties were measured for each soil sample. Multivariate analysis of correlation, regression, principal component analysis and isotopic tracers were used. The results showed that the concentrations of trace elements significantly differed based on land uses, especially for Cd, Cu and Zn. For the seven trace elements, the Cd, Cu and Zn in crop soils are contaminant elements. In the peri-urban soils, Cr and Ni are dominated by parent material and paedogenic processes. Difference in As and Pb concentrations between land uses maybe attributed to atmospheric deposition induced by fossil fuel combustion. Applications of fertilisers, calcium phosphate and calcium superphosphate, livestock manure and compost, are the dominant sources of pollutants in peri-urban soils, especially for Cd, Cu and Zn, indicating the key point for pollution control for this area. Calcium and P are effective indicators of Cd, Cu and Zn contamination for the peri-urban catchment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khashman OA (2004) Heavy metal distribution in dust, street dust and soils from the work place in Karak Industrial Estate, Jordan. Atmos Environ 38:6803–6812
Alloway BJ (2013) Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soils environmental pollution. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 11–50
Barton D, Hope D, Billett M, Cresser M (1994) Sulphate adsorption capacity and pH of upland podzolic soils in Scotland: effects of parent material, texture and precipitation chemistry. Appl Geochem 9:127–139
Bolan NS, Khan M, Donaldson J, Adriano D, Matthew C (2003) Distribution and bioavailability of copper in farm effluent. Sci Total Environ 309:225–236
Chen J, Tan M, Li Y, Zhang Y, Lu W, Tong Y, Zhang G, Li Y (2005a) A lead isotope record of Shanghai atmospheric lead emissions in total suspended particles during the period of phasing out of leaded gasoline. Atmos Environ 39:1245–1253
Chen T, Zheng Y, Lei M, Huang Z, Wu H, Chen H, Fan K, Yu K, Wu X, Tian Q (2005b) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 60:542–551
Chen J, Tan M, Li Y, Zheng J, Zhang Y, Shan Z, Zhang G, Li Y (2008a) Characteristics of trace elements and lead isotope ratios in PM 2.5 from four sites in Shanghai. J Hazard Mater 156:36–43
Chen T, Liu X, Zhu M, Zhao K, Wu J, Xu J, Huang P (2008b) Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban–rural transitional area of Hangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 151:67–78
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512–513:143–153
Cheng S (2003) Heavy metal pollution in China: origin, pattern and control. Environ Sci Pollut R 10:192–198
Cheng H, Hu Y (2010) Lead (Pb) isotopic fingerprinting and its applications in lead pollution studies in China: a review. Environ Pollut 158:1134–1146
Dach J, Starmans D (2005) Heavy metals balance in Polish and Dutch agronomy: actual state and previsions for the future. Agr Ecosyst Environ 107:309–316
de la Cueva AV, Marchant BP, Quintana JR, de Santiago A, Lafuente AL, Webster R (2014) Spatial variation of trace elements in the peri-urban soil of Madrid. J Soils Sediments 14:78–88
De Vries W, Vel E, Reinds G, Deelstra H, Klap J, Leeters E, Hendriks C, Kerkvoorden M, Landmann G, Herkendell J (2003) Intensive monitoring of forest ecosystems in Europe: 1. Objectives, set-up and evaluation strategy. For Ecol Manag 174:77–95
Dong Y, Zheng W, Zhou J (2007) Soil geochemical background in Zhejiang (in Chinese). Agro-geological Environment Survey in Zhejiang. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Duan J, Tan J (2013) Atmospheric heavy metals and arsenic in China: situation, sources and control policies. Atmos Environ 74:93–101
Eghball B, Gilley JE (1999) Phosphorus and nitrogen in runoff following beef cattle manure or compost application. J Environ Qual 28:1201–1210
Erel Y, Veron A, Halicz L (1997) Tracing the transport of anthropogenic lead in the atmosphere and in soils using isotopic ratios. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:4495–4505
Ettler V, Konecny L, Kovarova L, Mihaljevic M, Sebek O, Kribek B, Majer V, Veselovsky F, Penizek V, Vanek A, Nyambe I (2014) Surprisingly contrasting metal distribution and fractionation patterns in copper smelter-affected tropical soils in forested and grassland areas (Mufulira, Zambian Copperbelt). Sci Total Environ 473–474:117–124
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313–324
Fu B, Zhuang X, Jiang G, Shi J, Lu Y (2007) Feature: environmental problems and challenges in China. ACS Publications, Washington, DC
Gimeno-García E, Andreu V, Boluda R (1996) Heavy metals incidence in the application of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides to rice farming soils. Environ Pollut 92:19–25
Guagliardi I, Buttafuoco G, Cicchella D, De Rosa R (2013) A multivariate approach for anomaly separation of potentially toxic trace elements in urban and peri-urban soils: an application in a southern Italy area. J Soils Sediments 13:117–128
Guo J, Liu X, Zhang Y, Shen J, Han W, Zhang W, Christie P, Goulding K, Vitousek P, Zhang F (2010) Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 327:1008–1010
Hernandez L, Probst A, Probst JL, Ulrich E (2003) Heavy metal distribution in some French forest soils: evidence for atmospheric contamination. Sci Total Environ 312:195–219
Hu W, Wang H, Dong L, Huang B, Borggaard OK, Hansen HCB, He Y, Holm PE (2018) Source identification of heavy metals in peri-urban agricultural soils of southeast China: an integrated approach. Environ Pollut 237:650–661
Huang B, Shi X, Yu D, Öborn I, Blombäck K, Pagella TF, Wang H, Sun W, Sinclair FL (2006) Environmental assessment of small-scale vegetable farming systems in peri-urban areas of the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 112:391–402
Huang S-L, Wang S-H, Budd WW (2009) Sprawl in Taipei’s peri-urban zone: responses to spatial planning and implications for adapting global environmental change. Landsc Urban Plan 90:20–32
Imperato M, Adamo P, Naimo D, Arienzo M, Stanzione D, Violante P (2003) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environ Pollut 124:247–256
Iverfeldt Å (1991) Mercury in forest canopy throughfall water and its relation to atmospheric deposition. Water Air Soil Pollut 56:553–564
Khai NM, Ha PQ, Öborn I (2007) Nutrient flows in small-scale peri-urban vegetable farming systems in Southeast Asia: a case study in Hanoi. Agr Ecosyst Environ 122:192–202
Komárek M, Ettler V, Chrastný V, Mihaljevič M (2008) Lead isotopes in environmental sciences: a review. Environ Int 34:562–577
Kříbek B, Majer V, Veselovský F, Nyambe I (2010) Discrimination of lithogenic and anthropogenic sources of metals and sulphur in soils of the central-northern part of the Zambian Copperbelt Mining District: a topsoil vs. subsurface soil concept. J Geochem Explor 104:69–86
Li Z, Ma Z, van der Kuijp TJ, Yuan Z, Huang L (2014) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: pollution and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 468–469:843–853
Lindberg SE (1989) Behavior of Cd, Mn, and Pb in forest-canopy throughfall. Springer, Berlin, pp 233–257
Liu W, Zhao J, Ouyang Z, Söderlund L, Liu G (2005) Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metal distribution and contamination in Beijing, China. Environ Int 31:805–812
Liu Y, Liu Y, Chen Y, Long H (2010) The process and driving forces of rural hollowing in China under rapid urbanization. J Geogr Sci 20:876–888
Lu A, Wang J, Qin X, Wang K, Han P, Zhang S (2012) Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 425:66–74
Madrid L, Dı́az-Barrientos E, Madrid F (2002) Distribution of heavy metal contents of urban soils in parks of Seville. Chemosphere 49:1301–1308
Manta DS, Angelone M, Bellanca A, Neri R, Sprovieri M (2002) Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci Total Environ 300:229–243
Meharg AA (2016) Perspective: city farming needs monitoring. Nature 531:S60
Micó C, Recatalá L, Peris M, Sánchez J (2006) Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 65:863–872
Morton-Bermea O, Hernández-Álvarez E, González-Hernández G, Romero F, Lozano R, Beramendi-Orosco L (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in urban topsoils from the metropolitan area of Mexico City. J Geochem Explor 101:218–224
Mukai H, Machida T, Tanaka A, Vera YP, Uematsu M (2001) Lead isotope ratios in the urban air of eastern and central Russia. Atmos Environ 35:2783–2793
Nicholson F, Smith S, Alloway B, Carlton-Smith C, Chambers B (2003) An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Sci Total Environ 311:205–219
Oh GH, Park CR (2002) Preparation and characteristics of rice-straw-based porous carbons with high adsorption capacity. Fuel 81:327–336
Ravankhah N, Mirzaei R, Masoum S (2017) Determination of heavy metals in surface soils around the brick kilns in an arid region, Iran. J Geochem Explor 176:91–99
Rodriguez Martin JA, Arias ML, Grau Corbi JM (2006) Heavy metals contents in agricultural topsoils in the Ebro basin (Spain). Application of the multivariate geoestatistical methods to study spatial variations. Environ Pollut 144:1001–1012
Rodriguez JA, Nanos N, Grau JM, Gil L, Lopez-Arias M (2008) Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in Spanish agricultural topsoils. Chemosphere 70:1085–1096
Scudlark JR, Church TM (1988) The atmospheric deposition of arsenic and association with acid precipitation. Atmos Environ 22:937–943
Sheppard D, Claridge G, Campbell I (2000) Metal contamination of soils at Scott Base, Antarctica. Appl Geochem 15:513–530
Shi L, Ganne B (2009) Understanding the Zhejiang industrial clusters: questions and re-evaluations. In: Ganne B, Lecler Y (eds) Asian industrial clusters, global competitiveness and new policy initiatives. World Scientific Publishing Co, Singapore, pp 239–266
Shi G, Chen Z, Teng J, Bi C, Zhou D, Sun C, Li Y, Xu S (2012) Fluxes, variability and sources of cadmium, lead, arsenic and mercury in dry atmospheric depositions in urban, suburban and rural areas. Environ Res 113:28–32
Shotyk W, Cheburkin AK, Appleby PG, Fankhauser A, Kramers JD (1996) Two thousand years of atmospheric arsenic, antimony, and lead deposition recorded in an ombrotrophic peat bog profile, Jura Mountains, Switzerland. Earth Planet Sci Lett 145:E1–E7
Simon D (2008) Urban environments: issues on the peri-urban fringe. Ann Rev Environ Resour 33:167–185
Singh S, Kumar M (2006) Heavy metal load of soil, water and vegetables in peri-Urban Delhi. Environ Monit Assess 120:79–91
Sun Y, Zhou Q, Xie X, Liu R (2010) Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. J Hazard Mater 174:455–462
Sun C, Liu J, Wang Y, Sun L, Yu H (2013) Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere 92:517–523
Teng Y, Wu J, Lu S, Wang Y, Jiao X, Song L (2014) Soil and soil environmental quality monitoring in China: a review. Environ Int 69:177–199
Tóth G, Hermann T, Da Silva M, Montanarella L (2016) Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ Int 88:299–309
Ungureanu T, Iancu GO, Pintilei M, Chicoș MM (2017) Spatial distribution and geochemistry of heavy metals in soils: a case study from the NE area of Vaslui county, Romania. J Geochem Explor 176:20–32
Wang J, Guo P, Li X, Zhu J, Reinert T, Heitmann J, Spemann D, Vogt J, Flagmeyer R-H, Butz T (2000) Source identification of lead pollution in the atmosphere of Shanghai City by analyzing single aerosol particles (SAP). Environ Sci Technol 34:1900–1905
Webster D, Muller L (2002) Challenges of peri-urbanization in the Lower Yangtze Region: The case of the Hangzhou-Ningbo Corridor. Asia/Pacific Research Center
Wei B, Yang L (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94:99–107
Wong SC, Li XD, Zhang G, Qi SH, Min YS (2002) Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ Pollut 119:33–44
Xiang Q, Chen Q-L, Zhu D, An X-L, Yang X-R, Su J-Q, Qiao M, Zhu Y-G (2018) Spatial and temporal distribution of antibiotic resistomes in a peri-urban area is associated significantly with anthropogenic activities. Environ Pollut 235:525–533
Xu X, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Wang Y, Deng W (2014) Sources of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of a rapidly industrializing area in the Yangtze Delta of China. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 108:161–167
Yeomans JC, Bremner JM (1988) A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil 1. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19:1467–1476
Zhao L, Xu Y, Hou H, Shangguan Y, Li F (2014) Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Sci Total Environ 468:654–662
Zheng J, Tan M, Shibata Y, Tanaka A, Li Y, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Shan Z (2004) Characteristics of lead isotope ratios and elemental concentrations in PM 10 fraction of airborne particulate matter in Shanghai after the phase-out of leaded gasoline. Atmos Environ 38:1191–1200
Zheng J, Zhou Z, Wei Y, Chen T, Feng W, Chen H (2018) High-throughput profiling of seasonal variations of antibiotic resistance gene transport in a peri-urban river. Environ Int 114:87–94
Zhu S, Pickles J, He C (2017a) Geographical dynamics and industrial relocation: spatial strategies of apparel firms in Ningbo, China, Geographical Dynamics and Firm Spatial Strategy in China. Springer, pp. 51–72
Zhu Y-G, Reid BJ, Meharg AA, Banwart SA, Fu B-J (2017b) Optimizing Peri-URban Ecosystems (PURE) to re-couple urban-rural symbiosis. Sci Total Environ 586:1085–1090
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos 41571130064, 41701018), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017M611018), UK NERC Newton Critical Zone funded Project NE/N007417/1 and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences (2018057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Carey, M., Yang, L. et al. Source Identification of Trace Elements in Peri-urban Soils in Eastern China. Expo Health 11, 195–207 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0290-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0290-1