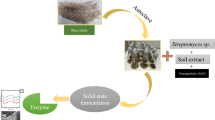
Abstract
Often, clean energy concept is tagged with the bio-ethanol production from the agricultural sources. Herein, we are first to report on use of nanoscale materials (nano-CaO and nano-MgO) in fermentation process for bio-ethanol production from nanoscale materials (zinc, calcium and magnesium)-driven bio-fortified sweet sorghum. A field experiment was conducted during 2014 and 2015, and nanoscale materials of CaO and MgO (mean size 69.6 nm and 42 nm) at concentrations of 10 ppm and 20 ppm, respectively, alone and in combination were added during the fermentation process. Ethanol production significantly increased by 24.7% and 17.5% by adding nano-CaO and nano-MgO, respectively. Significantly higher ethanol content (8.83% and 8.94%) was recorded in the treatment which received nanoscale-driven bio-fortified sweet sorghum juice with added nanoscale nutrients (CaO and MgO) during fermentation process. Thus, nanoscale materials increase the rate of fermentation process which may lead to the enhanced bio-ethanol production.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bafrncova, P., D. Smogrovicova, I. Slavikova, J. Patkova, and Z. Domeny. 1999. Improvement of very high gravity ethanol fermentation by media supplementation using Sacchromyces cerevisiae. Biotechnology Letters 21: 337–341.
Bai, F.W., L.J. Chen, Z. Zhang, W.A. Anderson, and M. Moo-Young. 2004. Continuous ethanol production and evaluation loss under very high gravity medium conditions. Journal of Biotechnology 110: 287–293.
Birch, R.M., and G.W. Walker. 2000. Influence of magnesium ions on heat shock and ethanol stress responses of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 26: 678–687.
Bravo, V., F. Camacho, S. Sanchez, and E. Castro. 1995. Influence of the concentrations of D-xylose and yeast extract on ethanol production by Pachyiolen tannophilus. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering 79: 566–571.
Claudia, P., V. Mauro, and E. Rodriguez-Cerezo. 2015. Agricultural Nanotechnologies: What are the current possibilities? Nano Today 10: 124–127.
Deepa, M., P. Sudhakar, K.V. Nagamadhuri, K. Balakrishna Reddy, T. Giridhara Krishna, and T.N.V.K.V. Prasad. 2015. First evidence on phloem transport of nanoscale calcium oxide in groundnut using solution culture technique. Applied Nanoscience 5: 545–551.
Deesuth, O., P. Laopaiboon, P. Jaisil, and L. Laopaiboon. 2012. Optimization of nitrogen and metal ions supplementation for very high gravity bioethanol fermentation from sweet sorghum juice using an orthogonal array design. Energies 5: 3178–3197.
Dubios, M., K.A. Gillis, J.K. Hamilton, P.A. Rebers, and F. Smith. 1956. Calorimetric method for determination of sugar and related substances. Analytical Chemistry 28: 350–356.
Elizabeth, M.R., and Rises, and G. Graham. 1997. The effects of increased magnesium and calcium concentrations on yeast fermentation performance in high gravity worts. Journal of the Institute of Brewing 103: 287–291.
Gayathri, M., N.C. Venkateswarlu, T. Muralikrishna, S. Jayalakshmi Devi, T.N.V.K. Prasad, and G. Mohan Naidu. 2018. Influence of Calcium, Magnesium, Iron and Zinc Nanomaterials on the Growth of Biopesticide Bacillus thuringiensis. International Journal of Pure and Applied Bioscience 6 (5): 1103–1105.
Khongsay, N., L. Laopaiboon, P. Jaisil, and P. Laopaiboo. 2012. Optimization of agitation and aeration for very high gravity ethanol fermentation from sweet sorghum juice by Saccharomyces cerevisiae using an orthogonal array design. Energies 5: 561–576.
Laopaiboon, L., S. Nuanpang, P. Srinophakun, P. Klanrit, and P. Laopaiboon. 2009. Ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice using very high gravity technology: Effects of carbon and nitrogen supplementations. Bioresource Technology 100: 4176–4182.
Linko, M., A. Haikara, A. Ritala, and M. Penttila. 1998. Recent advances in the malting and brewing industry. Journal of Biotechnology 65: 85–98.
Naseeruddin, R., V. Sumathi, T.N. Prasad, P. Sudhakar, V. Chandrika, and B. Ravindra Reddy. 2018. Unprecedented synergistic effects of nanoscale nutrients on growth, productivity of sweet sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench], and nutrient biofortification. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 66 (5): 1075–1084.
Okon, A.A., and T.U. Nwabueze. 2010. Optimization of divalent cation in Saccharomyces pastorianus medium conditions for ethanol production. African Journal of Biotechnology 9 (3): 5423–5429.
Prasad, T.N.V.K.V., P. Sudhakar, Y. Sreenivasulu, P. Latha, V. Munaswamy, K. Raja Reddy, T.S. Sreeprasad, P.R. Sajanlal, and T. Pradeep. 2012. Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. Journal of Plant Nutrition 35: 905–927.
Pulingundla, P.S.D., O.V.S. Reddy, and K. Sanghoon. 2010. Very high gravity (VHG) ethanolic brewing and fermentation: A research update. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology 38: 133–1144.
Ratnavathi, C.V., B. Dayakar Rao, and N. Seetharama. 2003. Sweet sorghum stalk: A suitable raw material for fuel alcohol production. National Research Center for sorghum (NRCS), NRCS Report Number-12/2003, NATP (NRCS) series No.1 pp.8.
Reddy, B.V., S. Ramesh, P.S. Reddy, B. Ramaiah, M. Salimath, and R. Kachapur. 2005. Sweet sorghum-a potential alternate raw material for bio-ethanol and bio-energy. International Sorghum and Millets Newsletter 46: 79–86.
Rees, E.M.R., and G.G. Stewart. 1997. The effects of increased magnesium and calcium concentrations on yeast fermentation performance in high gravity worts. Journal of the Institute of Brewing 103: 287–291.
Schepers, A.W., J. Thibault, and C. Lacroix. 2002. Lactobacillus helveticus growth and lactic acid production during pH controlled batch cultures in whey permeate/yeast extract medium. Part I. multiple factor kinetic analysis. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 30: 176–186.
Silva, J.P.A., S.I. Mussatto, and I.C. Roberto. 2010. The influence of initial xylose concentration, agitation, and aeration on ethanol production by Pichia stipitis from rice straw hemicellulosic hydrolysate. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8867-6
Subbaiah, L.V., T.N.V.K.V. Prasad, T.G. Krishna, P. Sudhakar, B.R. Reddy, and T. Pradeep. 2016. Novel effects of nanoparticulate delivery of zinc on growth, productivity, and zinc biofortification in maize (Zea mays L.). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 64 (19): 3778–3788.
Walker, G.M. 1994. The role of magnesium in Biotechnology. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology 14 (4): 311–354.
Walker, G.M., and A.I. Maynard. 1996. Accumulation of magnesium ions during fermentative metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology 18: 1–3.
Acknowledgements
Naseeruddin R. is highly thankful to DST for sponsoring INSPIRE Fellowship to this research program. The authors are grateful to the administration of Acharya N G Ranga Agricultural University for allowing them to conduct this research.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naseeruddin, R., Sumathi, V., Prasad, T.N.V.K.V. et al. A First Report on the Effects of Nanoscale Nutrients on Fermentation Process and Bio-Ethanol Production from Bio-Fortified Sweet Sorghum. Sugar Tech 24, 870–881 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-022-01137-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-022-01137-z