Abstract
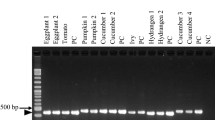
Sugarcane white leaf (SCWL) is one of the major sugarcane diseases in the Asian continent associated with phytoplasmas. It occurs in all sugarcane-growing areas of Sri Lanka, causing substantial economic losses. However, subgroup level identification has been not reported so far for the phytoplasma strains associated with this disease in Sri Lanka. In the present study, the geographical distribution of phytoplasma strains associated with SCWL in Sri Lanka, identification of their weed reservoirs and ribosomal subgroup analysis based on phytoplasma 16S rRNA gene were carried out. A total of 27 SCWL samples representing six main sugarcane-growing areas of Sri Lanka and six samples of two grass species (Cynodon dactylon and Brachiaria distachya) showing putative symptoms of phytoplasma were analyzed. A nested PCR product of 1.2 kb size was consistently amplified in all the symptomatic samples with primers amplifying the 16S rRNA gene. A higher level of sequence identity from 99.03 to 100% was shared among the 16S rRNA gene sequences of all tested SCWL phytoplasma strains. Both Bermudagrass white leaf (BGWL) and Brachiaria grass white leaf (BraWL) phytoplasma strains shared 97.5–98.1% identity of their 16S rRNA gene with SCWL strains. The 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons and virtual RFLP analysis of SCWL, BGWL, and BraWL phytoplasma isolates allowed their affiliations with ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma sacchari’ (16SrXI-B subgroup) with SCWL and ‘Ca. P. cynodontis’ (16SrXIV-A subgroup) with the grasses samples. The phytoplasma subgroup 16SrXI-B was identified as the most widespread SCWL phytoplasma subgroup in commercial sugarcane varieties in Sri Lanka.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng, S., and C. Hiruki. 1991. Amplification of 16S rRNA genes from culturable and non-culturable mollicutes. Journal of Microbiology Methods 14: 53–61.
Doyle, J.J., and J.L. Doyle. 1990. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12: 13–15.
Duduk, B., S. Paltrinieri, I.-M. Lee, and A. Bertaccini. 2013. Nested PCR and RFLP analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene. In Phytoplasma methods in molecular biology (methods and protocols), vol. 938, ed. M. Dickinson and J. Hodgetts. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-089-2_14.
Firrao, G., K. Gibb, and C. Streten. 2005. Short Taxonomic guide to the genus ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ . Journal of Plant Pathology 87(4): 249–263.
Gundersen, D., and I.-M. Lee. 1996. Ultrasensitive detection of phytoplasmas by nested-PCR assays using two universal primer pairs. Phytopathologia Mediterranea 35(3): 144–151.
Jung, H.Y., T. Sawayanagi, P. Wongkaew, S. Kakizawa, H. Nishigawa, W. Wei, K. Oshima, S. Miyata, M. Ugaki, T. Hibi, and S. Namba. 2003. Candidatus Phytoplasma oryzae’, a novel phytoplasma taxon associated with rice yellow dwarf disease. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 53(6): 1925–1929.
Keerthipala, A.P. 2016. Development of sugar industry in Sri Lanka. Sugar Tech 18: 612–626.
Kirdat, K., B. Tiwarekar, V. Thorat, N. Narawade, D. Dhotre, S. Sathe, Y. Shouche, and A. Yadav. 2020a. Draft genome sequences of two phytoplasma strains associated with sugarcane grassy shoot (SCGS) and bermuda grass white leaf (BGWL) diseases. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 33(5): 715–717.
Kirdat, K., B. Tiwarekar, V. Thorat, S. Sathe, Y. Shouche, and A. Yadav. 2020b. Candidatus Phytoplasma sacchari’, a novel taxon-associated with Sugarcane Grassy Shoot (SCGS) disease. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 71(1): 004591.
Kumar, S., G.P. Rao, J.V. Singh, and V.K. Baranwal. 2018. Genetic diversity of phytoplasmas associated with sugarcane grassy shoot and leaf yellows diseases in India. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 8 (2): 74–88.
Kumar, S., G. Stecher, and K. Tamura. 2016. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution 33(7): 1870–1874.
Kumarasinghe, N.C., and P. Jones. 2001. Identification of white leaf disease of sugarcane in Sri Lanka. Sugar Tech 3: 55–58.
Lee, I.M., D.E. Gundersen, R.E. Davis, and I.M. Bartoszyk. 1998. Revised classification scheme of phytoplasma based on RFLP analysis of 16S rRNA and ribosomal protein gene sequences. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology 48: 1153–1169.
Lee, I.M., M. Pastore, M. Vibio, A. Danielli, S. Attathorn, R.E. Davis, and A. Bertaccini. 1997. Detection and characterization of a phytoplasma associated with annual blue grass (Poa annua) white leaf disease in southern Italy. European Journal of Plant Pathology 103: 251–254.
Lee, I.M., R.E. Davis, and D.E. Gundersen. 2000. Phytoplasma: phytopathogenic mollicutes. Annual Review of Microbiology 54: 221–255.
Nakashima, K., T. Hayashi, W. Chaleeprom, P. Wongkaew, and P. Sirithorn. 1996. Complex phytoplasma flora in northeast Thailand as revealed by 16S rDNA analysis. Annals of the Phytopathological Society of Japan 62: 57–60.
Nasare, K., A. Yadav, A.K. Singh, K.B. Shivasharanappa, Y.S. Nerkar, and V.S. Reddy. 2007. Molecular and symptoms analysis reveal the presence of new phytoplasmas associated with sugarcane grassy shoot disease in India. Plant Disease 91: 1413–1418. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-91-11-1413.
Nithya, K., B. Parameswari, A. Bertaccini, G.P. Rao, and R. Viswanathan. 2020. Grassy shoot: The destructive disease of sugarcane. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 10(1): 10–24.
Quan, M.V., V.L. Nguyen, M.L. Quang, N.Q. Huy, V.L. Xuan, C.H.H. Viet, D.T. Nguyen, H.T.B. Thao, V.H. Nguyen, D.H. Nguyen, P.G. Weintraub, C. Keswani, L.T. Hang, M.H. Nguyen, and T.H. Hoat. 2020. A new phytoplasma strain associated with the sugarcane white leaf disease in Vietnam. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 10(1): 60–68.
Rao, G.P., E. Alvarez, and A. Yadav. 2018. Phytoplasma diseases of industrial crops. In Phytoplasma: Plant Pathogenic Bacteria—I, ed. G.P. Rao, A. Bertaccini, N. Fiore, and L.W. Liefting, 91–122. Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-008-0013-1.
Rao, G.P., S. Mall, and C. Marcone. 2012. Recent biotechnological approaches in diagnosis and management of sugarcane phytoplasma diseases. Functional Plant Science and Biotechnology 6: 19–29.
Rao, G.P., S. Srivastava, P.S. Gupta, A. Singh, M. Singh, and C. Marcone. 2008. Detection of sugarcane grassy shoot phytoplasma infecting sugarcane in India and its phylogenetic relationships to closely related phytoplasmas. Sugar Tech 10: 74–80.
Rao, G.P., V. Madhupriya, A.K. Kumar, S. Tiwari, and V. Baranwal. 2014. Identification of sugarcane grassy shoot-associated phytoplasma and one of its putative vectors in India. Phytoparasitica 42: 349–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-013-0366-1.
Rao, G.P., V. Madhupriya, R. Thorat, A.K. Tiwari. Manimekalai, and A. Yadav. 2017. A century progress of research on phytoplasma diseases in India. Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 7(1): 1–38.
Salehi, M., K. Izadpanah, M. Siampour, and M. Taghizadeh. 2009. Molecular characterization and transmission of Bermuda grass white leaf phytoplasma in Iran. Journal of Plant Pathology 91: 655–661.
Schneider, B., E. Seemueller, C.D. Smart, and B.C. Kirkpatrick. 1995. Phylogenetic classification of plant pathogenic mycoplasma-like organisms or phytoplasmas. In Molecular and diagnostic procedures in mycoplasmology, ed. S. Razin and J.G. Tully, 369–380. San Diego, CA: Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012583805-4/50040-6.
Sdoodee, R., B. Schneider, A. Padovan, and K. Gibb. 1999. Detection and genetic relatedness of phytoplasmas associated with plant diseases in Thailand. The Journal of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics 3: 133–140.
Seemuller, E., C. Marcone, U. Lauer, A. Ragozzino, and M. Göschl. 1998. Current status of molecular classification of the phytoplasma. Journal of Plant Pathology 80: 3–26.
Seneviratne, J.A.U.T. 2008. An investigation of the secondary transmission of sugarcane white leaf disease in Sri Lanka, PhD Thesis, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka.
Tran-Nguyen, L., K.R. Blanche, B. Egan, and K.S. Gibb. 2000. Diversity of phytoplasmas in northern Australian sugarcane and other grasses. Plant Pathology 49: 666–679.
Viswanathan, R., and G.P. Rao. 2011. Disease scenario and management of major sugarcane diseases in India. Sugar Tech 13: 336–353.
Wongkaew, P., Y. Hanboonsong, P. Sirithorn, C. Choosai, S. Boonkrong, T. Tinnangwattana, R. Kitchareonpanya, and S. Damak. 1997. Differentiation of phytoplasma associated with sugarcane and gramineous weed white leaf disease and sugarcane grassy shoot disease by RFLP and sequencing. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 95: 660–663.
Yadav, A., V. Thorat, S. Deokule, Y. Shouche, and D.T. Prasad. 2017. New subgroup 16SrXI-F phytoplasma strain associated with sugarcane grassy shoot (SCGS) disease in India. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 67: 374–378.
Zhang, R.Y., W.F. Li, Y.K. Huang, X.Y. Wang, H.L. Shan, Z.M. Luo, and Z.Y. Yin. 2016. Group 16SrXI phytoplasma strains, including subgroup 16SrXI-B and a new subgroup, 16SrXI-D, are associated with sugar cane white leaf. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 66: 487–491.
Zhao, Y., W. Wei, I.M. Lee, J. Shao, X. Sou, and R.E. Davis. 2009. Construction of an interactive online phytoplasma classification tool, iPhyClasifier, and its application in analysis of peach X-disease phytoplasma group (16SrIII). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 59: 2582–2593.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the Dr. M.S. Perera Director (acting) and members of the paper reviewing committee of Sugarcane Research Institute (SRI) Sri Lanka, Prof. P.G.C. Bandaranayake, Mrs. A.G.M.L.K. Dayananda from the University of Peradeniya, Mr. L.M.J.R. Wijayawardhna and other supported members of SRI and sugar industries of Sri Lanka.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dayasena, Y.A.P.K., Panda, P., Thushari, A.N.W.S. et al. Geographical Distribution and Identification of Phytoplasma Strain Associated with Sugarcane White Leaf Disease in Sri Lanka. Sugar Tech 23, 1351–1358 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-021-00980-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-021-00980-w